Abstract
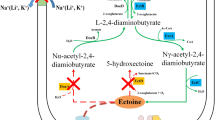
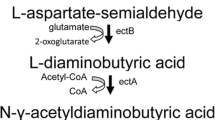
Halophilic bacteria strain Halomonas salina DSM 5928 was found to excrete ectoine, suggesting its potential in the development of a new method of ectoine production. We performed HPLC and LC–MS analyses that showed that Halomonas salina DSM 5928 excreted ectoine under constant extracellular osmolarity. Medium adopting monosodium glutamate as a sole source of carbon and nitrogen was beneficial for ectoine synthesis. The total concentration of ectoine was not affected by NaCl concentration in the range 0.5–2 mol l−1. The total concentration of ectoine and productivity in a 10-l fermentor with 0.5 mol l−1 NaCl were 6.9 g l−1 and 7.9 g l−1 d−1, respectively. These findings show that Halomonas salina DSM 5928 efficiently produces ectoine at relatively low NaCl concentration. This research also indicates the potential application of free or immobilized cells for continuous culture to produce ectoine.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galinski EA (1993) Compatible solutes of halophilic eubacteria: molecular principles, water-solute interaction, stress protection. Cell Mol Life Sci 49:487–496
Galinski EA, Pfeiffer HP, Trüper HG (1985) 1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4- pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur J Biochem 149:135–139
Grammann K, Volke A, Kunte HJ (2002) New type of osmoregulated solute transporter identified in halophilic members of the bacteria domain: TRAP-transporter TeaABC mediates the uptake of ectoine and hydroxyectoine in Halomonas elongata DSM 2581T. J Bacteriol 184:3078–3085
Hagemann M, Richter S, Mikkat S (1997) The ggtA gene encodes a subunit of the transport system for the osmoprotective compound glucosylglycerol in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 179:714–720
Kanapathipillai M, Lentzen G, Sierks M, Park CB (2005) Ectoine and hydroxyectoine inhibit aggregation and neurotoxicity of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid. FEBS Lett 579:4775–4780
Kappes RM, Kempf B, Kneip S, Boch J, Gade J, Meier-Wagner J, Bremer E (1999) Two evolutionarily closely related ABC transporters mediate the uptake of choline for synthesis of the osmoprotectant glycine betaine in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 32:203–216
Kunte HJ (2006) Osmoregulation in bacteria: compatible solute accumulation and osmosensing. Environ Chem 3:94–99
Kunte HJ, Galinski EA, Bestvater T, Volke A, Grammann K (2002) Producing compounds, especially ectoine, useful e.g. for stabilizing biological macromolecules, in organisms in which uptake systems for the compounds have been deleted. German patent DE 101 14 189 A1
Larsen PI, Sydnes LK, Landfald B, Strom AR (1987) Osmoregulation in Escherichia coli by accumulation of organic osmolytes: betaines, glutamic acid, and trehalose. Arch Microbiol 147:1–7
Lentzen G, Schwarz T (2006) Extremolytes: natural compounds from extremophiles for versatile applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:623–634
Onraedt AE, Walcarius BA, Soetaert WK, Vandamme EJ (2005) Optimization of ectoine synthesis through fed-batch fermentation of Brevibacterium epidermis. Biotechnol Prog 21:1206–1212
Roberts MF (2005) Organic compatible solutes of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms. Saline Syst 1:5
Robertson DE, Noll D, Roberts MF, Menaia JAGF, Boone DR (1990) Detection of the osmoregulator betaine in methanogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:563–565
Sauer T, Galinski EA (1998) Bacterial milking: a novel bioprocess for production of compatible solutes. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:306–313
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ (1995) Biotechnological applications and potentialities of halophilic microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotech 11:85–94
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Wang CX, Zhu DC, Nagata S (2006) Supplementation effects of hydroxyectoine on proline uptake of downshocked Brevibacterium sp. JCM 6894. J Biosci Bioeng 101:178–184
Zhang LH, Wang Y, Zhang CY, Wang YJ, Zhu DC, Wang CX, Nagata S (2006) Supplementation effect of ectoine on thermostability of phytase. J Biosci Bioeng 102:560–563
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 20776021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Santos.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Lh., Lang, Yj. & Nagata, S. Efficient production of ectoine using ectoine-excreting strain. Extremophiles 13, 717–724 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0262-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0262-2