Abstract
Background
Given the dosing limitations of methylphenidate short–acting preparations in treating ADHD, galenics with longer release of the substance were developed mainly to avoid drug intake during school hours.
Objectives
This investigation was conducted to assess the efficacy and the duration of action of a new extended-release formulation of methylphenidate (Medikinet® retard) as a once–daily treatment for children with attention–deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Method
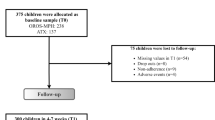
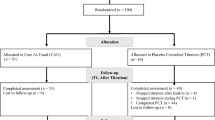
This was a randomized, double–blind, crossover multicentre study with three treatment conditions: once–daily extended–release methylphenidate, twice–daily immediate–release methylphenidate and placebo given to 79 children (8–14 years old) with ADHD. Daily assessments in an analogue classroom setting included blind ratings of attention and deportment and a performance measure (math test) obtained 5 times over an 8–hour period. Secondary measures included an ADHD rating scale, based on DSMIV/ ICD–10 separately rated for the morning and the afternoon.
Results
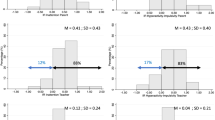
Both active treatment conditions displayed significant time course effects and were superior to placebo in improving all efficacy measures. Once a day extended–release methylphenidate was not different from the same dose of twice daily immediate–release methylphenidate.
Conclusions
These data provide support for the benefit of this novel, once-daily methylphenidate preparation in the treatment of ADHD. The longer duration of action of Medikinet Retard has the potential to simplify psychostimulant treatment, thus reducing dose diversion and eliminating the need for in–school administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biedermann J, Lopez FA, Boellner SW, Chandler MC (2002) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel- group study of SLI381 (Adderall XR) in children with attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 110:258–266
Birmaher B, Greenhill LL, Cooper TB, Fried J, Maminski B (1989) Sustained released methylphenidate: pharmacokinetic studies in ADDH males. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 28:768–772
Breuer D, Döpfner M, Heise CA (2004) Reliabilität und Validität einer Skala zur Erfassung von Störungen der Aufmerksamkeit und Regelbeachtung im Unterricht (in preparation)
Brown GL, Hunt RD, Ebert MH, Bunney WE, Kopin IJ (1979) Plasma levels of damphetamine in hyperactive children: serial behavior and motor responses. Psychopharmacology 62:133–140
Brühl B, Döpfner M, Lehmkuhl G (2000) Der Fremdbeurteilungsbogen für hyperkinetische Störungen (FBB-HKS) – Prävalenz hyperkinetischer Störungen im Elternurteil und psychometrische Kriterien. Kindheit und Entwicklung 9:116–126
Döpfner M, Banaschewski T, Schmidt J, Uebel H, Schmeck K, Gerber WD, Günter M, Knölker U, Gehrke M, Häßler F, Möhler E, Brünger M, Ose C, Fischer, R, Poustka F, Lehmkuhl G, Rothenberger A (2003) Langwirksames Methylphenidat bei Kindern mit Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit-/ Hyperaktivitätsstörung. Eine multizentrische Studie. Nervenheilkunde 22:85–92
Döpfner M, Breuer D, Schürmann S, Wolff Metternich T, Rademacher C, Lehmkuhl G (2004) Effectiveness of an adaptive multimodal treatment in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – global outcome. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 13(Suppl 1):I117–I129
Döpfner M, Lehmkuhl G (2000) Diagnostik- System für Psychische Störungen im Kindes- und Jugendalter nach ICD-10 und DSM-IV (DISYPS-KJ), 2nd edn. Huber, Bern
Döpfner M, Lehmkuhl G (2002) Evidenzbasierte Therapie von Kindern und Jugendlichen mit Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit-/ Hyperaktivitätsstörung (ADHS). Praxis der Kinderpsychologie und Kinderpsychiatrie 51:419–440
Döpfner M, Deutsche Methylphenidat Gruppe (2004) Wirkdauer und Sicherheit von Methylphenidat-Retard im Vergleich zu einer zweimaligen Gabe von schnell freigesetztem Methylphenidat bei Kindern und Jugendlichen mit Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit-/Hyperaktivitätsstörungen (in preparation)
DuPaul GJ, Power TJ, Anastopoulos AD, Reid R (1998) ADHD Rating Scale IV: Checklists, Norms, and Clinical Interpretation. Guilford Press, New York
Greenhill LL (1995) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: the stimulants. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Clin North Am 4:123–168
Greenhill LL, Findling RL, Swanson JM, MPH MR ADHD Study Group (2002) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of modified-release methylphenidate in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 109:1–7
Jadad AR, Booker L, Gauld M, Kakuma R, Boyle M, Cunningham CE, Kim M, Schachar R (1999)The treatment of attention- deficit hyperactivity disorder: an annotated bibliography and critical appraisal of published systematic reviews and metaanalyses. Can J Psychiatry 44:1025–1035
Lord J, Paisley S (2000) The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate for hyperactivity in childhood. National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) version 2, London
Lopez F, Silva R, Pestreich L, Muniz R (2003) Comperative Efficacy of two once daily methylphenidate formulations (Ritalin® LA and Concerta®) and placebo in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder across the school day. Pediatr Drugs 5:545–555
Lyseng-Williamson KA, Keating GM (2002) Extended-Release Methylphenidate (Ritalin® LA). Drugs 62:2251–2259
McBurnett K, Swanson JM, Pfittner LJ, Tamm L (1997) A measure of ADHD-related classroom apairment based on targets for behavioral intervention. J Attention Disord 2:69–76
McCracken JT, Biedermann J, Greenhill LL, Laurence L, Swanson J, McGough J, Spencer TJ, Posner K, Wigal S, Pataki C, Zhang Y, Tulloch S (2003) Analog classroom assessment of a once-daily mixed amphetamine formulation, SLI381 (Adderall XR), in children with ADHD. J Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:673–683
McGough JJ, Biederman J, Greenhill LL, McCracken JT, Spencer TJ, Posner K, Wigal S, Gornbein J, Tulloch S, Swanson JM (2003) Pharmacokinetics of SLI381 (ADDERALL XR), an extended-release formulation of Adderall. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:684–691
Pelham WE, Gnagy EM, Burrows- Maclean L, Williams A, Fabiano G, Morisey SM, Chronis AM, Forehand GL, Nguyen CA, Hoffman MT, Lock TM, Fiebelkorn K, Coles EK, Panahon CJ, Steiner RL, Meichenbaum DL, Onyango AN, Morse GD (2001) Once-a-day concerta methylphenidate versus threetimes- daily methylphenidate in laboratory and natural settings. Pediatrics 107:1–15
Pelham WE, Gnagy EM, Chronis AM, Burrows-Maclean L, Fabiano GA, Onyango AN, Meichenbaum DL, Williams A, Aronoff HR, Steiner RL (1999) A comparison of morning-only and morning/late afternoon Adderall to morning-only, twice-daily, and threetimes- daily methylphenidate in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 104:1300–1311
Pelham WE, Karen E, Greenslade KE, Vodde-Hamilton M, Murphy DA, Greenstein JJ, Gnagy EM, Guthrie KJ, Hoover MD, Dahl RE (1990) Relative efficacy of long-acting stimulants on children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder: A comparison of standard methylphenidate, sustainedrelease methylphenidate, sustained-release dextroamphetamine, and Pemoline. Pediatrics 86:226–236
Pelham WE, Sturges J, Hoza J, Schmidt C, Bijlsma JJ ,Milich R, Moorer S (1987) Sustained release and standard methylphenidate effects on cognitive and social behavior in children with attention deficit disorder. Pediatrics 80:491–501
Pelham WE, Swanson JM, Bender Furman M, Schwindt H (1995) Pemoline effects on children with ADHD: A timeresponse by dose-response analysis on classroom measures. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 34:1504–1513
Pelham WE, Wheeler T, Chronis A (1998) Empirically supported psychosocial treatments for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Psychol 27:190–205
Schubert I, Köster I, Adam C, Ihle P, Döpfner M,Lehmkuhl G (2003) Psychopharmakaverordnungen bei Kindern und Jugendlichen mit Behandlungsanlass “Hyperkinetische Störung”. Zeitschrift für Gesundheitswissenschaften 11:306–324
Sherman M, Hertzig ME (1991) Prescribing practices of Ritalin: the Suffolk County, New York study. In: Greenhill LL,Osman BB (eds) Ritalin: Theory and Patient Management. New York, Mary Ann Liebert, pp 187–193
Sinzig J, Döpfner M, Plück J, Banaschewski T, Stephani U, Lehmkuhl G, Rothenberger A, Arbeitsgruppe Methylphenidat (2004) Lassen sich hyperkinetische Auffälligkeiten am Nachmittag durch eine Morgengabe von Methylphenidat Retard vermindern? Zeitschrift für Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie (in press)
Sleator EK, Ullmann RK, von Neumann A (1982) How do hyperactive children feel about taking stimulants and will they tell the doctor? Clin Pediatr (Phila) 21:474–479
Swanson, JM (1992) School based assessment and interventions for ADD students. KC, Publishing, Irvine
Swanson JM, Agler D, Fineberg E, Wigal S, Flynn D, Fineberg K, Quintana Y, Talebi H (2000) University of California, Irvine, Laboratory School Protocol for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies. In: Greenhill LL, Osman BB (eds) Ritalin: Theory and Practice. Mary Ann Liebert, New York, pp 405–432
Swanson JM, Gupta S, Lam A, Shoulson I, Lerner M, Modi N, Lindemulder E, Wigal S (2003) Development of a new once-a-day formulation of methylphenidate for treatment of attentiondeficit/ hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:204–211
Swanson JM, Gupta S, Williams L, Agler D, Lerner M, Wigal S (2002b) Efficacy of a new pattern of delivery of methylphenidate for the treatment of ADHD: effects on activity level in the classroom and on the playground. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41:1306–1314
Swanson JM, Lerner M, Wigal T, Steinhoff K, Greenhill L, Posner K, Freid J, Wigal S (2002a) The use of a laboratory school protocol to evaluate concepts about efficacy and side effects of new formulations of stimulant medications. J Attention Disord 6(Suppl 1):S73–S88
Swanson JM, Wigal S, Greenhill LL, Browne R, Waslik B, Lerner M, Williams L, Flynn D, Agler D, Crowley K, Fineberg E, Baren M, Cantwell DP (1998) Analog classroom assessment of Adderall in children with ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37:519–526
Wilens T, Pelham W, Stein M, Conners KC, Abikoff H, Atkins M, August G, Greenhill L, McBurnett K, Palumbo D, Swanson J, Wolraich M (2003) ADHD treatment with once-daily OROS® methylphenidate: interim 12-month results from a long-term open-label study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:424–433
Wolraich ML, Greenhill LL, Pelham W, Swanson J, Wilens T, Palumbo D, Atkins M, McBurnett K, Bukstein O, August G (2001) Randomized, controlled, trial of OROS methylphenidate once a day in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 180:883–982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Döpfner, M., Gerber, W.D., Banaschewski, T. et al. Comparative efficacy of once–a–day extended–release methylphenidate, two–times–daily immediate–release methylphenidate, and placebo in a laboratory school setting. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 13 (Suppl 1), i93–i101 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-004-1009-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-004-1009-3