Abstract
Objective
An important factor in the assessment of caries risk is the presence of specific oral microflora, especially Streptococcus mutans. Some S. mutans strains possess proteins capable of binding collagen, such as the Cnm and Cbm proteins. The aim is to determine the presence of S. mutans strains carrying collagen binding proteins in a group of subjects with severe early childhood caries (S-ECC).
Materials and methods
S. mutans strains isolated from 15 S-ECC children were analyzed for collagen binding domains (cbd) of the cnm (cbd/cnm) and cbm (cbd/cbm) genes and their ability to bind to collagen.
Results
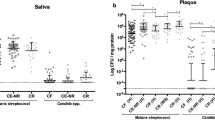
S. mutans strains positive for cbd/cnm or cbd/cbm were only found in 3 subjects with the most severe caries profile, with one subject having both cbd/cnm and cbd/cbm, and the other two with one of each. cnm/cbm-positive S. mutans strains bound to collagen substrate more avidly compared with negative S. mutans strains from each of the three groups.
Conclusions
Our findings of an association between the presence of the collagen binding domains of the cnm/cbm genes in plaque S. mutans and the most aggressive form of caries profile in children offer a potential strategy to identify an individual’s risk for caries progression. Our study should be replicated in other settings and communities in longitudinal and longer-term studies.
Clinical relevance
Our data offer a potential tool in the caries risk management and assessment in children.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAPD. Policy on Early Childhood Caries (ECC): Classifications, consequences, and preventive strategies. ed. 2014: 15–16
Meyer F, Enax J (2018) Early childhood caries: epidemiology, aetiology, and prevention. Int J Dent 2018:1415873
Hajishengallis E, Parsaei Y, Klein MI, Koo H (2017) Advances in the microbial etiology and pathogenesis of early childhood caries. Mol Oral Microbiol 32:24–34
Casamassimo PS, Thikkurissy S, Edelstein BL, Maiorini E (2009) Beyond the dmft: the human and economic cost of early childhood caries. J Am Dent Assoc 140:650–657
Folayan M, Olatubosun S (2018) Early childhood caries - a diagnostic enigma. Eur J Paediatr Dent 19:88
Kanellis MJ, Damiano PC, Momany ET (2000) Medicaid costs associated with the hospitalization of young children for restorative dental treatment under general anesthesia. J Public Health Dent 60:28–32
AAPD (2017) Caries-risk assessment and management for infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Dent 39:197–204
Tanner ACR, Kressirer CA, Rothmiller S, Johansson I, Chalmers NI (2018) The caries microbiome: implications for reversing dysbiosis. Adv Dent Res 29:78–85
Parisotto TM, Steiner-Oliveira C, Silva CM, Rodrigues LK, Nobre-dos-Santos M (2010) Early childhood caries and mutans streptococci: a systematic review. Oral Health Prev Dent 8:59–70
Bowen WH, Burne RA, Wu H, Koo H (2017) Oral biofilms: pathogens, matrix, and polymicrobial interactions in microenvironments. Trends Microbiol
Banas JA (2004) Virulence properties of Streptococcus mutans. Front Biosci 9:1267–1277
Kuramitsu HK (1993) Virulence factors of mutans streptococci: role of molecular genetics. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 4:159–176
Avilés-Reyes A, Miller JH, Lemos JA, Abranches J (2017) Collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans and related streptococci. Mol Oral Microbiol 32:89–106
Orsini G, Majorana A, Mazzoni A, Putignano A, Falconi M, Polimeni A, Breschi L (2014) Immunocytochemical detection of dentin matrix proteins in primary teeth from patients with dentinogenesis imperfecta associated with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur J Histochem 58:2405
Sato Y, Okamoto K, Kagami A, Yamamoto Y, Igarashi T, Kizaki H (2004) Streptococcus mutans strains harboring collagen-binding adhesin. J Dent Res 83:534–539
Singh B, Fleury C, Jalalvand F, Riesbeck K (2012) Human pathogens utilize host extracellular matrix proteins laminin and collagen for adhesion and invasion of the host. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:1122–1180
Avilés-Reyes A, Miller JH, Simpson-Haidaris PJ, Lemos JA, Abranches J (2014) Cnm is a major virulence factor of invasive Streptococcus mutans and part of a conserved three-gene locus. Mol Oral Microbiol 29:11–23
Nomura R, Nakano K, Naka S, Nemoto H, Masuda K, Lapirattanakul J, Alaluusua S, Matsumoto M, Kawabata S, Ooshima T (2012) Identification and characterization of a collagen-binding protein, Cbm, in Streptococcus mutans. Mol Oral Microbiol 27:308–323
Fujihara S, Yokozeki M, Oba Y, Higashibata Y, Nomura S, Moriyama K (2006) Function and regulation of osteopontin in response to mechanical stress. J Bone Miner Res 21:956–964
Abranches J, Miller JH, Martinez AR, Simpson-Haidaris PJ, Burne RA, Lemos JA (2011) The collagen-binding protein Cnm is required for Streptococcus mutans adherence to and intracellular invasion of human coronary artery endothelial cells. Infect Immun 79:2277–2284
Nakano K, Hokamura K, Taniguchi N, Wada K, Kudo C, Nomura R, Kojima A et al (2011) The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke. Nat Commun 2:485
Nomura R, Nakano K, Taniguchi N, Lapirattanakul J, Nemoto H, Grönroos L, Alaluusua S, Ooshima T (2009) Molecular and clinical analyses of the gene encoding the collagen-binding adhesin of Streptococcus mutans. J Med Microbiol 58:469–475
Nomura R, Naka S, Nemoto H, Inagaki S, Taniguchi K, Ooshima T, Nakano K (2013) Potential involvement of collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans in infective endocarditis. Oral Dis 19:387–393
Lapirattanakul J, Nakano K, Nomura R, Leelataweewud P, Chalermsarp N, Klaophimai A, Srisatjaluk R, Hamada S, Ooshima T (2011) Multilocus sequence typing analysis of Streptococcus mutans strains with the cnm gene encoding collagen-binding adhesin. J Med Microbiol 60:1677–1684
Nakano K, Nomura R, Matsumoto M, Ooshima T (2010) Roles of oral bacteria in cardiovascular diseases--from molecular mechanisms to clinical cases: cell-surface structures of novel serotype k Streptococcus mutans strains and their correlation to virulence. J Pharmacol Sci 113:120–125
NIDCR. Dental Caries (Tooth Decay) in Children Age 2 to 11. ed.: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/research/data-statistics/dental-caries/children#units-of-measure 2018. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
Chen Z, Saxena D, Caufield PW, Ge Y, Wang M, Li Y (2007) Development of species-specific primers for detection of Streptococcus mutans in mixed bacterial samples. FEMS Microbiol Lett 272:154–162
Li Y, Caufield PW (1998) Arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction fingerprinting for the genotypic identification of mutans streptococci from humans. Oral Microbiol Immunol 13:17–22
Lévesque CM, Voronejskaia E, Huang YC, Mair RW, Ellen RP, Cvitkovitch DG (2005) Involvement of sortase anchoring of cell wall proteins in biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun 73:3773–3777
Nakano K, Nomura R, Nakagawa I, Hamada S, Ooshima T (2004) Demonstration of Streptococcus mutans with a cell wall polysaccharide specific to a new serotype, k, in the human oral cavity. J Clin Microbiol 42:198–202
Momeni SS, Ghazal T, Grenett H, Whiddon J, Moser SA, Childers NK (2019) Streptococcus mutans serotypes and collagen-binding proteins Cnm/Cbm in children with caries analysed by PCR. Mol Oral Microbiol 34:64–73
Misaki T, Naka S, Hatakeyama R, Fukunaga A, Nomura R, Isozaki T, Nakano K (2016) Presence of Streptococcus mutans strains harbouring the cnm gene correlates with dental caries status and IgA nephropathy conditions. Sci Rep 6:36455
Esberg A, Sheng N, Mårell L, Claesson R, Persson K, Borén T, Strömberg N (2017) Streptococcus mutans adhesin biotypes that match and predict individual caries development. EBioMedicine 24:205–215
Miller JH, Avilés-Reyes A, Scott-Anne K, Gregoire S, Watson GE, Sampson E, Progulske-Fox A et al (2015) The collagen binding protein Cnm contributes to oral colonization and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans OMZ175. Infect Immun 83:2001–2010
Liversidge HM, Molleson T (2004) Variation in crown and root formation and eruption of human deciduous teeth. Am J Phys Anthropol 123:172–180
Lunt RC, Law DB (1974) A review of the chronology of eruption of deciduous teeth. J Am Dent Assoc 89:872–879
Colak H, Dülgergil CT, Dalli M, Hamidi MM (2013) Early childhood caries update: a review of causes, diagnoses, and treatments. J Nat Sci Biol Med 4:29–38
Anil S, Anand PS (2017) Early childhood caries: prevalence, risk factors, and prevention. Front Pediatr 5:157
Feldens CA, Rodrigues PH, de Anastácio G, Vítolo MR, Chaffee BW (2018) Feeding frequency in infancy and dental caries in childhood: a prospective cohort study. Int Dent J 68:113–121
Wyne AH (1999) Early childhood caries: nomenclature and case definition. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 27:313–315
Dimitropoulos Y, Holden A, Gwynne K, Irving M, Binge N, Blinkhorn A (2018) An assessment of strategies to control dental caries in aboriginal children living in rural and remote communities in New South Wales. Australia BMC Oral Health 18:177
American Academy of Pediatrics CoNACH, Canadian Paediatric Society, First Nations, I.uit and Métis Committee (2011) Early childhood caries in indigenous communities. Pediatrics 127:1190–1198
Westerlund B, Korhonen TK (1993) Bacterial proteins binding to the mammalian extracellular matrix. Mol Microbiol 9:687–694
Engels-Deutsch M, Pini A, Yamashita Y, Shibata Y, Haikel Y, Schöller-Guinard M, Klein JP (2003) Insertional inactivation of pac and rmlB genes reduces the release of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 induced by Streptococcus mutans in monocytic, dental pulp, and periodontal ligament cells. Infect Immun 71:5169–5177
Tamura GS, Kuypers JM, Smith S, Raff H, Rubens CE (1994) Adherence of group B streptococci to cultured epithelial cells: roles of environmental factors and bacterial surface components. Infect Immun 62:2450–2458
Misaki T, Naka S, Kuroda K, Nomura R, Shiooka T, Naito Y, Suzuki Y, Yasuda H, Isozaki T, Nakano K (2015) Distribution of Streptococcus mutans strains with collagen-binding proteins in the oral cavity of IgA nephropathy patients. Clin Exp Nephrol 19:844–850
De Menezes Oliveira MA, Torres CP, Gomes-Silva JM, Chinelatti MA, De Menezes FC, Palma-Dibb RG, Borsatto MC (2010) Microstructure and mineral composition of dental enamel of permanent and deciduous teeth. Microsc Res Tech 73:572–577
Lucchese A, Storti E (2011) Morphological characteristics of primary enamel surfaces versus permanent enamel surfaces: SEM digital analysis. Eur J Paediatr Dent 12:179–183
Wilson PR, Beynon AD (1989) Mineralization differences between human deciduous and permanent enamel measured by quantitative microradiography. Arch Oral Biol 34:85–88
Zamudio-Ortega CM, Contreras-Bulnes R, Scougall-Vilchis RJ, Morales-Luckie RA, Olea-Mejía OF, Rodríguez-Vilchis LE (2014) Morphological, chemical and structural characterisation of deciduous enamel: SEM, EDS, XRD, FTIR and XPS analysis. Eur J Paediatr Dent 15:275–280
Zhou Q, Qin X, Qin M, Ge L (2011) Genotypic diversity of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus in 3-4-year-old children with severe caries or without caries. Int J Paediatr Dent 21:422–431
Jiang Q, Yu M, Min Z, Yi A, Chen D, Zhang Q (2012) AP-PCR detection of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus in caries-free and caries-active subjects. Mol Cell Biochem 365:159–164
Corby PM, Lyons-Weiler J, Bretz WA, Hart TC, Aas JA, Boumenna T, Goss J, Corby AL, Junior HM, Weyant RJ, Paster BJ (2005) Microbial risk indicators of early childhood caries. J Clin Microbiol 43:5753–5759
Neves BG, Stipp RN, Bezerra DDS, Guedes SFF, Rodrigues LKA (2018) Quantitative analysis of biofilm bacteria according to different stages of early childhood caries. Arch Oral Biol 96:155–161
Jiang W, Ling Z, Lin X, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yu J, Xiang C, Chen H (2014) Pyrosequencing analysis of oral microbiota shifting in various caries states in childhood. Microb Ecol 67:962–969
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Ryota Nomura, Osaka University, for the kind gift of the S. mutans strains, NN2193-1 (k); Dr. Aaron Bottner for the recruitment and collection of plaque samples of some of the subjects in the study and to Andrea Sarbu for some of the initial analyses of the plaque samples.
Funding
This study was funded by the University of Toronto Dentistry Research Funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study that involved human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the University of Toronto (Research Ethics Board Protocol No.: 32740) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from guardians of all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamba, G.S., Dufour, D., Nainar, S.M.H. et al. Association of Streptococcus mutans collagen binding genes with severe childhood caries. Clin Oral Invest 24, 3467–3475 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03217-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03217-4