Abstract
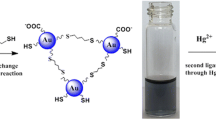
A method is described for the colorimetric determination of mercury(II). In the absence of Hg(II), aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) which is positively charged at pH 7 is electrostatically absorbed on the surface of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). This neutralizes the negative charges of the AuNPs and leads to NP aggregation and a color change from red to blue-purple. However, in the presence of Hg(II), reduced Hg (formed through the reaction between Hg(II) and citrate on the AuNP surface) will replace the APTES on the AuNPs. Hence, the formation of aggregates is suppressed and the color of the solution does not change. The assay is performed by measuring the ratio of absorbances at 650 and 520 nm and can detect Hg(II) at nanomolar levels with a 10 nM limit of detection. The specific affinity between mercury and gold warrants the excellent selectivity for Hg(II) over other environmentally relevant metal ions.

Schematic of the method for determination of Hg2+ based on the gold amalgam-induced deaggregation of gold nanoparticles in the presence of APTES with the LOD of 10.1 nM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bings NH, Bogaerts A, Broekaert JAC (2006) Atomic spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 78:3917–3945
Nolan EM, Lippard SJ (2008) Tools and tactics for the optical detection of mercuric ion. Chem. Rev. 108:3443–3480
Fan Y, Long YF, Li YF (2009) A sensitive resonance light scattering spectrometry of trace Hg2+ with sulfur ion modified gold nanoparticle. Anal. Chim. Acta 653:207–211
Wang Y, Yang F, Yang XR (2010) Colorimetric biosensing of mercury(II) ion using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes and thrombin-binding aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 25:1994–1998
Onyido I, Norris AR, Buncel E (2004) Biomolecule-mercuryinteractions: modalities of DNA base-mercury binding mechanisms. Remediation strategies. Chem. Rev. 104:5911–5929
Kim HN, Ren WX, Kim JS, Yoon J (2012) Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41:3210–3244
Burin GJ, Becking GC (1991) The World-Health-Organization (WHO) guidelines for drinking-water quality: a global perspective on trace contaminants of dinking-water. Trace Substances in Environmental Health-XXIV 207-219.
Han FX, Dean Patterson W, Xia YJ, Maruthi Sridhar BB, Su YJ (2006) Rapid determination of mercury in plant and soil samples using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy, a comparative study. Water Air SoilPollut. 170:161–171
Leermakers M, Baeyens W, Quevauviller P, Horvat M (2005) Mercury inenvironmental samples: speciation, artifacts and validation, Trends Anal. Chem. 24:383–393
Kopysc E, Pyrzynska K, Garbos S, Bulska E (2000) Determination of mercury by cold-vapor atomic absorption spectrometry with preconcentration on a gold-trap. Anal. Sci. 16:1309–1312
Tianyu H, Xu Y, Weidan N, Xingguang S (2016) Aptamer-based aggregation assay for mercury(II) using gold nanoparticles and fluorescent CdTe quantum dots. Microchimica Acta 183:2131–2137
Fong B, Mei W, Siu TS, Lee J, Sai K, Tam S (2007) Determination of mercury inwhole blood and urine by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 31:281–287
Li Y, Chen C, Li B, Sun J, Wang JX, Gao YX, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2006) Elimination efficiency of different reagents for the memory effect of mercury using ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 21:94–96
Zhu H, Zhang S, Li M, Shao Y, Zhu Z (2010) Electrochemical sensor for melamine based on its copper complex. Chem. Commun. 46:2259–2261
Zhang ZP, Tang AA, Liao SZ, Chen PF, Wu ZY, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2011) Oligonucleotide probes applied for sensitive enzyme-amplified electrochemical assay of mercury(II) ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26:3320–3324
Ding YN, Yang BC, Liu H, Liu ZX, Zhang X, Zheng XW, Liu QY (2018) FePt-Au ternary metallic nanoparticles with the enhanced peroxidase-like activity for ultrafast colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators, B 2018(259):775–783
Liu QY, Yang YT, Li H, Zhu RR, Shao Q, Yang SG, Xu JJ (2015) NiO nanoparticles modified with 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyl pheyl)-porphyrin: Promising peroxidase mimetics for H2O2 and glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 64:147–153
Zhang LY, Chen MX, Jiang YL, Chen MM, Ding YN, Liu QY (2017) A facile preparation of montmorillonite-supported copper sulfide nanocomposites and their application in the detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators, B 239:28–35
Sun LF, Ding YY, Jiang YL, Liu QY (2017) Montmorillonite-loaded ceria nanocomposites with superior peroxidase-like activity for rapid colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators, B 239:848–856
Hong M, Zeng B, Li M, Xu X, Chen G (2018) An ultrasensitive conformation-dependent colorimetric probe for the detection of mercury(II) using exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and gold nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta 185:72
Shamsipur M, Safavi A, Mohammadpour Z, Ahmadi R (2016) Highly selective aggregation assay for visual detection of mercury ion based on competitive binding of sulfur-doped carbon nanodots to gold nanoparticles and mercury ions. Microchimica Acta 183:2327–2335
Zarlaida F, Adlim M (2017) Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury(II) ions: a review. Microchimica Acta 184:45–58
Liu S, Leng X, Wang X, Pei Q, Cui X, Wang Y, Huang J (2017) Enzyme-free colorimetric assay for mercury(II) using DNA conjugated to gold nanoparticles and strand displacement amplification. Microchimica Acta 184:1969–1976
Chen ZB, Zhang CM, Tan Y, Zhou TH, Ma H, Wan CQ, Lin YQ, Li K (2015) Chitosan-functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of mercury ions based on chelation-induced aggregation. Microchim Acta 182:611–616
Du J, Zhu B, Peng X, Chen X (2014) Optical reading of contaminants in aqueous media based on gold nanoparticles. Small 10:3461–3479
Song Y, Wei W, Qu X (2011) Colorimetric biosensing using smart materials. Adv. Mater. 23:4215–4236
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 112:2739–2779
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 11:55–75
Alvand M, Shemirani F (2017) A Fe3O4@SiO2@graphene quantum dot core-shell structured nanomaterial as a fluorescent probe and for magnetic removal of mercury(II) ion. Microchim Acta 184:1621–1629
Butwong N, Kunthadong P, Soisungnoen P, Chotichayapong C, Srijaranai S, Luong John HT (2018) Silver-doped CdS quantum dots incorporated into chitosan-coated cellulose as a colorimetric paper test stripe for mercury. Microchimica Acta 185:126
Xu HY, Zhang KN, Liu QS, Liu Y, Xie MX (2017) Visual and fluorescent detection of mercury ions by using a dually emissive ratiometric nanohybrid containing carbon dots and CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184:1199–1206
Zhan L, Yang T, Zhen SJ, Huang CZ (2017) Cytosine triphosphate-capped silver nanoparticles as a platform for visual and colorimetric determination of mercury(II) and chromium(III). Microchim Acta 184:3171–3178
Bi N, Hu MH, Xu J, Jia L (2017) Colorimetric determination ofmercury(II) based on the inhibition of the aggregation of gold nanorods coated with 6-mercaptopurine. Microchim Acta 184:3961–3967
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 132 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y. Colorimetric determination of Hg(II) via the gold amalgam induced deaggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2900-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2900-9