Abstract
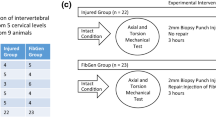
Needle puncture is a common method of inducing intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration in small animal models and may have some similarities to IVD injury conditions such as herniation. Yet, the influence of puncture injuries on IVD biomechanics is not well understood. This study quantified the acute effects of anular injury on the biomechanics of rat caudal IVDs in compression and torsion following puncture with 30, 25 and 21 G needles. In compression, puncture injury reduced elastic stiffness by 20% for all needle sizes, but differences between control and punctured discs did not remain after compressive overload. In contrast, torsional parameters associated with anular fiber tension were affected proportionally with needle size. We conclude that IVD injuries that penetrate through the thickness of the annulus affect IVD biomechanics through different mechanisms for compression and torsion. Anular injuries affect torsional properties in a manner directly related to the amount of fiber disruption and compressive properties in a manner that affects pressurization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Urban JPG, Roberts S (2003) Degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther 5:120–130
Iatridis JC, Michalek AJ, Purmessur D, Korecki CL (2009) Localized intervertebral disc injury leads to organ level changes in structure, cellularity, and biosynthesis. Cell Mol Bioeng 2:437–447
Pollintine P, van Tunen MS, Luo J, Brown MD, Dolan P, Adams MA (1976) Time-dependent compressive deformation of the ageing spine: relevance to spinal stenosis. Spine 35:386–394
Costi JJ, Stokes IA, Gardner-Morse MG, Iatridis JC (2008) Frequency-dependent behavior of the intervertebral disc in response to each of six degree of freedom dynamic loading: solid phase and fluid phase contributions. Spine 33:1731–1738
Carragee EJ, Don AS, Hurwitz EL, Cuellar JM, Carrino J, Herzog R (2009) Does discography cause accelerated progression of degeneration changes in the lumbar disc: a ten-year matched cohort study. Spine 34:2338–2345
Aoki Y, Akeda K, An H, Muehleman C, Takahashi K, Moriya H, Masuda K (2006) Nerve fiber ingrowth into scar tissue formed following nucleus pulposus extrusion in the rabbit anular-puncture disc degeneration model: effects of depth of puncture. Spine 31:E774–E780
Kim KS, Yoon ST, Li J, Park JS, Hutton WC (2005) Disc degeneration in the rabbit: a biochemical and radiological comparison between four disc injury models. Spine 30:33–37
Korecki CL, Costi JJ, Iatridis JC (2008) Needle puncture injury affects intervertebral disc mechanics and biology in an organ culture model. Spine 33:235–241
Miyamoto K, Masuda K, Kim JG, Inoue N, Akeda K, Andersson GB, An HS (2006) Intradiscal injections of osteogenic protein-1 restore the viscoelastic properties of degenerated intervertebral discs. Spine J 6:692–703
Sobajima S, Kim JS, Gilbertson LG, Kang JD (2004) Gene therapy for degenerative disc disease. Gene Ther 11:390–401
Sobajima S, Kompel JF, Kim JS, Wallach CJ, Robertson DD, Vogt MT, Kang JD, Gilbertson LG (2005) A slowly progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray, and histology. Spine 30:15–24
Hsieh AH, Hwang D, Ryan DA, Freeman AK, Kim H (2009) Degenerative anular changes induced by puncture are associated with insufficiency of disc biomechanical function. Spine 34:998–1005
Fazzalari NL, Costi JJ, Hearn TC, Fraser RD, Vernon-Roberts B, Hutchinson J, Manthey BA, Parkinson IH, Sinclair C (2001) Mechanical and pathologic consequences of induced concentric anular tears in an ovine model. Spine 26:2575–2581
Holm S, Ekstrom L, Kaigle Holm A, Hansson T (2007) Intradiscal pressure in the degenerated porcine intervertebral disc. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 20:29–33
Kaigle A, Ekstrom L, Holm S, Rostedt M, Hansson T (1998) In vivo dynamic stiffness of the porcine lumbar spine exposed to cyclic loading: influence of load and degeneration. J Spinal Disord 11:65–70
Keller TS, Holm SH, Hansson TH, Spengler DM (1990) 1990 Volvo Award in experimental studies. The dependence of intervertebral disc mechanical properties on physiologic conditions. Spine 15:751–761
Thompson RE, Pearcy MJ, Barker TM (2004) The mechanical effects of intervertebral disc lesions. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 19:448–455
Thompson RE, Pearcy MJ, Downing KJ, Manthey BA, Parkinson IH, Fazzalari NL (2000) Disc lesions and the mechanics of the intervertebral joint complex. Spine 25:3026–3035
Elliott DM, Yerramalli CS, Beckstein JC, Boxberger JI, Johannessen W, Vresilovic EJ (2008) The effect of relative needle diameter in puncture and sham injection animal models of degeneration. Spine 33:588–596
Beckstein JC, Sen S, Schaer TP, Vresilovic EJ, Elliott DM (2008) Comparison of animal discs used in disc research to human lumbar disc: axial compression mechanics and glycosaminoglycan content. Spine 33:E166–E173 (Phila Pa 1976)
Elliott DM, Sarver JJ (2004) Young investigator award winner: validation of the mouse and rat disc as mechanical models of the human lumbar disc. Spine 29:713–722 (Phila Pa 1976)
O’Connell GD, Vresilovic EJ, Elliott DM (2007) Comparison of animals used in disc research to human lumbar disc geometry. Spine 32:328–333 (Phila Pa 1976)
Espinoza Orias AA, Malhotra NR, Elliott DM (2008) Rat disc torsional mechanics: effect of lumbar and caudal levels and axial compression load. Spine J 9:204–209
Masuoka K, Michalek AJ, MacLean JJ, Stokes IA, Iatridis JC (2007) Different effects of static versus cyclic compressive loading on rat intervertebral disc height and water loss in vitro. Spine 32:1974–1979
MacLean JJ, Lee CR, Alini M, Iatridis JC (2005) The effects of short-term load duration on anabolic and catabolic gene expression in the rat tail intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res 23:1120–1127
Barbir A, Godburn KE, Michalek AJ, Lai A, Monsey RD, Iatridis J (2009) In vivo response of intervertebral discs to static and dynamic torsion. Orthopaedic Research Society, Las Vegas, NV
Pearcy M, Portek I, Shepherd J (1984) Three-dimensional X-ray analysis of normal movement in the lumbar spine. Spine 9:294–297 (Phila Pa 1976)
Veres SP, Robertson PA, Broom ND (2008) ISSLS Prize winner: microstructure and mechanical disruption of the lumbar disc annulus part II: how the annulus fails under hydrostatic pressure. Spine 33:2711–2720
Stokes I, Greenapple DM (1985) Measurement of surface deformation of soft tissue. J Biomech 18:1–7
Stokes IA (1987) Surface strain on human intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res 5:348–355
Adams MA, Green TP (1993) Tensile properties of the annulus fibrosus I. The contribution of fibre–matrix interactions to tensile stiffness and strength. Eur Spine J 2:203–208
Krismer M, Haid C, Rabl W (1996) The contribution of anulus fibers to torque resistance. Spine 21:2551–2557
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1666-5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michalek, A.J., Funabashi, K.L. & Iatridis, J.C. Needle puncture injury of the rat intervertebral disc affects torsional and compressive biomechanics differently. Eur Spine J 19, 2110–2116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1473-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1473-z