Abstract
Background
Serotonin regulates gastrointestinal function, and mast cells are a potential nonneuronal source of serotonin in the esophagus. Tight junction (TJ) proteins in the esophageal epithelium contribute to the barrier function, and the serotonin signaling pathway may contribute to epithelial leakage in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the role of serotonin on barrier function, TJ proteins, and related signaling pathways.
Methods
Normal primary human esophageal epithelial cells were cultured with use of an air–liquid interface system. Serotonin was added to the basolateral compartment, and transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was measured. The expression of TJ proteins and serotonin receptor 7 (5-HT7) was assessed by Western blotting. The involvement of 5-HT7 was assessed with use of an antagonist and an agonist. The underlying cellular signaling pathways were examined with use of specific blockers.
Results
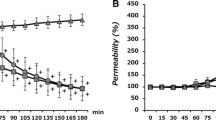
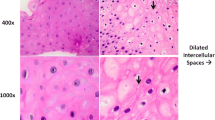
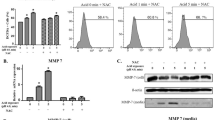
Serotonin decreased TEER and reduced the expression of TJ proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin 1, but not claudin 4. A 5-HT7 antagonist blocked the serotonin-induced decrease in TEER, and a 5-HT7 agonist decreased TEER. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) reduced the serotonin-induced decrease in TEER. Inhibition of p38 MAPK blocked the decrease of ZO-1 levels, whereas extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) inhibition blocked the decrease in occludin levels. Cell signaling pathway inhibitors had no effect on serotonin-induced alterations in claudin 1 and claudin 4 levels. Serotonin induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and ERK, and a 5-HT7 antagonist partially blocked serotonin-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK but not that of ERK.
Conclusions
Serotonin disrupted esophageal squamous epithelial barrier function by modulating the levels of TJ proteins. Serotonin signaling pathways may mediate the pathogenesis of gastroesophageal reflux disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gershon MD. Review article: serotonin receptors and transporters—roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20(Suppl 7):3–14.
Bertrand PP, Bertrand RL. Serotonin release and uptake in the gastrointestinal tract. Auton Neurosci. 2010;153:47–57.
Hornung JP. The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system. J Chem Neuroanat. 2003;26:331–43.
Watanabe H, Rose MT, Aso H. Role of peripheral serotonin in glucose and lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011;22:186–91.
Tozzi A, Staiano A, Paparo F, et al. Characterization of the inflammatory infiltrate in peptic oesophagitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2001;33:452–8.
Moons LM, Kusters JG, Bultman E, et al. Barrett’s oesophagus is characterized by a predominantly humoral inflammatory response. J Pathol. 2005;207:269–76.
Heidmann DE, Metcalf MA, Kohen R, et al. Four 5-hydroxytryptamine7 (5-HT7) receptor isoforms in human and rat produced by alternative splicing: species differences due to altered intron-exon organization. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1372–81.
Li HF, Liu JF, Zhang K, et al. Expression of serotonin receptors in human lower esophageal sphincter. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:49–54.
Forster C. Tight junctions and the modulation of barrier function in disease. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;130:55–70.
Kushnir-Sukhov NM, Brown JM, Wu Y, et al. Human mast cells are capable of serotonin synthesis and release. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:498–9.
Kushnir-Sukhov NM, Gilfillan AM, Coleman JW, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine induces mast cell adhesion and migration. J Immunol. 2006;177:6422–32.
Yang L, Cai H, Tou J, et al. The role of the 5-hydroxytryptamine pathway in reflux-induced esophageal mucosal injury in rats. World J Surg Oncol. 2012;10:219.
Kimura Y, Shiozaki H, Hirao M, et al. Expression of occludin, tight-junction-associated protein, in human digestive tract. Am J Pathol. 1997;151:45–54.
Rendon-Huerta E, Valenzano MC, Mullin JM, et al. Comparison of three integral tight junction barrier proteins in Barrett’s epithelium versus normal esophageal epithelium. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1901–3.
Richter JE. Role of the gastric refluxate in gastroesophageal reflux disease: acid, weak acid and bile. Am J Med Sci. 2009;338:89–95.
Chen X, Oshima T, Tomita T, et al. Acidic bile salts modulate the squamous epithelial barrier function by modulating tight junction proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;301:G203–9.
Oshima T, Gedda K, Koseki J, et al. Establishment of esophageal-like non-keratinized stratified epithelium using normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;300:C1422–9.
Shan J, Oshima T, Muto T, et al. Epithelial-derived nuclear IL-33 aggravates inflammation in the pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis. J Gastroenterol. 2015;50:414–23.
Chen X, Oshima T, Shan J, et al. Bile salts disrupt human esophageal squamous epithelial barrier function by modulating tight junction proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G199–208.
Oshima T, Koseki J, Chen X, et al. Acid modulates the squamous epithelial barrier function by modulating the localization of claudins in the superficial layers. Lab Investig. 2012;92:22–31.
Oshima T, Sasaki M, Kataoka H, et al. Wip1 protects hydrogen peroxide-induced colonic epithelial barrier dysfunction. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:3139–47.
Bueno L, Fioramonti J. Protease-activated receptor 2 and gut permeability: a review. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008;20:580–7.
Raymond JR, Mukhin YV, Gelasco A, et al. Multiplicity of mechanisms of serotonin receptor signal transduction. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;92:179–212.
Kim DY, Camilleri M. Serotonin: a mediator of the brain-gut connection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:2698–709.
Pehlivanov N, Sarosiek I, Whitman R, et al. Effect of cisapride on nocturnal transient lower oesophageal sphincter relaxations and nocturnal gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients with oesophagitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:743–7.
Willis S, Allescher HD, Stoschus B, et al. Double blind placebo controlled study on the effect of the nitric oxide donor molsidomin and the 5-HT3 antagonist ondansetron on human esophageal motility. Z Gastroenterol. 1994;32:632–6.
Koutsoumbi P, Epanomeritakis E, Tsiaoussis J, et al. The effect of erythromycin on human esophageal motility is mediated by serotonin receptors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3388–92.
Grossi L, Ciccaglione AF, Marzio L. Effect of the 5-HT1 agonist sumatriptan on oesophageal motor pattern in patients with ineffective oesophageal motility. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2003;15:9–14.
Barnette MS, Grous M, Manning CD, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and SK&F 103829 contract canine lower esophageal sphincter smooth muscle by stimulating 5-HT2 receptors. Receptor. 1992;2:155–67.
Szczesniak MM, Fuentealba SE, Zhang T, et al. Modulation of esophageal afferent pathways by 5-HT3 receptor inhibition. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25:383–e293.
Liu H, Irving HR, Coupar IM. Expression patterns of 5-HT7 receptor isoforms in the rat digestive tract. Life Sci. 2001;69:2467–75.
Iceta R, Mesonero JE, Aramayona JJ, et al. Expression of 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptors in Caco-2 cells and their role in the regulation of serotonin transporter activity. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;60:157–64.
Guseva D, Holst K, Kaune B, et al. Serotonin 5-HT7 receptor is critically involved in acute and chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20:1516–29.
Zou BC, Dong L, Wang Y, et al. Expression and role of 5-HT7 receptor in brain and intestine in rats with irritable bowel syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007;120:2069–74.
Prins NH, Briejer MR, Van Bergen PJ, et al. Evidence for 5-HT7 receptors mediating relaxation of human colonic circular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;128:849–52.
Stull MA, Pai V, Vomachka AJ, et al. Mammary gland homeostasis employs serotonergic regulation of epithelial tight junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:16708–13.
Pai VP, Horseman ND. Biphasic regulation of mammary epithelial resistance by serotonin through activation of multiple pathways. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:30901–10.
Witte AB, D’Amato M, Poulsen SS, et al. Duodenal epithelial transport in functional dyspepsia: role of serotonin. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2013;4:28–36.
Piche T, Barbara G, Aubert P, et al. Impaired intestinal barrier integrity in the colon of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: involvement of soluble mediators. Gut. 2009;58:196–201.
Martinez C, Lobo B, Pigrau M, et al. Diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: an organic disorder with structural abnormalities in the jejunal epithelial barrier. Gut. 2013;62:1160–8.
Coeffier M, Gloro R, Boukhettala N, et al. Increased proteasome-mediated degradation of occludin in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:1181–8.
Bertiaux-Vandaele N, Youmba SB, Belmonte L, et al. The expression and the cellular distribution of the tight junction proteins are altered in irritable bowel syndrome patients with differences according to the disease subtype. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:2165–73.
Zhang L, Liu G, Han X, et al. Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation attenuates esophageal mucosal damage in a chronic model of reflux esophagitis. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27:1648–56.
Costantini TW, Peterson CY, Kroll L, et al. Role of p38 MAPK in burn-induced intestinal barrier breakdown. J Surg Res. 2009;156:64–9.
Wu HL, Gao X, Jiang ZD, et al. Attenuated expression of the tight junction proteins is involved in clopidogrel-induced gastric injury through p38 MAPK activation. Toxicology. 2013;304:41–8.
Ju Y, Wang T, Li Y, et al. Coxsackievirus B3 affects endothelial tight junctions: possible relationship to ZO-1 and F-actin, as well as p38 MAPK activity. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31:1207–13.
Kevil CG, Oshima T, Alexander B, et al. H2O2-mediated permeability: role of MAPK and occludin. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;279:C21–30.
Samak G, Aggarwal S, Rao RK. ERK is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions, but not adherens junctions, in acetaldehyde-treated Caco-2 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;301:G50–9.
Kim EK, Choi EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802:396–405.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mayumi Yamada and Chiyomi Ito for excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (25460939 to Tadayuki Oshima).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Oshima, T., Tomita, T. et al. Serotonin disrupts esophageal mucosal integrity: an investigation using a stratified squamous epithelial model. J Gastroenterol 51, 1040–1049 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1195-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1195-z