Abstract
Purpose
MicroRNAs are small, non-coding RNAs that are critical regulators of various diseases including cancer, and may represent a novel class of cancer biomarkers. Recent reports have highlighted the oncogenic aspects of miR-125b. However, the level and clinical relevance of circulating miR-125b transcripts in human serum of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients are unclear. The purpose of this study was to identify circulating miR-125b transcripts in human serum for use as a biomarker for stratification and prediction of prognosis in NSCLC.
Methods
We analyzed serum levels of miR-125b in 193 patients with different stages of NSCLC. Blood samples were collected before surgery and therapy. Quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction of circulating miR-125b transcripts was performed directly in serum to improve the efficiency of miRNA assessment. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of serum miR-125b.
Results
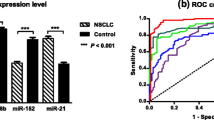
We found that serum miR-125b was consistently expressed in the non-tumor group and was significantly associated with NSCLC stage. miR-125b expression was capable of separating NSCLC patients from control groups with an area under the curve of 0.786. Furthermore, patients with high miR-125b expression displayed a significantly poorer prognosis compared with patients with low expression (p < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis indicated that high miR-125b expression was an independent prognostic factor for survival.
Conclusions
We propose that serum miR-125b may represent a novel biomarker in NSCLC patients and that high miR-125b expression is an independent prognostic factor for survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asaga S, Kuo C, Nguyen T, Terpenning M, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS (2011) Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin Chem 57(1):84–91
Bousquet M, Harris MH, Zhou B, Lodish HF (2010) MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(50):21558–21563
Cabrera-Alarcon JL, Carrillo-Vico A, Santotoribio JD, Leon-Justel A, Sanchez-Gil R, Gonzalez-Castro A, Guerrero JM (2011) CYFRA 21-1 as a tool for distant metastasis detection in lung cancer. Clin Lab 57(11–12):1011–1014
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, Li Q, Li X, Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Jiang X, Xiang Y, Xu C, Zheng P, Zhang J, Li R, Zhang H, Shang X, Gong T, Ning G, Wang J, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY (2008) Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18(10):997–1006
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9:102–114
Gao W, Shen H, Liu L, Xu J, Xu J, Shu Y (2011) miR-21 overexpression in human primary squamous cell lung carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(4):557–566
Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Tian T, Jin G, Shu Y, Chen Y, Xu L, Zen K, Zhang C, Shen H (2010) Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(10):1721–1726
Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S (2010) MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(4):252–263
Le MT, Teh C, Shyh-Chang N, Xie H, Zhou B, Korzh V, Lodish HF, Lim B (2009) MicroRNA-125b is a novel negative regulator of p53. Genes Dev 23(7):862–876
Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S, Ding J, Yao J, Yan M, Li J, Yao M, Ng IO, He X (2010) MicroRNA-125b suppressesed human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting oncogene LIN28B2. Hepatology 52(5):1731–1740
Lin M, Chen W, Huang J, Gao H, Ye Y, Song Z, Shen X (2011) MicroRNA expression profiles in human colorectal cancers with liver metastases. Oncol Rep 25(3):739–747
Liu LH, Li H, Li JP, Zhong H, Zhang HC, Chen J, Xiao T (2011) miR-125b suppresses the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells through down-regulation of STAT3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 416(1–2):31–38
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10513–10518
Nishida N, Yokobori T, Mimori K, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Ishii H, Doki Y, Kuwano H, Mori M (2011) MicroRNA miR-125b is a prognostic marker in human colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol 38(5):1437–1443
Shen J, Todd NW, Zhang H, Yu L, Lingxiao X, Mei Y, Guarnera M, Liao J, Chou A, Lu CL, Jiang Z, Fang H, Katz RL, Jiang F (2011) Plasma microRNAs as potential biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Lab Invest 91(4):579–587
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212–236
Su L, Zhao S, Zhu M, Yu M (2010) Differential expression of microRNAs in porcine placentas on days 30 and 90 of gestation. Reprod Fertil Dev 22(8):1175–1182
Zhang H, Luo XQ, Feng DD, Zhang XJ, Wu J, Zheng YS, Chen X, Xu L, Chen YQ (2011) Upregulation of microRNA-125b contributes to leukemogenesis and increases drug resistance in pediatric acute promyelocytic leukemia. Mol Cancer 10:108
Acknowledgments
We thank the respiratory physicians and pathologists for providing patient clinical information.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuxia, M., Zhennan, T. & Wei, Z. Circulating miR-125b is a novel biomarker for screening non-small-cell lung cancer and predicts poor prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 2045–2050 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1285-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1285-0