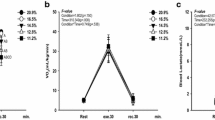
Abstract
This study focuses on the effect of hyperoxia on maximal oxygen uptake \( {\left( {\ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\.\fi{V}{\text{O}}_{{2\max }} } \right)} \) and maximal power (Pmax) in subjects exhibiting exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia (EIH) at sea level. Sixteen competing male cyclists \( \ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\.\fi{V}{\text{O}}_{{2\max }} \)>60 ml·min−1·kg−1) performed exhaustive ramp exercise (cycle-ergometer) under normoxia and moderate hyperoxia (FIO2=30%). After the normoxic trial, the subjects were divided into those demonstrating EIH during exercise [arterial O2 desaturation (Δ SaO2) >5%; n=9] and those who did not (n=7). Under hyperoxia, SaO2 raised and the increase was greater for the EIH than for the non-EIH group (P<0.001). \( \ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\.\fi{V}{\text{O}}_{{2\max }} \) improved for both groups and to a greater extent for EIH (12.8±5.7% vs. 4.2±4.6%, P<0.01; mean±SD) and the increase was correlated to the gain in SaO2 for all subjects (r=0.71, P<0.01). Pmax improved by 3.3±3.3% (P<0.01) regardless of the group. These data suggest that pulmonary gas exchange contributes to a limitation in \( \ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\.\fi{V}{\text{O}}_{{2\max }} \) and power for especially EIH subjects.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barthelemy JC, Geyssant A, Riffat J, Antoniadas A, Berruyer J, Lacour JR (1990) Accuracy of pulse oximetry during moderate exercise: a comparative study. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 50:533–539
Benoit H, Costes F, Feasson L, Lacour JR, Roche F, Denis C, Geyssant A, Barthelemy JC (1997) Accuracy of pulse oximetry during intense exercise under severe hypoxic conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 76:260–263
Benoit H, Busso T, Castells J, Geyssant A, Denis C (2003) Decrease in peak heart rate with acute hypoxia in relation to sea level VO2max. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:514–519
Chapman RF, Emery M, Stager JM (1999) Degree of arterial desaturation in normoxia influences VO2max decline in mild hypoxia. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:658–663
Dempsey JA, Hanson PG, Henderson KS (1984) Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in healthy human subjects at sea level. J Physiol (Lond) 355:161–175
Dempsey JA, Wagner PD (1999) Exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia. J Appl Physiol 87:1997–2006
Ekblom B, Huot R, Stein EM, Thorstensson AT (1975) Effect of changes in arterial oxygen content on circulation and physical performance. J Appl Physiol 39:71–75
Gonzalez-Alonso J, Olsen DB, Saltin B (2002) Erythrocyte and the regulation of human skeletal muscle blood flow and oxygen delivery: Role of circulating ATP. Circ Res 91:1046–1055
Gore CJ, Hahn AG, Scroop GC, Watson DB, Norton KI, Wood RJ, Campbell DP, Emonson DL (1996) Increased arterial desaturation in trained cyclists during maximal exercise at 580 m altitude. J Appl Physiol 80:2204–2210
Harms CA, McClaran SR, Nickele GA, Pegelow DF, Nelson WB, Dempsey JA (2000) Effect of exercise-induced arterial O2 desaturation on VO2max in women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1101–1108
Knight DR, Schaffartzik W, Poole DC, Hogan MC, Bebout DE, Wagner PD (1993) Effects of hyperoxia on maximal leg O2 supply and utilization in men. J Appl Physiol 75:2586–2594
Lawler J, Powers SK, Thompson D (1988) Linear relationship between VO2max and VO2max decrement during exposure to acute hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 64:1486–1492
Mourtzakis M, Gonzáles-Alonso J, Graham TE, Saltin B (2004) Hemodynamics and O2 uptake during maximal knee extensor exercise in untrained and trained human quadriceps muscle: effects of hyperoxia. J Appl Physiol 97:1796–1802
Nielsen HB (2003) Arterial desaturation during exercise in man: implication for O2 uptake and work capacity. Scand J Med Sci Sports 13:339–358
Nielsen HB, Boushel R, Madsen P, Secher NH (1999) Cerebral desaturation during exercise reversed by O2 supplementation. Am J Physiol 277:H1045–H1052
Nielsen HB, Madsen P, Svendsen LB, Roach RC, Secher NH (1998) The influence of PaO2, pH and SaO2 on maximal oxygen uptake. Acta Physiol Scand 164: 89–87
Peltonen JE, Tikkanen HO, Rusko HK (2001) Cardiorespiratory responses to exercise in acute hypoxia, hyperoxia and normoxia. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:82–88
Powers SK, Lawler J, Dempsey JA, Dodd S, Landry G (1989) Effects of incomplete pulmonary gas exchange on VO2max. J Appl Physiol 66:2491–2495
Powers SK, Martin D, Cicale M, Collop N, Huang D, Criswell D (1992) Exercise-induced hypoxemia in athletes: role of inadequate hyperventilation. Eur J Appl Physiol 65:37–42
Powers SK, Martin D, Dodd S (1993) Exercise-induced hypoxaemia in elite endurance athletes. Incidence, causes and impact on VO2max. Sports Med 16:14–22
Prefaut C, Durand F, Mucci P, Caillaud C (2000) Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in athletes: a review (in process citation). Sports Med 30:47–61
Prieur F, Benoit H, Busso T, Castells J, Geyssant A, Denis C (2002) Effects of moderate hyperoxia on oxygen consumption during submaximal and maximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 88:235–242
Prieur F, Busso T, Castells J, Bonnefoy R, Benoit H, Geyssant A, Denis C (1998a) A system to simulate gas exchange in humans to control quality of metabolic measurements. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 78:549–554
Prieur F, Busso T, Castells J, Bonnefoy R, Benoit H, Geyssant A, Denis C (1998b) Validity of oxygen uptake measurements during exercise under moderate hyperoxia. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:958–962
Richardson RS, Leigh JS, Wagner PD, Noyszewski EA (1999) Cellular PO2 as a determinant of maximal mitochondrial O2 consumption in trained human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 87:325–331
Scholander PF (1947) Analyser for accurate estimation of respiratory gases in one-half cubic centimeter samples. J Biol Chem 167:235–250
Welch HG, Bonde-Petersen F, Graham T, Klausen K, Secher N (1977) Effects of hyperoxia on leg blood flow and metabolism during exercise. J Appl Physiol 42:385–390
Welch HG (1982) Hyperoxia and human performance: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:253–262
Welch HG, Pedersen PK (1981) Measurement of metabolic rate in hyperoxia. J Appl Physiol 51:725–731
Zavorsky GS (2000) Evidence and possible mechanisms of altered maximum heart rate with endurance training and tapering (in process citation). Sports Med 29:13–26
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to R. Bonnefoy for technical assistance. The authors declare that the experiments complied with the current French laws.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grataloup, O., Prieur, F., Busso, T. et al. Effect of hyperoxia on maximal O2 uptake in exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemic subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 94, 641–645 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1361-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1361-0