Abstract
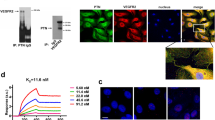
Integrins, a family of transmembrane heterodimeric polypeptides, mediate various biological responses including cell adhesion and migration. In this report, we show that sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) activates integrin αvβ3 in endothelial cells (ECs) via the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor subtype 1 (S1P1)-mediated signaling pathway. S1P treatment results in the activation of integrin αvβ3 in the lamellipodia region of ECs, suggesting that integrin αvβ3 plays a critical role in the S1P-stimulated chemotactic response of ECs. Indeed, S1P treatment induces the association of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and cytoskeletal proteins with integrin αvβ3, the ligation of αv and β3 subunits, as well as enhances endothelial migration on vitronectin-coated substrata. Knockdown endothelial S1P1 receptor, treatments with pertussis toxin or dominant-negative-Rho family GTPases abrogates the S1P-induced integrin αvβ3 activation in ECs. Consequently, these treatments markedly inhibit the S1P-induced endothelial migratory response on vitronectin-coated substrata. Collectively, these data indicate that the S1P-mediated signaling via the S1P1/Gi/Rho GTPases pathway activates integrin αvβ3, which is indispensable for S1P-stimulated chemotactic response of ECs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- S1P:
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate
- S1P1:
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor subtype 1 (old nomenclature EDG-1, endothelial differentiating gene-1)
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- GPCR:
-
G-Protein coupled receptor
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- ECs:
-
Cultured endothelial cells
- MOI:
-
Multiplicity of infection
- PTx:
-
Pertussis toxin
References
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994a) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264:569–571
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, Cheresh DA (1994b) Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79:1157–1164
Cascone I, Napione L, Maniero F, Serini G, Bussolino F (2005) Stable interaction between alpha5beta1 integrin and Tie2 tyrosine kinase receptor regulates endothelial cell response to Ang-1. J Cell Biol 170:993–1004
Chen NS, Leu J, Todorovic V, Lam SC, Lau LF (2004) Identification of a novel integrin alphavbeta3 binding site in CCN1 (CYR61) critical for pro-angiogenic activities in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279:44166–44176
Gamble JR, Matthias LJ, Meyer G, Kaur P, Russ G, Faull R, Berndt MC, Vadas MA (1993) Regulation of in vitro capillary tube formation by anti-integrin antibodies. J Cell Biol 121:931–943
Gao R, Brigstock DR (2004) Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) induces adhesion of rat activated hepatic stellate cells by binding of its C-terminal domain to integrin alpha(v)beta(3) and heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J BioChem 279:8848–8855
Hla T, Maciag T (1990) An abundant transcript induced in differentiating human endothelial cells encodes a polypeptide with structural similarities to G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 265:9308–9313
Kalman D, Gomperts SN, Hardy S, Kitamura M, Bishop JM (1999) Ras family GTPases control growth of astrocyte processes. Mol Biol Cell 10:1665–1683
Kanda S, Tomasini-Johansson B, Klint P, Dixelius J, Rubin K, Claesson-Welsh L (1999) Signaling via fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 is dependent on extracellular matrix in capillary endothelial cell differentiation. Exp Cell Res 248:203–213
Lee MJ, Evans M, Hla T (1996) The inducible G protein-coupled receptor edg-1 signals via the G(i)/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 271:11272–11279
Lee MJ, VanBrocklyn JR, Thangada S, Liu CH, Hand AR, Menzeleev R, Spiegel S, Hla T (1998) Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1. Science 279:1552–1555
Lee MJ, Thangada S, Claffey KP, Ancellin N, Liu CH, Kluk M, Volpi M, Sha’afi RI, Hla T (1999) Vascular endothelial cell adherens junction assembly and morphogenesis induced by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Cell 99:301–312
Lee MJ, Thangada S, Paik JH, Sapkota GP, Ancellin N, Wu M, Morales-Ruiz M, Sessa WC, Alessi D, Hla T (2001) Akt-mediated phosphorylation of the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 is required for endothelial cell chemotaxis. Molecular Cell 8:1–20
Lee JF, Zeng Q, Ozaki H, Wang L, Hand AR, Hla T, Wang E, Lee MJ (2006) Dual roles of tight junction associated protein, zonula occludens-1, in sphingosine-1-phosphate mediated endothelial chemotaxis and barrier integrity. J Biol Chem 281:29190–29200
Leu SJ, Lam SCT, Lau LF (2002) Pro-angiogenic activities of CYR61 (CCN1) mediated through integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha6beta1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:46248–46255
Liu CH, Thangada S, Lee MJ, VanBrocklyn JR, Spiegel S, Hla T (1999) Ligand-induced trafficking of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG-1. Mol Biol Cell 10:1179–1190
Liu Y, Wada R, Yamashita T, Mi Y, Deng CX, Hobson JP, Rosenfeldt HM, Nava VE, Chae SS, Lee MJ, Liu CH, Hla T, Spiegel S, Proia RL (2000) Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation. J Clin Invest 106:951–961
Paik JH, Chae SS, Lee MJ, Thangada S, Hla T (2001) Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced endothelial cell migration requires the expression of EDG-1 and EDG-3 receptors and Rho-dependent activation of alphavbeta3- and beta1-containing integrins. J Biol Chem 276:11830–11837
Retta SF, Cassarà G, D’Amato M, Alessandro R, Pellegrino M, Degani S, DeLeo G, Silengo L, Tarone G (2001) Cross talk between beta(1) and alpha(V) integrins: beta(1) affects beta(3) mRNA stability. Mol Biol Cell 12:3126–3138
Saalbach A, Wetzel A, Haustein UF, Sticherling M, Simon JC, Anderegg U (2005) Interaction of human Thy-1 (CD 90) with the integrin alphavbeta3 (CD51/CD61): an important mechanism mediating melanoma cell adhesion to activated endothelium. Oncogene 24:4710–4720
Schneller M, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E (1997) Alphavbeta3 integrin associates with activated insulin and PDGFbeta receptors and potentiates the biological activity of PDGF. EMBO J 16:5600–5607
Simon KO, Nutt EM, Abraham DG, Rodan GA, Duong LT (1997) The alphavbeta3 integrin regulates alpha5beta1-mediated cell migration toward fibronectin. J Biol Chem 272:29380–29389
Soldi R, Mitola S, Strasly M, Defilippi P, Tarone G, Bussolino F (1999) Role of alphavbeta3 integrin in the activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. EMBO J 18:882–892
Spiegel S, Cuvillier O, Edsall L, Kohama T, Menzeleev R, Olivera A, Thomas D, Tu Z, VanBrocklyn JR, Wang F (1998) Roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate in cell growth, differentiation, and death. Biochemistry 63:69–73
Tsou R, Isik FF (2001) Integrin activation is required for VEGF and FGF receptor protein presence on human microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 224:81–89
VanBrocklyn JR, Lee MJ, Menzeleev R, Olivera A, Edsall L, Cuvillier O, Thomas DM, Thangada S, Hla T, Spiegel S (1998) Dual actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate: extracellular through the Gi-coupled receptor Edg-1 and intracellular to regulate proliferation and survival. J Cell Biol 142:229–240
Varner JA, Cheresh DA (1996) Integrins and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8:724–730
Wang F, VanBrocklyn JR, Hobson JP, Movafagh S, Zukowska-Grojec Z, Milstien S, Spiegel S (1999) Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates cell migration through a G(i)-coupled cell surface receptor. Potential involvement in angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 274:35343–35350
Wu J, Spiegel S, Sturgill TW (1995) Sphingosine 1-phosphate rapidly activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by a G protein-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 270:11484–11488
Yatomi Y, Ruan F, Hakomori S, Igarashi Y (1995) Sphingosine-1-phosphate: a platelet-activating sphingolipid released from agonist-stimulated human platelets. Blood 86:193–202
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Robert Gray and Binks Wattenberg for critical discussion. This work is supported by NIH grant R01HL071071 and AHA grant-in-aid 0755245B (M.-J.L).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Lee, JF., Lin, CY. et al. Rho GTPases mediated integrin αvβ3 activation in sphingosine-1-phosphate stimulated chemotaxis of endothelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol 129, 579–588 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0389-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0389-8