Abstract
Objective
To investigate the safety and efficacy of intensive statin in the acute phase of ischemic stroke after intravenous thrombolysis therapy.
Methods
A total of 310 stroke patients treated with rt-PA were randomly scheduled into the intensive statin group (rosuvastatin 20 mg daily × 14 days) and the control group (rosuvastatin 5 mg daily × 14 days). The primary clinical endpoint was excellent functional outcome (mRS ≤ 1) at 3 months, and the primary safety endpoint was symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) in 90 days.
Results
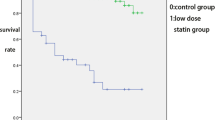
The intensive statin users did not achieve a favorable outcome in excellent functional outcome (mRS ≤ 1) at 3 months compared with controls (70.3% vs. 66.5%, p = 0.464). Intensive statin also not significantly improved the overall distribution of scores on the modified Rankin scale, as compared with controls (p = 0.82 by the Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test). The incidence of primary safety endpoint events (sICH) in 90 days did not significantly differ between the intensive statin group and control group (0.6% vs. 1.3%, p > 0.999).
Conclusion
The INSPIRE study indicated that intensive statin therapy may not improve clinical outcomes compared with the low dose of statin therapy in AIS patients undergoing intravenous thrombolysis, and the two groups had similar safety profile.
Clinical trial registration
URL: http://www.chictr.org. Unique identifier: ChiCTR-IPR-16008642



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data of the INSPIRE trial were included in the article and Online Resource document. The raw data of this trial are available from the corresponding author for reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- INSPIRE:
-
Intensive statin plus intravenous rtPA in acute ischemic stroke
- sICH:
-
Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage
- AIS:
-
Acute ischemic stroke
- rt-PA:
-
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal
- IV:
-
Intravenous
- mRS:
-
Modified Rankin scale
References
Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L, Truelsen T, O’Donnell M, Venketasubramanian N, Barker-Collo S, Lawes CM, Wang W, Shinohara Y, Witt E, Ezzati M, Naghavi M, Murray C (2014) Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (London, England) 383(9913):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(13)61953-4
Furie KL, Jayaraman MV (2018) 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 49(3):509–510. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.118.020176
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW Jr, Qureshi AI, Rosenfield K, Scott PA, Summers DR, Wang DZ, Wintermark M, Yonas H (2013) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44(3):870–947. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e318284056a
Xu AD, Wang YJ, Wang DZ (2013) Consensus statement on the use of intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator to treat acute ischemic stroke by the Chinese Stroke Therapy Expert Panel. CNS Neurosci Ther 19(8):543–548. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12126
Emberson J, Lees KR, Lyden P, Blackwell L, Albers G, Bluhmki E, Brott T, Cohen G, Davis S, Donnan G, Grotta J, Howard G, Kaste M, Koga M, von Kummer R, Lansberg M, Lindley RI, Murray G, Olivot JM, Parsons M, Tilley B, Toni D, Toyoda K, Wahlgren N, Wardlaw J, Whiteley W, del Zoppo GJ, Baigent C, Sandercock P, Hacke W (2014) Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet (London, England) 384(9958):1929–1935. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60584-5
Martí-Fàbregas J, Bravo Y, Cocho D, Martí-Vilalta JL, Díaz-Manera J, San Román L, Puig M, Blanco M, Castellanos M, Millán M, Roquer J, Obach V, Maestre J (2007) Frequency and predictors of symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage in patients with ischemic stroke treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator outside clinical trials. Cerebrovasc Dis (Basel, Switzerland) 23(2–3):85–90. https://doi.org/10.1159/000097043
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Dávalos A, Ford GA, Grond M, Hacke W, Hennerici MG, Kaste M, Kuelkens S, Larrue V, Lees KR, Roine RO, Soinne L, Toni D, Vanhooren G (2007) Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the safe implementation of thrombolysis in stroke-monitoring study (SITS-MOST): an observational study. Lancet (London, England) 369(9558):275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60149-4
LaRosa JC, Grundy SM, Waters DD, Shear C, Barter P, Fruchart JC, Gotto AM, Greten H, Kastelein JJ, Shepherd J, Wenger NK (2005) Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary disease. New Engl J Med 352(14):1425–1435. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa050461
Nc D, Callaly EL, Duggan J, Merwick Á, Hannon N, Sheehan Ó, Marnane M, Horgan G, Williams EB, Harris D, Kyne L, McCormack PM, Moroney J, Grant T, Williams D, Daly L, Kelly PJ (2011) Association between acute statin therapy, survival, and improved functional outcome after ischemic stroke: the North Dublin Population Stroke Study. Stroke 42(4):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.110.596734
Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A 3rd, Goldstein LB, Hennerici M, Rudolph AE, Sillesen H, Simunovic L, Szarek M, Welch KM, Zivin JA (2006) High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. New Engl J Med 355(6):549–559. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa061894
Scheitz JF, Seiffge DJ, Tutuncu S, Gensicke H, Audebert HJ, Bonati LH, Fiebach JB, Tranka C, Lyrer PA, Endres M, Engelter ST, Nolte CH (2014) Dose-related effects of statins on symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage and outcome after thrombolysis for ischemic stroke. Stroke 45(2):509–514. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.002751
Alvarez-Sabin J, Huertas R, Quintana M, Rubiera M, Delgado P, Ribo M, Molina CA, Montaner J (2007) Prior statin use may be associated with improved stroke outcome after tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 38(3):1076–1078. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000258075.58283.8f
Uyttenboogaart M, Koch MW, Koopman K, Vroomen PC, Luijckx GJ, De Keyser J (2008) Lipid profile, statin use, and outcome after intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol 255(6):875–880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0797-7
Miedema I, Uyttenboogaart M, Koopman K, De Keyser J, Luijckx GJ (2010) Statin use and functional outcome after tissue plasminogen activator treatment in acute ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis (Basel, Switzerland) 29(3):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1159/000275500
Martinez-Ramirez S, Delgado-Mederos R, Marin R, Suarez-Calvet M, Sainz MP, Alejaldre A, Vidal-Jordana A, Marti-Vilalta JL, Marti-Fabregas J (2012) Statin pretreatment may increase the risk of symptomatic intracranial haemorrhage in thrombolysis for ischemic stroke: results from a case-control study and a meta-analysis. J Neurol 259(1):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6137-3
Giroud M, Creisson E, Fayolle H, Andre N, Becker F, Martin D, Dumas R (1995) Risk factors for primary cerebral hemorrhage: a population-based study—the Stroke Registry of Dijon. Neuroepidemiology 14(1):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1159/000109775
Cappellari M, Deluca C, Tinazzi M, Tomelleri G, Carletti M, Fiaschi A, Bovi P, Moretto G (2011) Does statin in the acute phase of ischemic stroke improve outcome after intravenous thrombolysis? A retrospective study. J Neurol Sci 308(1–2):128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2011.05.026
Cappellari M, Bovi P, Moretto G, Zini A, Nencini P, Sessa M, Furlan M, Pezzini A, Orlandi G, Paciaroni M, Tassinari T, Procaccianti G, Di Lazzaro V, Bettoni L, Gandolfo C, Silvestrelli G, Rasura M, Martini G, Melis M, Calloni MV, Chiodo-Grandi F, Beretta S, Guarino M, Altavista MC, Marcheselli S, Galletti G, Adobbati L, Del Sette M, Mancini A, Orrico D, Monaco S, Cavallini A, Sciolla R, Federico F, Scoditti U, Brusaferri F, Grassa C, Specchio L, Bongioanni MR, Sparaco M, Zampolini M, Greco G, Colombo R, Passarella B, Adami A, Consoli D, Toni D (2013) The thrombolysis and statins (THRaST) study. Neurology 80(7):655–661. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318281cc83
Geng J, Song Y, Mu Z, Xu Q, Shi G, Sun Y, Chen Y, Lin Y, Pan Y, Yu L, Yang GY, Li Y (2016) Early use of statin in patients treated with alteplase for acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurochir Suppl 121:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18497-5_47
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, Larrue V, Bluhmki E, Davis S, Donnan G, Schneider D, Diez-Tejedor E, Trouillas P (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet (London, England) 352(9136):1245–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08020-9
Allen LM, Hasso AN, Handwerker J, Farid H (2012) Sequence-specific MR imaging findings that are useful in dating ischemic stroke. Radiographics 32(5):1285–1297; discussion 1297–1289. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.325115760
Šimić I, Reiner Ž (2015) Adverse effects of statins—myths and reality. Curr Pharm Des 21(9):1220–1226. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612820666141013134447
Lu D, Liu Y, Mai H, Zang J, Shen L, Zhang Y, Xu A (2018) Rosuvastatin reduces neuroinflammation in the hemorrhagic transformation after rt-PA treatment in a mouse model of experimental stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 12:225. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00225
Kelly P, Prabhakaran S (2017) Statins for neuroprotection after acute ischemic stroke: assorted results but more trials needed. Stroke 48(11):2922–2923. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.117.018725
Nc D, Asplund K, Åsberg S, Callaly E, Cuadrado-Godia E, Díez-Tejedor E, Di Napoli M, Engelter ST, Furie KL, Giannopoulos S, Gotto AM Jr, Hannon N, Jonsson F, Kapral MK, Martí-Fàbregas J, Martínez-Sánchez P, Milionis HJ, Montaner J, Muscari A, Pikija S, Probstfield J, Rost NS, Thrift AG, Vemmos K, Kelly PJ (2013) Statin therapy and outcome after ischemic stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized trials. Stroke 44(2):448–456. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.112.668277
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, Biller J, Brown M, Demaerschalk BM, Hoh B, Jauch EC, Kidwell CS, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Ovbiagele B, Scott PA, Sheth KN, Southerland AM, Summers DV, Tirschwell DL (2018) 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 49(3):e46–e110. https://doi.org/10.1161/str.0000000000000158
Engelter ST, Soinne L, Ringleb P, Sarikaya H, Bordet R, Berrouschot J, Odier C, Arnold M, Ford GA, Pezzini A, Zini A, Rantanen K, Rocco A, Bonati LH, Kellert L, Strbian D, Stoll A, Meier N, Michel P, Baumgartner RW, Leys D, Tatlisumak T, Lyrer PA (2011) IV thrombolysis and statins. Neurology 77(9):888–895. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822c9135
Hong KS, Lee JS (2015) Statins in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Journal of stroke 17(3):282–301. https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2015.17.3.282
Bourcier T, Libby P (2000) HMG CoA reductase inhibitors reduce plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(2):556–562
Sanguigni V, Pignatelli P, Lenti L, Ferro D, Bellia A, Carnevale R, Tesauro M, Sorge R, Lauro R, Violi F (2005) Short-term treatment with atorvastatin reduces platelet CD40 ligand and thrombin generation in hypercholesterolemic patients. Circulation 111(4):412–419. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000153810.81187.7d
Notarbartolo A, Davi G, Averna M, Barbagallo CM, Ganci A, Giammarresi C, La Placa FP, Patrono C (1995) Inhibition of thromboxane biosynthesis and platelet function by simvastatin in type IIa hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 15(2):247–251
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staffs of the Department of Neurology and Stroke Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University and Clinical Neuroscience Institute of Jinan University, China.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81171084, 81671167, and 81801150), the Guangzhou Science and Technology Program of China (No. 2014Y2-00505), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong, China (No. 2014A030313384, 201508020004 and 2017A020215049), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2018A0303130182).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
An-Ding Xu, Qing-Yu Shen, Wan-Yong Yang and Yu-Feng Li contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Zi-Ran Wang, Tian-Xia Yu, Dong-Juan Xu, Nan Yang, Xiao-Yuan Niu, Li-An Huang, Yu-Sheng Zhang, Dan Lu, Ying Guan, Ze-Feng Tan, Hui-Li Zhu, Bing Yang, Da-Wei Dong, Niu He, Xue-Li Cai, Wen-Yan Zhuo, Xue-Mei Wu, Min Yan, Jun-Shan Zhou, Hao-Wen Zhang, Zhi-Gang Liang, Wen-Jun Wu, Jian-Hua Cheng. Analysis and interpretation of the data were done by Ying Guan and Yu-Feng Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yu-Feng Li, and An-Ding Xu, Wan-Yong Yang and Ze-Feng Tan commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, WY., Li, YF., Wang, ZR. et al. Combined therapy of intensive statin plus intravenous rt-PA in acute ischemic stroke: the INSPIRE randomized clinical trial. J Neurol 268, 2560–2569 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-10388-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-10388-3