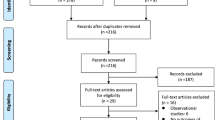
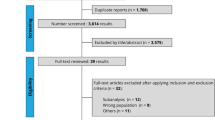
Abstract
To review the literature for randomized control trials (RCTs) and prospective cohort studies investigating the safety and efficacy of tirofiban and eptifibatide in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane library were searched for available papers published up to September 2021. The efficacy was evaluated based on the 3-month favorable outcome [modified Rankin scale (mRS) = 0–1], functional outcome (mRS = 0–2), and the last available National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score measured in each study. Twelve studies (two RCTs and 10 prospective cohorts) and 2926 patients were included. Treatment with tirofiban or eptifibatide had no effects on the favorable outcome (RR = 1.09, 95% CI 0.89–1.35, P = 0.411), functional outcome (RR = 1.12, 95% CI 0.98–1.28, P = 0.010), and last available NIHSS (WMD = − 2.32, 95% CI − 5.14 to 0.50, P = 0.106), but might increase mortality (RR = 0.84, 95% CI 0.71–0.99, P = 0.121). The sensitivity analyses showed that the meta-analyses were robust. There was no significant publication bias. Tirofiban did not increase the risk of ICH (P = 0. 423) and sICH (P = 0. 990) but increased the risk of fatal ICH (RR = 3.59, 95% CI 1.62–7.96, P = 0.002). Thrombolysis/thrombectomy did not influence any of the outcomes. Adding tirofiban or eptifibatide to thrombolysis/thrombectomy was not significantly associated with a favorable outcome (mRS = 0–1) nor functional outcome (mRS = 0–2) in patients with AIS at 3 months, but might be associated with mortality, possibly due to fatal ICH. The NIHSS was also not significantly different between the intervention and control groups after treatments.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, Biller J, Brown M, Demaerschalk BM, Hoh B, Jauch EC, Kidwell CS, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Ovbiagele B, Scott PA, Sheth KN, Southerland AM, Summers DV, Tirschwell DL, American Heart Association Stroke C (2018) 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 49(3):e46–e110. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000158
van den Berg LA, Dijkgraaf MG, Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, Lingsma HF, Majoie CB, Dippel DW, van der Lugt A, van Oostenbrugge RJ, van Zwam WH, Roos YB, Investigators MC (2017) Two-year outcome after endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 376(14):1341–1349. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1612136
Kang DH, Kim YW, Hwang YH, Park SP, Kim YS, Baik SK (2014) Instant reocclusion following mechanical thrombectomy of in situ thromboocclusion and the role of low-dose intra-arterial tirofiban. Cerebrovasc Dis 37(5):350–355. https://doi.org/10.1159/000362435
Powers WJ, Derdeyn CP, Biller J, Coffey CS, Hoh BL, Jauch EC, Johnston KC, Johnston SC, Khalessi AA, Kidwell CS, Meschia JF, Ovbiagele B, Yavagal DR, American Heart Association Stroke C (2015) 2015 American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Focused Update of the 2013 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke Regarding Endovascular Treatment: a Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 46(10):3020–3035. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000074
Rubiera M, Alvarez-Sabin J, Ribo M, Montaner J, Santamarina E, Arenillas JF, Huertas R, Delgado P, Purroy F, Molina CA (2005) Predictors of early arterial reocclusion after tissue plasminogen activator-induced recanalization in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 36(7):1452–1456. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000170711.43405.81
Global Use of Strategies to Open Occluded Coronary Arteries I (1997) A comparison of reteplase with alteplase for acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 337(16):1118–1123. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199710163371603
Qureshi AI, Luft AR, Sharma M, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN (2000) Prevention and treatment of thromboembolic and ischemic complications associated with endovascular procedures: part I-Pathophysiological and pharmacological features. Neurosurgery 46(6):1344–1359. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200006000-00012
Yasuda T, Gold HK, Fallon JT, Leinbach RC, Garabedian HD, Guerrero JL, Collen D (1989) A canine model of coronary artery thrombosis with superimposed high grade stenosis for the investigation of rethrombosis after thrombolysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 13(6):1409–1414. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-1097(89)90319-7
Niu J, Ding Y, Zhai T, Ju F, Lu T, Xue T, Yin D, Fang D, Chen H, Zhao G (2019) The efficacy and safety of tirofiban for patients with acute ischemic stroke: a protocol for systematic review and a meta-analysis. Medicine 98(9):e14673. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000014673
Bansal AB, Sattar Y, Jamil RT (2021) Eptifibatide. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL)
McClellan KJ, Goa KL (1998) Tirofiban: a review of its use in acute coronary syndromes. Drugs 56(6):1067–1080. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199856060-00017
Harker LA (1998) Therapeutic inhibition of platelet function in stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 8(Suppl 5):8–18. https://doi.org/10.1159/000047513
Dubey D, Banerjee C, Sawhney A, Sharma A, Alberts MJ (2014) Combination therapy of intravenous glycoprotein IIB/IIIA inhibitors and tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. Neurol India 62(6):631–634. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.149385
Ciccone A, Motto C, Abraha I, Cozzolino F, Santilli I (2014) Glycoprotein IIb-IIIa inhibitors for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD005208. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005208.pub3
Guo Y, Lin Y, Tang Y, Tang Q, Wang X, Pan X, Zou J, Yang J (2019) Safety and efficacy of early antiplatelet therapy in acute ischemic stroke patients receiving endovascular treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci 66:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2019.05.028
Zhou J, Gao Y, Ma QL (2020) Safety and efficacy of tirofiban in acute ischemic stroke patients not receiving endovascular treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(3):1492–1503. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202002_20208
Gong J, Shang J, Yu H, Wan Q, Su D, Sun Z, Liu G (2020) Tirofiban for acute ischemic stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 76(4):475–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02817-8
Fu Z, Xu C, Liu X, Wang Z, Gao L (2020) Safety and efficacy of tirofiban in acute ischemic stroke patients receiving endovascular treatment: a meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis 49(4):442–450. https://doi.org/10.1159/000509054
Selcuk AA (2019) A Guide for Systematic Reviews: PRISMA. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 57(1):57–58. https://doi.org/10.5152/tao.2019.4058
Aslam S, Emmanuel P (2010) Formulating a researchable question: a critical step for facilitating good clinical research. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS 31(1):47–50. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7184.69003
Pancioli AM, Broderick J, Brott T, Tomsick T, Khoury J, Bean J, del Zoppo G, Kleindorfer D, Woo D, Khatri P, Castaldo J, Frey J, Gebel J Jr, Kasner S, Kidwell C, Kwiatkowski T, Libman R, Mackenzie R, Scott P, Starkman S, Thurman RJ, Investigators CT (2008) The combined approach to lysis utilizing eptifibatide and rt-PA in acute ischemic stroke: the CLEAR stroke trial. Stroke 39(12):3268–3276. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.517656
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D, Lesaffre E, von Kummer R, Boysen G, Bluhmki E, Hoxter G, Mahagne MH et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274(13):1017–1025
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, Larrue V, Bluhmki E, Davis S, Donnan G, Schneider D, Diez-Tejedor E, Trouillas P (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 352(9136):1245–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08020-9
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Davalos A, Guidetti D, Larrue V, Lees KR, Medeghri Z, Machnig T, Schneider D, von Kummer R, Wahlgren N, Toni D, Investigators E (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359(13):1317–1329. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0804656
Li W, Lin L, Zhang M, Wu Y, Liu C, Li X, Huang S, Liang C, Wang Y, Chen J, Feng W (2016) Safety and preliminary efficacy of early tirofiban treatment after alteplase in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke 47(10):2649–2651. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.014413
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (2019) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane Collaboration, London
Lo CK, Mertz D, Loeb M (2014) Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol 14:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-45
Torgano G, Zecca B, Monzani V, Maestroni A, Rossi P, Cazzaniga M, Manganaro D, Boiti C, Zilioli E, Borutti G, Falaschi F, Mandelli C (2010) Effect of intravenous tirofiban and aspirin in reducing short-term and long-term neurologic deficit in patients with ischemic stroke: a double-blind randomized trial. Cerebrovasc Dis 29(3):275–281. https://doi.org/10.1159/000275503
Sun C, Li X, Zhao Z, Chen X, Huang C, Li X, Shan Y, Zou Y, Liu Y, Ibrahim M, Nyame L, Song B, Wang F, Zheng X, Hu J, Zhao Z, Zhou J, Zou J (2019) Safety and efficacy of tirofiban combined with mechanical thrombectomy depend on ischemic stroke etiology. Front Neurol 10:1100. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.01100
Pan X, Zheng D, Zheng Y, Chan PWL, Lin Y, Zou J, Zhou J, Yang J (2019) Safety and efficacy of tirofiban combined with endovascular treatment in acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol 26(8):1105–1110. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13946
Wu C, Sun C, Wang L, Lian Y, Xie N, Huang S, Zhao W, Ren M, Wu D, Ding J, Song H, Wang Y, Ma Q, Ji X (2019) Low-dose tirofiban treatment improves neurological deterioration outcome after intravenous thrombolysis. Stroke 50(12):3481–3487. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026240
Wu Y, Yin C, Yang J, Jiang L, Parsons MW, Lin L (2018) Endovascular thrombectomy. Stroke 49(11):2783–2785. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022919
Yang M, Huo X, Gao F, Wang A, Ma N, Shi H, Chen W, Wang S, Wang Y, Miao Z (2020) Low-dose rescue tirofiban in mechanical thrombectomy for acute cerebral large-artery occlusion. Eur J Neurol 27(6):1056–1061. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14170
Zhao W, Che R, Shang S, Wu C, Li C, Wu L, Chen J, Duan J, Song H, Zhang H, Ling F, Wang Y, Liebeskind D, Feng W, Ji X (2017) Low-dose tirofiban improves functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with endovascular thrombectomy. Stroke 48(12):3289–3294. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019193
Kellert L, Hametner C, Rohde S, Bendszus M, Hacke W, Ringleb P, Stampfl S (2013) Endovascular stroke therapy: tirofiban is associated with risk of fatal intracerebral hemorrhage and poor outcome. Stroke 44(5):1453–1455. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000502
Huo X, Raynald WA, Mo D, Gao F, Ma N, Wang Y, Wang Y, Miao Z (2021) Safety and efficacy of tirofiban for acute ischemic stroke patients with large artery atherosclerosis stroke etiology undergoing endovascular therapy. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.630301
Ma G, Li S, Jia B, Mo D, Ma N, Gao F, Huo X, Luo G, Wang A, Pan Y et al (2021) Safety and efficacy of low-dose tirofiban combined with intravenous thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke: a matched-control analysis from a Nationwide Registry. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.666919
Siebler M, Hennerici MG, Schneider D, von Reutern GM, Seitz RJ, Rother J, Witte OW, Hamann G, Junghans U, Villringer A, Fiebach JB (2011) Safety of tirofiban in acute ischemic stroke: the SaTIS trial. Stroke 42(9):2388–2392. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.599662
Mangiafico S, Cellerini M, Nencini P, Gensini G, Inzitari D (2005) Intravenous glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor (tirofiban) followed by intra-arterial urokinase and mechanical thrombolysis in stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(10):2595–2601
Kwon JH, Shin SH, Weon YC, Hwang JC, Baik SK (2011) Intra-arterial adjuvant tirofiban after unsuccessful intra-arterial thrombolysis of acute ischemic stroke: preliminary experience in 16 patients. Neuroradiology 53(10):779–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0939-y
Kim JW, Jeon P, Kim GM, Bang OY, Byun HS, Kim KH (2012) Local intraarterial tirofiban after formation of anterograde flow in patients with acute ischemic stroke: preliminary experience and short term follow-up results. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114(10):1316–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.04.022
Ottani F, La Vecchia L, De Vita M, Catapano O, Tarantino F, Galvani M (2010) Comparison by meta-analysis of eptifibatide and tirofiban to abciximab in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol 106(2):167-174 e161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.03.012
Antoniucci D (2007) Differences among GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors: different clinical benefits in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome percutaneous coronary intervention patients. Eur Heart J 9(Suppl_a):A32–A36
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LJT conceived and supervised the study; YYH searched for studies; LJT analyzed the data; XX, LJT wrote the manuscript; LHB made manuscript revisions. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Yang, Y. & Liu, H. Efficacy outcomes and safety measures of intravenous tirofiban or eptifibatide for patients with acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Thromb Thrombolysis 53, 898–910 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-021-02584-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-021-02584-3