Abstract
Background
Many Chinese patients who experience chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) have been shown to exhibit specifically enhanced TH1/TH17 responses and excessive neutrophil accumulation without demonstrating significant eosinophilia. These patients may be subject to different pathologies and therapies compared to Western patients. YKL40 can be produced by neutrophil and is associated with many inflammatory diseases, while its role in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) has yet to be determined.
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between the expression level and biologic role of YKL40 in CRS.
Methods
YKL40 expression was examined via quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), immunohistochemistry, and Western blot. Human nasal epithelia cells (HNECs) were isolated to detect YKL40 expression in response to specific inflammatory stimulation.
Results
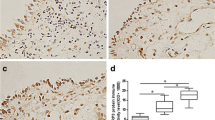
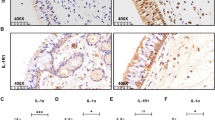
YKL40 expression levels were significantly higher in NP patients compared to the turbinates of CRSsNP/CRSwNP and the control group and can be strongly activated by stimulation with IL-4 in vitro and suppressed by the other pro-inflammatory cytokines; lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and dexamethasone also caused significant decreases in YKL40 expression in HNECs.
Conclusions
YKL40 may play a significant role in Chinese patients with CRSwNP. The molecular mechanisms identified here may aid in the design of new therapeutic strategies for improving the clinical outcomes of Chinese patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Zele T, Claeys S, Gevaert P, Van Maele G, Holtappels G, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2006) Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy 61(11):1280–1289. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01225.x
Tomassen P, Van Zele T, Zhang N, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Gevaert P, Bachert C (2011) Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 8(1):115–120. https://doi.org/10.1513/pats.201005-036RN
Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, Wang DY, Desrosiers M, Liu Z (2009) Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124(3):478–484, 484.e471–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017
Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia W, Luo Q, Zheng J, Wang H, Li Z, Xia J, Jiang H, Liu Z, Shi J, Li H, Xu G (2012) Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129(6):1522–1528.e1525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.079
Meng G, Zhao Y, Bai X, Liu Y, Green TJ, Luo M, Zheng X (2010) Structure of human stabilin-1 interacting chitinase-like protein (SI-CLP) reveals a saccharide-binding cleft with lower sugar-binding selectivity. J Biol Chem 285(51):39898–39904. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.130781
Kawada M, Hachiya Y, Arihiro A, Mizoguchi E (2007) Role of mammalian chitinases in inflammatory conditions. Keio J Med 56(1):21–27
Mizoguchi E (2006) Chitinase 3-like-1 exacerbates intestinal inflammation by enhancing bacterial adhesion and invasion in colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 130(2):398–411. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.007
Lai T, Wu D, Chen M, Cao C, Jing Z, Huang L, Lv Y, Zhao X, Lv Q, Wang Y, Li D, Wu B, Shen H (2016) YKL-40 expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: relation to acute exacerbations and airway remodeling. Respir Res 17:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-016-0338-3
Zhou Y, Peng H, Sun H, Peng X, Tang C, Gan Y, Chen X, Mathur A, Hu B, Slade MD, Montgomery RR, Shaw AC, Homer RJ, White ES, Lee CM, Moore MW, Gulati M, Lee CG, Elias JA, Herzog EL (2014) Chitinase 3-like 1 suppresses injury and promotes fibroproliferative responses in Mammalian lung fibrosis. Sci Transl Med 6(240):240ra276. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3007096
Park SJ, Jun YJ, Kim TH, Jung JY, Hwang GH, Jung KJ, Lee SH, Lee HM, Lee SH (2013) Increased expression of YKL-40 in mild and moderate/severe persistent allergic rhinitis and its possible contribution to remodeling of nasal mucosa. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27(5):372–380. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3941
Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, Brook I, Kumar KA, Kramper M, Orlandi RR, Palmer JN, Patel ZM, Peters A, Walsh SA, Corrigan MD (2015) Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis executive summary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 152(4):598–609. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599815574247
Wang H, Bai J, Ding M, Liu W, Xu R, Zhang J, Shi J, Li H (2013) Interleukin-17A contributes to the expression of serum amyloid A in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol Off J Eur Fed Otorhinolaryngol Soc (EUFOS) Affil Ger Soc Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 270(6):1867–1872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2295-x
Van Bruaene N, Derycke L, Perez-Novo CA, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, Cuvelier C, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2009) TGF-beta signaling and collagen deposition in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124(2):253–259, 259.e251–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.04.013
Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2008) Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122(5):961–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.07.008
Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, Lanza DC, Marple BF, Nicklas RA, Bachert C, Baraniuk J, Baroody FM, Benninger MS, Brook I, Chowdhury BA, Druce HM, Durham S, Ferguson B, Gwaltney JM, Kaliner M, Kennedy DW, Lund V, Naclerio R, Pawankar R, Piccirillo JF, Rohane P, Simon R, Slavin RG, Togias A, Wald ER, Zinreich SJ (2004) Rhinosinusitis: establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114(6 Suppl):155–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.09.029
Lui JK, Lutchen KR (2017) The role of heterogeneity in asthma: a structure-to-function perspective. Clin Transl Med 6(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-017-0159-0
Hew M, Bhavsar P, Torrego A, Meah S, Khorasani N, Barnes PJ, Adcock I, Chung KF (2006) Relative corticosteroid insensitivity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in severe asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174(2):134–141. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200512-1930OC
Capone M, Maggi L, Santarlasci V, Rossi MC, Mazzoni A, Montaini G, Cimaz R, Ramazzotti M, Piccinni MP, Barra G, De Palma R, Liotta F, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F, Cosmi L (2016) Chitinase 3-like-1 is produced by human Th17 cells and correlates with the level of inflammation in juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients. Clin Mol Allergy CMA 14:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12948-016-0053-0
Specjalski K, Chelminska M, Jassem E (2015) YKL-40 protein correlates with the phenotype of asthma. Lung 193(2):189–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-015-9693-y
Lai T, Chen M, Deng Z, L Y, Wu D, Li D, Wu B (2015) YKL-40 is correlated with FEV1 and the asthma control test (ACT) in asthmatic patients: influence of treatment. BMC Pulm Med 15:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2466-15-1
Zhu Z, Zheng T, Homer RJ, Kim YK, Chen NY, Cohn L, Hamid Q, Elias JA (2004) Acidic mammalian chitinase in asthmatic Th2 inflammation and IL-13 pathway activation. Science 304(5677):1678–1682. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1095336
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all the authors who have made efforts in the whole program, and also thank all the researchers of the primary studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yue Ma declares that she has no conflict of interest. Chunquan Zheng declares that he has no conflict of interest. Le Shi declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Zheng, C. & Shi, L. The role of YKL40 in the pathogenesis of CRS with nasal polyps. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 431–438 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4859-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4859-2