Abstract
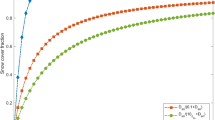
The influence of soil moisture on Asian monsoon simulation/prediction was less studied, partly due to a lack of available and reliable soil moisture datasets. In this study, we firstly compare several soil moisture datasets over the Tibetan Plateau, and find that the remote sensing products from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for Earth Observing System (AMSR-E) can capture realistic temporal variations of soil moisture better than the two reanalyses (NCEP and ECMWF) during the pre-monsoon seasons. Using the AMSR-E soil moisture product, we investigate the impacts of soil moisture over the Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer monsoon onset based on a Spectral Atmospheric Model developed at IAP/LASG (SAMIL). Comparison between results with and without the assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture data demonstrates that with soil moisture assimilated into SAMIL, the land-sea thermal contrast during pre-monsoon seasons is more realistic. Accordingly, the simulation of summer monsoon onset dates over both the Bay of Bengal and South China Sea regions are more accurate with AMSR-E soil moisture assimilated. This study reveals that the application of the soil moisture remote sensing products in a numerical model could potentially improve prediction of the Asian summer monsoon onset.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthakrishnan, R., and M. K. Soman, 1988: The onset of south-west monsoon over Kerala: 1901–1980. J. Climate, 8, 283–296.
Bao, Q., Y. M. Liu, T. J. Zhou, Z. Z. Wang, G. X. Wu, and P. F. Wang, 2006: The sensitivity of the Spectral Atmospheric General Circulation Model of LASG/IAP to the land process. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 30, 1077–1090. (in Chinese)
Dai, Y. J., and Coauthors, 2003: The Common Land Model. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 84, 1013–1023.
Douville, H., P. Viterbo, J. F. Mahfouf, and A. C. M. Beljaars, 2000: Evaluation of the optimum interpolation and nudging techniques for soil moisture analysis using FIFE data. Mon. Wea. Rev., 128, 1733–1756.
Edwards, J. M., and A. Slingo, 1996: Studies with a flexible new radiation code. 1. Choosing a configuration for a large-scale model. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 122, 689–719.
Fasullo, J., and P. J. Webster, 2003: A hydrological definition of Indian monsoon onset and withdrawal. J. Climate, 16, 3200–3211.
Kaihotsu, I., and T. Koike, 2005: Improving our understanding of climate change—Observing our water planet using AMSR and AMSRE. Chapter 6, Terrestrial Hydrology: Soil Moisture and Snow. [Available online from http://sharaku.eorc.jaxa.jp/AMSR/doc/index.html]
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–471.
Koster, R. D., and Coauthors, 2004: Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science, 305, 1138–1140.
Kripalani, R. H., J. H. Oh, and H. S. Chaudhari, 2007: Response of the East Asian summer monsoon to doubled atmospheric CO2: Coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 87, 1–28.
Lau, K.-M., and S. Yang, 1997: Climatology and interannual variability of the southeast Asian summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 141–162.
Liang, X. Y., Y. M. Liu, and G. X. Wu, 2006: Roles of tropical and subtropical land-sea distribution and the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in the formation of the Asian summer monsoon. Chinese J. Geophys., 49, 983–992. (in Chinese)
Liu, Y. M., J. C. L. Chan, J. Y. Mao, and G. X. Wu, 2002: The role of Bay of Bengal convection in the onset of the 1998 South China Sea summer monsoon. Mon. Wea. Rev., 130, 2731–2744.
Luo, H., and M. Yanai, 1984: The large-scale circulation and heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas during the early summer of 1979. Part: Heat and moisture budgets. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 966–989.
Ma, Z. G., Z. B. Fu, L. Xie, W. H. Chen, and S.W. Tao, 2001: Some problems in the study on the relationship between soil moisture and climatic change. Advances in Earth Science, 16, 563–568.
Mao, J. Y., G. X. Wu, and Y. M. Liu, 2002: Study on modal variation of subtropical high and its mechanism during seasonal transition part II: Seasonal transition index over Asian monsoon region. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 60(4) 409–420.
Nitta, T., 1983: Observational study of heat source over the eastern Tibetan Plateau during the summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 61, 590–605.
Njoku, E. G., T. J. Jackson, V. Lakshmi, T. K. Chan, and S. V. Nghiem, 2003: Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 41, 215–229.
Paniconi, C., M. Marrocu, M. Putti, and M. Verbunt, 2003: Newtonian nudging for a Richards equationbased distributed hydrological model. Advances in Water Resources, 26, 161–178.
Pitman, A. J., 2003: The evolution of, and revolution in, land surface schemes designed for climate models. International Journal of Climatology, 23, 479–510.
Qian, Y. F., Y. Q. Zheng, Y. Zhang, and M. Q. Miao, 2003: Responses of China’s summer monsoon climate to snow anomaly over the Tibetan Plateau. International Journal of Climatology, 23, 593–613.
Reynolds, R. W., and D. C. Marsico, 1993: An improved real-time global sea-surface temperature analysis. J. Climate, 6, 114–119.
Robock, A., and Coauthors, 2000: The global soil moisture data bank. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 81, 1281–1299.
Shen, X. H., M. Kimoto, and A. Sumi, 1998: Role of land surface processes associated with interannual variability of broad-scale Asian summer monsoon as simulated by the CCSR/NIES AGCM. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 76, 217–236.
Singh, O. P., H. R. Hatwar and O. Prasad, 2007: Surface and upper air meteorological features during onset phase of 2003 monsoon. Journal of Earth System Science, 116(4), 305–310.
Tanaka, M., 1992: Intraseasonal oscillation and the onset and retreat dates of the summer monsoon over the east, southeast and western North Pacific region using GMS high cloud amount data. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 613–629.
Tiedtke, M., 1989: A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large-scale models. Mon. Wea. Rev., 117, 1779–1800.
Uppala, S. M., and Coauthors, 2005: The ERA-40 reanalysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 2961–3012.
Viterbo, P., 1996: The representation of surface processes in general circulation models. Ph. D. dissertation, University of Lisbon, 201pp.
Walker, J. P., 1999: Estimating soil moisture profile dynamics from near-surface soil moisture measurements and standard meteorological data. Ph. D. dissertation, Department of Civil, Surveying and Environmental Engineering, University of Newcastle, 766pp.
Wang, B., and Lin Ho, 2002: Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsoon. J. Climate, 15, 386–398.
Wang, B., and Z. Fan, 1999: Choice of south Asian summer monsoon indices. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 80, 629–638.
Wang, B., Lin Ho, Y. S. Zhang, and M. M. Lu, 2004: Definition of South China Sea monsoon onset and commencement of the East Asia summer monsoon. J. Climate, 17, 699–710.
Wang, Z. Z., G. X. Wu, P. Liu, and T. W. Wu, 2005: The development of GOALS/LASG AGCM and its global climatological features in climate simulation, I: Influence of horizontal resolution. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 21, 225–237. (in Chinese)
Webster P. J., T. Palmer, M. Yanai, R. Tomas, V. Magana, J. Shukla, and A. Yasunari, 1998: Monsoons: Processes, predictability and the prospects for prediction. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 14451–14510.
Wu, G. X., H. Liu, Y. C. Zhao, and W. P. Li, 1996: A nine-layer atmospheric general circulation model and its performance. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 13(1), 1–18.
Wu, G. X., and Y. S. Zhang, 1998: Tibetan Plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Wea. Rev., 126, 913–927.
Xie, P. P., and Coauthors, 2003: GPCP Pentad precipitation analyses: An experimental dataset based on gauge observations and satellite estimates. J. Climate, 16, 2197–2214.
Xie, P. P., and P. A. Arkin, 1997: Global precipitation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 78, 2539–2558.
Yang, K., and Coauthors, 2007: Auto-calibration system developed to assimilate AMSR-E data into a land surface model for estimating soil moisture and the surface energy budget. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 85A, 229–242.
Yang, K., T. Koike, I. Kaihotsu, and J. Qin, 2009: Validation of a dual-pass microwave land data assimilation system for estimating surface soil moisture in semi-arid regions. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 10, 780–793.
Yang, M. X., T. D. Yao, X. H. Gou, T. Koike, and Y. Q. He, 2003: The soil moisture distribution, thawing-freezing processes and their effects on the seasonal transition on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 21, 457–465.
Ye, D. Z., and G. X. Wu, 1998: The role of the heat source of the Tibetan Plateau in the general circulation. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 67, 181–198.
Yeh, T. C., R. T. Wetherald, and S. Manabe, 1984: The effect of soil moisture on the short-term climate and hydrology change: A numerical experiment. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 474–490.
Zhang, Y. S., T. Li, B. Wang, and G. X. Wu, 2002: Onset of the summer monsoon over the Indochina Peninsula: Climatology and interannual variations. J. Climate, 15, 3206–3221.
Zhou, T. J., Y. Q. Yu, H. L. Liu, W. Li, X. B. You, and G. Q. Zhou, 2007: Progress in the development and application of climate ocean models and oceanatmosphere coupled models in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 1109–1120, doi: 10.1007/s00376-007-1109-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Q., Liu, Y., Shi, J. et al. Comparisons of soil moisture datasets over the Tibetan Plateau and application to the simulation of Asia summer monsoon onset. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 27, 303–314 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-8132-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-8132-5