Summary
The East Asian (China, Korea and Japan) summer monsoon precipitation and its variability are examined from the outputs of the coupled climate models performing coordinated experiments leading to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report (IPCC AR4). Out of the 22 models examined, 14 reproduce the observed shape of the annual cycle well with peak during the boreal summer (June through August), but with varying magnitude. Three models simulate the maximum a month later and with lower magnitudes. Only one model considerably underestimates the magnitude of the annual cycle. The remaining 4 models show some deviations from the observed. Models are unable to simulate the minimum in July with peaks in June and August associated with northward shifts of the Meiyu-Changma-Baiu precipitation band. The realistic simulation of the annual cycle does not appear to depend on the model resolution. The inter-model variation is slightly larger during summer, implying larger diversity of the models in simulating summer monsoon precipitation.
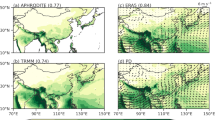
The spatial rainfall patterns are reasonably well simulated by most of the models, with several models able to simulate the precipitation associated with the Meiyu-Changma-Baiu frontal zone and that associated with the location of the subtropical high over the north Pacific. Simulated spatial distribution could be sensitive to model resolution as evidenced by two versions of MIROC3.2 model. The multi-model ensemble (MME) pattern reveals an underestimation of seasonal precipitation over the east coast of China, Korea-Japan peninsular and the adjoining oceanic regions. This may be related with the mass-flux based scheme employed for convective parameterization by majority of the models. Further the inter-model variation of precipitation is about 2 times stronger south of 30° N, than north of this latitude, indicating larger diversity of the coupled models in simulating low latitude precipitation. The simulated inter-annual variability is estimated by computing the mean summer monsoon seasonal rainfall and the coefficient of variability (CV). In general the mean observed seasonal precipitation of 542 mm and CV of 6.7% is very well simulated by most of the models. Except for one model mean seasonal precipitation varies from 400 to 650 mm. However the CV varies from 2 to 9%.
Future projections under the radiative forcing of doubled CO2 scenario are examined for individual models and by the MME technique. Changes in mean precipitation and variability are tested by the t-test and F-ratio respectively to evaluate their statistical significance. The changes in mean precipitation vary from −0.6% (CNRM-CM3) to about 14% (ECHO-G; UKMO-HadCM3). The MME technique reveals an increase varying from 5 to 10%, with an average of 7.8% (greater than the observed CV of 6.7%) over the East Asian region. However the increases are significant over the Korea-Japan peninsula and the adjoining north China region only. The increases may be attributed to the projected intensification of the subtropical high, Meiyu-Changma-Baiu frontal zone and the associated influx of moist air from the Pacific inland. The projected changes in the amount of precipitation are directly proportional to the projected changes in the strength of the subtropical high. Further the MME suggests a possible increase in the length of the summer monsoon precipitation period from late spring through early autumn. The changes in precipitation could be stabilized by controlling the CO2 emissions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AchutaRao K, Covey C, Doutriaux C, Fiorino M, Gleckler P, Phillips T, Sperber K, Taylor K (2004) An appraisal of coupled climate model simulations (Edited by D. Bader) UCRL-TR-202550 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, USA, 183 pp
AchutaRao K, Sperber KR (2006) ENSO simulation in coupled ocean-atmosphere models: are the current models better? Clim Dyn (in press-published online DOI 10.1007/S00382-006-0119-7)
Boo K-O, Kwon W-T, Oh J-H, Baek H-J (2004) Response of global warming on regional climate over Korea: An experiment with the MM5 model. Geophys Res Lett 31: doi: 10.1029/2004GL021171
P Bougeault (1985) ArticleTitleA simple parameterization of the large-scale effects of cumulus convection Mon Wea Rev 113 2108–2121 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1985)113<2108:ASPOTL>2.0.CO;2
M Chen D Pollard EJ Barron (2004) ArticleTitleRegional climate change in East Asia simulated by an interactive atmosphere-soil-vegetation model J Clim 17 557–572 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0557:RCCIEA>2.0.CO;2
Y-S Chung M-B Yoon H-S Kim (2004) ArticleTitleOn climate variations and changes observed in South Korea Clim Change 66 151–161 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:CLIM.0000043141.54763.f8
Collins WD, Bitz CM, Blackmon ML, Bonan GB, Bretherton CS, Carton JA, Chang P, Doney SC, Hack JJ, Henderson TB, Kiehl JT, Large WG, McKenna DS, Santer BD, Smith RD (2006) The Community Climate System Model: CCSM3. J Clim (in press)
C Covey KM AchutaRao U Cubasch P Jones SJ Lambert ME Mann TJ Phillips KE Taylor (2003) ArticleTitleAn overview of results from the Coupled Model Inter-comparison Project Glob Planet Change 37 103–133 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00193-5
Dai A (2006) Precipitation characteristics in eighteen coupled climate models. J Clim (in press)
A Dai GA Meehl WM Washington TML Wigley (2001) ArticleTitleClimate changes in the 21st century over Asia-Pacific region simulated by NCAR CSM and PCM Adv Atmos Sc 18 639–658
Del Genio A, Yao M-S (1993) Efficient cumulus parameterization for long-term climate studies. The GISS scheme. In: Emanuel K, Raymond D (eds) The representation of cumulus convection in numerical models. AMS Meteor Monograph, Amer Meteorol Soc 46: 181–184
TL Delworth AJ Broccoli A Rosati RJ Stouffer V Balaji JA Beesley WF Cooke KW Dixon J Dunne KA Dunne JW Durachta KL Findell P Ginoux A Gnanadesikan CT Gordon SM Griffies R Gudgil MJ Harrison IM Held RS Hemler LW Horowitz SA Klein TR Knutson PJ Kushner AR Langenhorst HC Lee SJ Lin J Lu SL Malyshev PCD Milly V Ramaswamy J Russel MD Schwarzkopf E Shevliakova JJ Sirutis MJ Spelman WF Stern M Winton AT Wittenberg B Wyman F Zeng R Zhang (2006) ArticleTitleGFDL’s CM2 global climate models-Part 1: Formulation and simulation characteristics J Clim 19 643–674 Occurrence Handle10.1175/JCLI3629.1
NA Diansky EM Volodin (2002) ArticleTitleSimulation of present-day climate with a coupled Atmosphere-Ocean general circulation model Izv Atmos Ocean Phys (Engl. Transl.) 38 732–747
Y Ding JCL Chan (2005) ArticleTitleThe East Asian summer monsoon: an overview Meteorol Atmos Phys 89 117–142 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00703-005-0125-z
Douville H, Salas-Melia D, Tyteca S (2005) On the tropical origin of uncertainties in the global land precipitation response to global warming. Clim Dyn (in press-published online DOI: 10.1007/s00382-005-0088-2)
GM Flato GJ Boer WG Lee NA McFarlane D Ramsden MC Reader AJ Weaver (2000) ArticleTitleThe Canadian Centre for Climate Modeling and Analysis of Global Coupled Model and its climate Clim Dyn 16 451–467 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003820050339
T Furevik M Bentsen H Drange IKT Kindem NG Kvamsto A Sorteberg (2003) ArticleTitleDescription and evaluation of the Bergen Climate Model: ARPEGE coupled with MICOM Clim Dyn 21 27–51 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00382-003-0317-5
WL Gates J Boyle C Covey C Dease C Doutriaux R Drach M Fiorino P Gleckler J Hnilo S Marlais T Phillips G Potter BD Santer KR Sperber K Taylor D Williams (1999) ArticleTitleAn overview of the results of the Atmospheric Model Inter-comparison Project (AMIP I) Bull Amer Meteor Soc 80 29–55 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<0029:AOOTRO>2.0.CO;2
Gordon HB, Rotstayn LD, McGregor JL, Dix MR, Kowalczyk, O’Farrell SP, Waterman LJ, Hirst AC, Wilson SG, Collier MA, Watterson IG, Elliott TI (2002) The CSIRO Mk3 Climate System Model (Electronic publication). Asoendale: CSIRO Atmospheric Research Technical Paper No. 60, 130pp (Available from http://www.dar.csiro.au/publications/gordon_2002a.pdf)
D Gregory PR Rowntree (1990) ArticleTitleA mass flux convection scheme with representation of ensemble characteristics dependent closure Mon Wea Rev 118 1883–1506 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118<1483:AMFCSW>2.0.CO;2
N Hirota M Takahashi N Sato M Kimoto (2005) ArticleTitleRecent climate trends in the East Asia during the Baiu season of 1979–2003 SOLA 1 137–140 Occurrence Handle10.2151/sola.2005-036
Z-Z Hu M Latif E Roeckner L Bengtsson (2000) ArticleTitleIntensified Asian summer monsoon and its variability in a coupled model forced by increasing greenhouse concentrations Geophys Res Lett 27 2681–2684 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2000GL011550
IPCC (2001) Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In: Houghton JT, Ding Y, Griggs DJ, Noguer M, van der Linden PJ, Dai X, Maskell K, Johnson CA (eds). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 881 pp
Johns T, Durman C, Banks H, Roberts M, McLaren A, Ridley J, Senior C, Williams K, Jones A, Keen A, Rickard G, Cusack S, Joshi M, Ringer M, Dong B, Spencer H, Hill R, Gregory J, Pardaens A, Lowe J, Bodas-Salcedo A, Start S, Searl Y (2005) HadGEM1-Model description and analysis of preliminary experiments for the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report. Hadley Centre Technical Note 55, UK Met Office, 74 pp (Available from www.metoffice.com/research/hadleycentre/pubs/HCTN/HCTN_55.pdf)
Jones C, Gregory J, Thorpe R, Cox P, Murphy J, Sexton D, Valdes H (2004) Systematic optimization and climate simulation of FAMOUS, a fast version of HADCM3. Hadley Centre Technical Note 60, 33 pp (Available at http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/research/hadleycentre/pubs/HCTN/HCTN_60.pdf)
Joseph R, Nigam S (2006) ENSO evolution and tele-connections in IPCC’s 20th century climate simulations: Realistic representation? J Clim (in press)
Jungclaus JH, Botzet M, Kaak H, Keenlyside N, Luo JJ, Latif M, Marotzke J, Mikolajewicz U, Roeckner E (2006) Ocean circulation and tropical variability in the AOGCM ECHAM5/MPI-OM. J Clim (in press)
K-1 Model Developers (2004) K-1 Coupled GCM (MIROC) description. K-1 Tech Report No. 1, Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo, National Institute for Environmental Studies, Frontier Research Center for Global Change (Hasumi and Emori eds), 39 pp (available at http://www.ccsr.u-tokyo.ac.jp/kyosei/hasumi/MIROC/tech-repo.pdf)
E Kalnay M Kanamitsu R Kistler W Collins D Deaven L Gandin M Iredell S Saha G White J Woollen Y Zhu A Leetmaa B Reynolds M Chelliah W Ebisuzaki W Higgins J Janowiak KC Mo C Ropelewski J Wang R Jenne D Joseph (1996) ArticleTitleThe NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project Bull Amer Meteor Soc 77 437–471 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
IS Kang K Jin B Wang KM Lau J Shukla V Krishnamurthy SD Schubert DE Waliser WF Stern A Kitoh GA Meehl M Kanamitsu VY Galin V Satyan CK Park Y Liu (2002) ArticleTitleIntercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian Summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs Clim Dyn 19 383–395 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00382-002-0245-9
BJ Kim RH Kripalani JH Oh SE Moon (2002) ArticleTitleSummer monsoon rainfall patterns over South Korea and associated circulation features Theor Appl Climatol 72 65–74 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007040200013
Kimoto M (2005) Simulated change of the East Asian circulation under global warming scenario. Geophys Res Lett 32: doi: 10.1029/2005GL023383
Kitoh A, Uchiyama T (2006) Changes in onset and withdrawal of the East Asian summer rainy season by multi-model global warming experiments. J Meteor Soc Japan 84 (in press)
A Kitoh S Yukimoto A Noda T Motoi (1997) ArticleTitleSimulated changes in the Asian summer monsoon at times of increased atmospheric CO2 J Meteor Soc Japan 75 1019–1031
RH Kripalani A Kulkarni (2001) ArticleTitleMonsoon rainfall variations and tele-connections over south and East Asia Int J Climatol 21 603–616 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.625
RH Kripalani SV Singh (1993) ArticleTitleLarge scale aspects of India-China summer monsoon rainfall Adv Atmos Sc 10 71–84
RH Kripalani BJ Kim JH Oh SE Moon (2002) ArticleTitleRelationship between Soviet snow and Korean rainfall Int J Climatol 22 1313–1325 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.809
RH Kripalani A Kulkarni SS Sabade (2005a) ArticleTitleSouth Asian monsoon precipitation variability: coupled climate model projections under IPCC AR4 CLIVAR Exchanges 10 IssueID3 13–15
RH Kripalani JH Oh JH Kang SS Sabade A Kulkarni (2005b) ArticleTitleExtreme monsoons over East Asia: Possible role of Indian Ocean Zonal Mode Theor Appl Climatol 82 81–94 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00704-004-0114-z
Kripalani RH, Oh JH, Kulkarni A, Sabade SS, Chaudhari HS (2006) South Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability: coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theor Appl Climatol (submitted)
K Kurihara K Ishihara H Sasaki Y Fukuyama H Saitou I Takayabu K Murazaki Y Sato S Yukimoto A Noda (2005) ArticleTitleProjection of climate change over Japan due to global warming by high-resolution Regional Climate Model in MRI SOLA 1 97–100 Occurrence Handle10.2151/sola.2005-026
M Lal H Harasawa (2000) ArticleTitleComparison of the present-day climate simulation over Asia in selected coupled atmosphere-ocean global climate models J Meteor Soc Japan 78 871–879
M Lal H Harasawa (2001) ArticleTitleFuture climate change scenarios for Asia as inferred from selected coupled atmosphere-ocean global climate models J Meteor Soc Japan 79 219–227 Occurrence Handle10.2151/jmsj.79.219
Legutke S, Voss R (1999) The Hamburg atmosphere-ocean coupled circulation model ECHO-G. DKRZ Technical Report No. 18, Deutsches Klimarechenzentrum, Hamburg, Germany, 62 pp
RY Lu (2001) ArticleTitleInter-annual variability of the summertime north Pacific subtropical high and its relation to atmospheric convection over the warm pool J Meteor Soc Japan 79 771–783 Occurrence Handle10.2151/jmsj.79.771
RY Lu BW Dong (2001) ArticleTitleWestward extension of the north Pacific subtropical high in summer J Meteor Soc Japan 79 1229–1241 Occurrence Handle10.2151/jmsj.79.1229
Marti O, Braconnot P, Bellier J, Benshile R, Bony S, Brockmann P, Cadulle P, Caubel A, Denvil S, Dufresne JL, Fairhead L, Filiberti MA, Fichefet T, Friedlingstein P, Grandpeix JY, Hourdin F, Krinner G, Levy C, Musat I, Talandier C (2005) The new IPSL climate system model: IPSL-CM4. Institut Pierre Simon Laplace, Paris, 86pp (Available at http://dods.ipsl.jussieu.fr/omamce/IPSLCM4/DocIPSLCM4/FILES/DocIPSLCM4.pdf)
Meehl GA, Arblaster JM, Tebaldi C (2005) Understanding future patterns of increased precipitation intensity in climate model simulations. Geophys Res Lett 32: doi: 10.1029/2005GL023680
GA Meehl GJ Boer C Covey M Latif RJ Stouffer (2000) ArticleTitleThe Coupled model intercomparison project (CMIP) Bull Amer Meteor Soc 81 313–318 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(2000)081<0313:TCMIPC>2.3.CO;2
Merryfield WJ (2006) Changes to ENSO under CO2 doubling in a multi-model ensemble. J Clim (in press)
Min S-K, Legutke S, Cubasch U, Kwon W-T, Oh J-H, Schlese M (2006) East Asian climate change in the 21st century as simulated by the coupled climate model ECHO-G under IPCC SRES scenarios. J Meteor Soc Japan (in press)
S-K Min E-H Park W-T Kwon (2004) ArticleTitleFuture projections of East Asian Climate Change from multi-AOGCM ensembles of IPCC SRES scenario simulations J Meteor Soc Japan 82 1187–1211 Occurrence Handle10.2151/jmsj.2004.1187
T Nitta (1987) ArticleTitleConvective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impacts on the northern summer circulation J Meteor Soc Japan 65 165–171
JH Oh HS Chaudhari RH Kripalani (2005) ArticleTitleImpacts of IODM and ENSO on the East Asian monsoon: simulation through NCAR community atmospheric model Korean J Agric Forest Meteorol 7 240–249
JH Oh T Kim MK Kim SH Lee SK Min WT Kwon (2004) ArticleTitleRegional climate simulation for Korea using dynamic downscaling and statistical adjustment J Meteor Soc Japan 82 1629–1643 Occurrence Handle10.2151/jmsj.82.1629
GJ Oldenborgh van SY Philip M Collins (2005) ArticleTitleEl Nino in a changing climate: a multi-model study Ocean Science 1 81–95 Occurrence Handle10.5194/os-1-81-2005
V Ramanathan C Chung D Kim T Bettge L Buja JT Kiehl WM Washington Q Fu DR Sikka M Wild (2005) ArticleTitleAtmospheric brown clouds: Impacts on South Asia climate and hydrological cycle Proc Nat Acad Sc USA 102 5326–5333 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.0500656102
GL Russell JR Miller D Rind (1995) ArticleTitleA coupled atmosphere-ocean model for transient climate change studies Atmos-Ocean 33 683–730
Saji NH, Xie S-P, Yamagata T (2006) Tropical Indian Ocean variability in the IPCC 20th century climate simulations. J Clim (in press)
Salas-Melia D, Chauvin F, Deque M, Douville H, Gueremy JF, Marquet P, Planton S, Royer JF, Tyteca S (2006) Description and validation of the CNRM-CM3 global coupled model. Clim Dyn (in press)
Schmidt GA, Ruedy R, Hansen JE, Aleinov I, Bell N, Bauer M, Bauer S, Cairns B, Canuto V, Cheng Y, DelGenio A, Faluvegi G, Friend AD, Hall TM, Hu Y, Kelley M, Kiang NY, Koch D, Lacis AA, Lerner J, Lo KK, Miller RL, Nazarenko L, Oinas V, Perlwitz Jan, Perlwitz Judith, Rind D, Romanou A, Russel GL, Sato M, Shindell DT, Stone PH, Sun S, Tausnev N, Thresher D, Yao MS (2006) Present day atmospheric simulations using GISS ModelE: Comparison to in-situ, satellite and reanalysis data. J Clim (in press)
BD Su T Jiang WB Jin (2006) ArticleTitleRecent trends in observed temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River basin, China Theor Appl Climatol 83 139–151 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00704-005-0139-y
Y Sun S Solomon A Dai R Portmann (2006) ArticleTitleHow often does it rain? J Clim 19 916–934 Occurrence Handle10.1175/JCLI3672.1
HL Tanaka N Ishizaki D Nohara (2005) ArticleTitleIntercomparison of the intensities and trends of Hadley, Walker and Monsoon Circulations in the Global Warming Projections SOLA 1 77–80 Occurrence Handle10.2151/sola.2005-021
M Tiedtke (1993) ArticleTitleRepresentation of clouds in large-scale models Mon Wea Rev 121 3040–3061 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121<3040:ROCILS>2.0.CO;2
Ueda H, Iwai A, Kuwako K, Hori ME (2006) Impact of anthropogenic forcing on the Asian summer monsoon as simulated by 8 GCMs. Geophys Res Lett 33: doi: 10.1029/2005GL025336
H Wang KM Lau (2006) ArticleTitleAtmospheric hydrological cycle in the tropics in twentieth century coupled climate simulations Int J Climatol 26 655–678 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.1279
WM Washington JW Weatherly GA Meehl AJ Semtner SuffixJr TW Bettge AP Craig WG Strand SuffixJr J Arblaster VB Wayland R James Y Zhang (2000) ArticleTitleParallel climate model (PCM) control and transient simulations Clim Dyn 16 755–774 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003820000079
P Xie PA Arkin (1997) ArticleTitleGlobal precipitation: a 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates and numerical model outputs Bull Amer Meteor Soc 78 2539–2558 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<2539:GPAYMA>2.0.CO;2
Y Yu X Zhang Y Guo (2004) ArticleTitleGlobal coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation models in LASG/IAP Adv Atmos Sc 21 444–455 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02915571
Yukimoto S, Noda A (2002) Improvements of the Meteorological Research Institute global ocean-atmosphere coupled GCM (MRI-CGCM2) and its climate sensitivity. CGER’s Supercomputer Activity Report No. 10, 37–44, NIES, Japan, 8pp (Available at http://www.mri-jma.go.jp/Dep/cl/c14/publications/yukimoto_CGER2002.pdf)
Yukimoto S, Noda A, Kitoh A, Sugi M, Kitamura Y, Hosaka M, Shibata K, Maeda S, Uchiyama T (2001) The new Meteorological Research Institute Coupled GCM (MRI-CGCM2)-Model climate and variability. Papers in Meteorology and Geophysics 51: 47–88 (Available http://www.mri-jma.go.jp/Dep/cl/c14/publications/yukimoto_pap2001.pdf)
GJ Zhang (1994) ArticleTitleEffects of cumulus convection on the simulated monsoon circulation in a General Circulation Model Mon Wea Rev 122 2022–2038 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1994)122<2022:EOCCOT>2.0.CO;2
Zhu C, Lee WS, Kang H, Park CK (2005) A proper monsoon index for seasonal and inter-annual variations of the East Asian monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 32: L02811, doi: 10.1029/2004GL021295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kripalani, R., Oh, J. & Chaudhari, H. Response of the East Asian summer monsoon to doubled atmospheric CO2: Coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 87, 1–28 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-006-0238-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-006-0238-4