Abstract
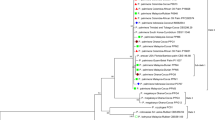
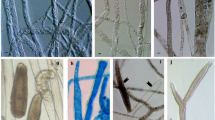
Pyropia yezoensis (formerly Porphyra yezoensis) is an economically important red alga that is cultured extensively in China. The red rot disease occurs commonly during Pyropia cultivation, causing serious economic losses. An incidence of red rot disease was found in a P. yezoensis farm from mid-November to mid-December 2015 at Lianyungang, Jiangsu Province, China. Histopathological examination revealed that the naturally infected thalli were infected apparently by a pathogen, leading to red rot symptoms. The causative agent was isolated and identified as the oomycete Pythium chondricola by morphological analysis and sequence analysis of the internal transcribed spacer and cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 (cox1). In artificial infection experiments on the P. yezoensis blades, the P. chondricola isolate was able to cause the same characteristic histopathology seen in natural infections. P. chondricola grew well at a wide range of temperatures in the range 8–31°C, salinities at 0–15 and pH 5–9. In an orthogonal test used to determine the effects of environmental factors (temperature, salinity, and zoospore concentration) on infection, the data revealed that temperature was the most important factor to affect red rot disease development, with the optimal conditions for disease expansion being 20°C, 35 salinity, and a zoospore concentration of 106 zoospores/mL. The results obtained from the present study prompted us to set up a comprehensive epidemiological study on Pyropia, which will provide support to maintain the healthy development of the Pyropia industry in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addepalli M K, Fujita Y. 2002. Regulatory role of external calcium on Pythium porphyrae (Oomycota) zoospore release, development and infection in causing red rot disease of Porphyra yezoensis (Rhodophyta). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 211(2): 253–257, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11233.x.
Arasaki S. 1947. Studies on the rot of Porohyra tenera by Pythium. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries, 13: 74–90.
Blouin N A, Brodie J A, Grossman A C, Xu P, Brawley S H. 2011. Porphyra: a marine crop shaped by stress. Trends in Plant Science, 16(1): 29–37, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.10.004.
Choi Y J, Beakes G, Glockling S, Kruse J, Nam B, Nigrelli L, Ploch S, Shin H D, Shivas R G, Telle S, Voglmayr H, Thines M. 2015. Towards a universal barcode of oomycetes-a comparison of the cox1 and cox2 loci. Molecular Ecology Resources, 15(6): 1 275–1 288, https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12398.
Diehl N, Kim G H, Zuccarello G C. 2017. A pathogen of New Zealand Pyropia plicata (Bangiales, Rhodophyta), Pythium porphyrae (Oomycota). Algae, 32(1): 29–39, https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2017.32.2.25.
Ding H Y, Ma J H. 2005. Simultaneous infection by red rot and chytrid diseases in Porphyra yezoensisUeda. Journal of Applied Phycology, 17(1): 51–56, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-005-5523-6.
Fuchs Y, Steller H. 2011. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell, 147(4): 742–758, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.033.
Fujita Y. 1990. Diseases of cultivated Porphyra in Japan. In: Akatsuka I ed. Introduction to Applied Phycology. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, Netherlands. p.177–190.
Fujita Y, Zenitani B. 1977. Studies on pathogenic Pythium of laver red rot in Ariake sea farm—II. Experimental conditions and nutritional requirements for growth. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries, 43(1): 89–95.
Gachon C M, Sime-Ngando T, Strittmatter M, Chambouvet A, Kim G H. 2010. Algal diseases: spotlight on a black box. Trends in Plant Science, 15(11): 633–640, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.08.005.
Guan X Y, Li J B, Zhang Z, Li F C, Yang R, Jiang P, Qin S. 2013. Characterizing the microbial culprit of white spot disease of the conchocelis stage of Porphyra yezoensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Journal of Applied Phycology, 25(5): 1 341–1 348, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-9976-8.
Kawamura Y, Yokoo K, Tojo M, Hishiike M. 2005. Distribution of Pythium porphyrae, the causal agent of red rot disease of Porphyrae spp., in the Ariake Sea, Japan. Plant Disease, 89(10): 1 041–1 047, https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-89-1041.
Kazama F Y, Fuller M S. 1973. Mineral nutrition of Pythium marinum, a marine facultative parasite. Canadian Journal of Botany, 51(4): 693–699, https://doi.org/10.1139/b73-086.
Kerwin J L, Johnson L M, Whisler H C, Tuininga A R. 1992. Infection and morphogenesis of Pythium marinum in species of Porphyra and other red algae. Canadian Journal of Botany, 70(5): 1 017–1 024, https://doi.org/10.1139/b92-126.
Kim G H, Klochkova T A, Lee D J, Im S H. 2016. Chloroplast virus causes green-spot disease in cultivated Pyropia of Korea. Algal Research, 17: 293–299, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.05.023.
Kim G H, Moon K H, Kim J Y, Shim J, Klochkova T A. 2014. A revaluation of algal diseases in Korean Pyropia (Porphyra) sea farms and their economic impact. Algae, 29(4): 249–265, https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2014.29.4.249.
Klochkova T A, Jung S, Kim G H. 2017. Host range and salinity tolerance of Pythium porphyrae may indicate its terrestrial origin. Journal of Applied Phycology, 29(1): 371–379, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0947-8.
Klochkova T A, Shim J B, Hwang M S, Kim G H. 2012. Host-parasite interactions and host species susceptibility of the marine oomycete parasite, Olpidiopsis sp., from Korea that infects red algae. Journal of Applied Phycology, 24(1): 135–144, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9661-8.
Lee S J, Hwang M S, Park M A, Baek J M, Ha D S, Lee J E, Lee S R. 2015. Molecular identification of the algal pathogen Pythium chondricola (Oomycetes) from Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta) using ITS and cox1 markers. Algae, 30(3): 217–222, https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2015.30.3.217.
Lee S J, Jee B Y, Son M H, Lee S R. 2017. Infection and cox2 sequence of Pythium chondricola (Oomycetes) causing red rot disease in Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta) in Korea. Algae, 32(2): 155–160, https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2017.32.5.16.
Lee S J, Park S W, Lee J H, Kim Y S. 2012. Diseases of the cultivated Porphyra at Seocheon area. Journal of Fish Pathology, 25(3): 249–256, https://doi.org/10.7847/jfp.2012.25.3.249.
LéVesque C A, De Cock A W A M. 2004. Molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Pythium. Mycological Research, 108(12): 1 363–1 383, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756204001431.
Ma J H. 1992. An investigation of chytrid-disease in Porphyra yezoensis in the coastal water of south Jiangsu. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 1(3–4): 185–188. (in Chinese)
Ma J H. 1996. A preliminary study on the red rot disease of Porphyra yezoensis. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 5(1): 1–7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mo Z L, Li S F, Kong F N, Tang X H, Mao Y X. 2016. Characterization of a novel fungal disease that infects the gametophyte of Pyropia yezoensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Journal of Applied Phycology, 28(1): 395–404, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0539-z.
Park C S, Sakaguchi K, Kakinuma M, Amano H. 2000. Comparison of the morphological and physiological features of the red rot disease fungus Pythium sp. isolated from Porphyra yezoensis from Korea and Japan. Fisheries Science, 66(2): 261–269, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1444-2906.2000.00043.x.
Park C S, Kakinuma M, Amano H. 2006. Forecasting infections of the red rot disease on Porphyra yezoensis Ueda (Rhodophyta) cultivation farms. Journal of Applied Phycology, 18(3–5): 295–299, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-006-9031-0.
Provasoli L. 1968. Media and prospects for the cultivation of marine algae. In: Proceedings of US-Japan Conference in Hakone. Japanese Society for Plant Physiology, Tokyo. p. 63–75.
Robideau G P, De Cock A W A M, Coffey M D, Voglmayr H, Brouwer H, Bala K, Chitty D W, Désaulniers N, Eggertson Q A, Gachon C M M, Hu C H, Küpper F C, Rintoul T L, Sarhan E, Verstappen E C P, Zhang Y H, Bonants P J M, Ristaino J B, Lévesque C A. 2011. DNA barcoding of oomycetes with cytochrome c oxidase subunit I and internal transcribed spacer. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11(6): 1 002–1 011, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.03041.x.
Schroeder K L, Martin F N, De Cock A W A M, Lévesque C A, Spies C F J, Okubara P A, Paulitz T C. 2013. Molecular detection and quantification of Pythium species: evolving taxonomy, new tools, and challenges. Plant Disease, 97(1): 4–20, https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-12-0243-FE.
Sekimoto S, Klochkova T A, West J A, Beakes G W, Honda D. 2009. Olpidiopsis bostrychiae sp. nov.: an endoparasitic oomycete that infects Bostrychia and other red algae (Rhodophyta). Phycologia, 48(6): 460–472, https://doi.org/10.2216/08-11.1
Sun P P, Mao Y X, Li G Y, Cao M, Kong F N, Wang L, Bi G Q. 2015. Comparative transcriptome profiling of Pyropia yezoensis (Ueda) M.S. Hwang & H.G. Choi in response to temperature stresses. BMC Genomics, 16(1): 463, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1586-1.
Sunairi M, Tsuchiya H, Tsuchiya T, Omura Y, Koyanagi Y, Ozawa M, Iwabuchi N, Murooka H, Nakajima M. 1995. Isolation of a bacterium that causes anaaki disease of the red algae Porphyra yezoensis. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 79(2): 225–229, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1995.tb00939.x.
Takahashi M, Ichitani T, Sasaki M. 1977. Pythium porphyrae Takahashi et Sasaki, sp. nov. causing red rot of marine red algae Porphyra spp. Transactions of the Mycological Society of Japan, 18: 279–285.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. 2013. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30(12): 2 725–2 729, https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197.
Thompson J D, Gibson T J, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins D G. 1997. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25(24): 4 876–4 882, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876.
White T J, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J. 1990. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications, 18(1): 315–322.
Zuccarello G C, Lokhorst G M. 2005. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Tribonema (Xanthophyceae) using rbcL gene sequence data: monophyly of morphologically simple algal species. Phycologia, 44(4): 384–392, https://doi.org/10.2216/0031-8884(2005)44[384:MPOTGT]2.0.CO;2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-50), the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 31372517), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 201562018), the National Infrastructure of Fishery Germplasm Resources (No. 2017DKA30470), and the Project of Aoshan Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (No. 2015ASKJ02)
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Availability Statement
All the sequence using in this study have been deposited in GenBank, with accession No. MF978164 and MF978165. Other data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, L., Mao, Y., Tang, L. et al. Characterization of Pythium chondricola associated with red rot disease of Pyropia yezoensis (Ueda) (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) from Lianyungang, China. J. Ocean. Limnol. 37, 1102–1112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8075-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8075-3