Abstract
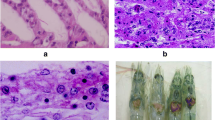
This paper presents the results of a study on the diseases of Porphyra yezoensisUeda along the north coast of China, where red rot (Pythium porphyrae) and the chytrid Olpidiopsis sp. diseases were both found to be present. Infection by the mycelia of Pythium porphyraeand the thallus of Olpidiopsis sp. was studied in detail. At the early stage of infecton the mycelia of Pythium porphyraeand the fungus of chytrid can be found in host cells at the same time. In the middle and late stages of the complication, it mainly appears as red rot disease, toward the end appearing almost completely as red rot disease. The complication even can be found on the cells of fronds from the freeze-storage nori nets. However, the freeze-storage nets can help prevent spread of the infection and improve nori quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addepalli MK, Fujita Y (2001) Serological detection of red rot disease initiation stages of microbial pathogen, Pythium porphyrae (Oomycota) on Porphyra yezoensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 13(3): 221–227.
Addepalli MK, Fujita Y (2002a) Regulatory role of external calcium on Pythium porphyrae (Oomycota) zoospore release, development and infection in causing red rot disease of Porphyra yezoensis (Rhodophyta). FEMS. Microbiol. Lett. 211: 253–257.
Addepalli MK, Fujita Y (2002b) A monoclonal antibody and the lectin wheat germ agglutinin induce zoospore encystment in Pythium porphyrae, a marine microbial pathogen. Mycologia 94(4): 712–722.
Amano H, Suginaga R, Arashima K, Noda H (1995) Immunological detection of the fungal parasite, Pythium sp., the causative organism of red rot disease in Porphyra yezoensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 7: 53–58.
Arasaki S (1947) Studies on the rot of Porphyra tenera by a Pythium. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 13(3): 74–90. (in Japanese).
Arasaki S, Inouye A, Kochi Y (1960) The disease of the cultured porphyra, with special reference to the cancer-disease and the chytrid-disease which occurred at the culture field in Tokyo Bay during 1959–1960. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 26(11): 1074–1079. (in Japanese).
Arasaki S (1960) A chytridean parasite on the Porphyra. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish.26(6): 543–548 (in Japanese).
Arasaki S, Akino K, Tomiyama Y (1968) A comparison of some physiological aspects in marine pythiumon the host and on the artificial medium. Bull. Misaki Mar. Biol. Inst. Kyoto Univ. 12: 203–206.
Correa JA (1997) Infectious diseases of marine algae: Current knowledge and approaches. In Round FE, Chapman DJ (eds), Progress in Phycological Research Vol. 12. Biopress Ltd., pp. 139–145.
Fujita Y (1978) Studies on the pathogenic Pythium of larve red rot in Arasake farm-V. Germination of Pythium porphyrae oospores. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Scient. Fish. 44: 15–19. (in Japanese).
Fujita Y & Migita S (1980) Death of parasitic Pythium porphyrae by drying and freeze-preservation of red rot infected thalli of Porphyra yezoensis. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 49: 11–16. (in Japanese).
Fujita, Y (1990) Diseases of cultivated Porphyra in Japan. In Akatsu I (ed.) Introduction to Applied Phycology. SPB Academic Publishing, The Netherlands. pp. 177–190.
Hemmingson JA (2002) Cell wall polysaccharides are informative in Porphyra species taxonomy. J. Appl. Phycol. 14(5): 357– 364.
Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries (1978) Disease of Porphyra. Koseisha Koseikaku (Tokyo) pp. 7–28. (in Japanese).
Ma JH (1992) Investigation research of the chytrid disease in Porphyra yezoensisUeda along south coast of Jiangsu. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 5(1): 1–7. (in Chinese).
Ma JH (1996) A preliminary study on the red rot disease of Porphyra yezoensisUeda. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 5(1): 1–7. (in Chinese).
Migita S (1969) Olpidiopsis disease of culture Porphyra. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 28: 131–145.
Park CS, Kakinuma M, Amano H (2001) Detection and quantitative analysis of zoospores of Pythium porphyrae, causative organism of red rot disease in Porphyra, by competitive PCR. J. Appl. Phycol. 13(5): 433–441.
Potin P, Bouarrab K, Salaun JP, Pohnert G, Kloareg P (2002) Biotic interactions of marine algae. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 5(4): 308–317.
Provasoli L (1968) Media and prospects for the cultivation of marine algae. In Watanabe A, Hattori A (ed.) Cultures and Collections of Algae. Proc. U.S. Japan Conf. Hakone. Sept. 1966. Jap. Plant Physiol. 63–75.
Smith GM (1955) Crytogamic botany vol. 1, Algae and Fungi. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc. New York, pp. 390–393, 401–409.
Takahashi M (1970) Identification of genus pythium. Plant Prot. 24(8): 339–346. (in Japanese).
Uppalapati SR, Fujita Y (2000) Carbohydrate regulation of attachment, encystment, and appressorium formation by Pythium porphyrae (Oomycota) zoospores on Porphyra yezoensis (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 36: 359–366.
Uppalapati SR, Kerwin JL, Fujita Y (2001) Epifluorescence and scanning electron microcopy of host-pathogen interactions between Pythium porphyrae (Peronosporales, Oomycota) and Porphyra yezoensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Botanica Marina. 44: 139–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Ma, J. Simultaneous infection by red rot and chytrid diseases in Porphyra yezoensisUeda. J Appl Phycol 17, 51–56 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-005-5523-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-005-5523-6