Abstract
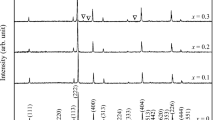
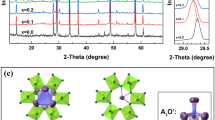
Cubic bismuth pyrochlores in the \(\mathrm{Bi}_{2}\mathrm{O}_{3}\)–MgO–\(\mathrm{Nb}_{2}\mathrm{O}_{5}\) system have been investigated as promising dielectric materials due to their high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss. Here, we report on the dielectric properties and microstructures of cubic pyrochlored \(\mathrm{Bi}_{1.5}\mathrm{MgNb}_{1.5}\mathrm{O}_{7}\) (BMN) ceramic samples synthesized via solid-state reactions. The dielectric constant (measured at 1 MHz) was measured to be \({\sim}120\) at room temperature, and the dielectric loss was as low as 0.001. X-ray diffraction patterns demonstrated that the BMN samples had a cubic pyrochlored structure, which was also confirmed by selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns. Raman spectrum revealed more than six vibrational models predicted for the ideal pyrochlore structure, indicating additional atomic displacements of the A and \(\mathrm{O}'\) sites from the ideal atomic positions in the BMN samples. Structural modulations of the pyrochlore structure along the [110] and [121] directions were observed in SAED patterns and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) images. In addition, HR-TEM images also revealed that the grain boundaries (GBs) in the BMN samples were much clean, and no segregation or impure phase was observed forming at GBs. The high dielectric constants in the BMN samples were ascribed to the long-range ordered pyrochlore structures since the electric dipoles formed at the superstructural direction could be enhanced. The low dielectric loss was attributed to the existence of noncontaminated GBs in the BMN ceramics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Subramanian, G. Aravamudan, G.V. SubbaRao, Prog. Solid State Chem. 15, 55 (1983)
M. Lanagan, D. Anderson, A. Baker, J. Nino, S. Perini, C.A. Randall, T.R. Strout, T. Sogabe, H. Youn, in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Microelectronics, Baltimore, MD, ed. by J. Graves (2001), p. 155
S.W. Jiang, Y.R. Li, R.G. Li, N.D. Xiong, L.F. Tan, X.Z. Liu, B.W. Tao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 162908 (2009)
L.X. Li, X.Y. Zhang, L.J. Ji, P.F. Ning, Q.W. Liao, Ceram. Int. 38, 3541 (2012)
L.B. Gao, S.W. Jiang, R.G. Li, B. Li, Y.R. Li, Thin Solid Films 520, 6295 (2012)
R.A.M. Osman, N. Masó, A.R. West, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 296 (2012)
R.A. McCauley, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 63, 721 (1973)
S. Brown, H.C. Gupta, J.A. Alonso, M.J. Martinez-Lope, J. Raman Spectrosc. 34, 240 (2003)
D.J. Arenas, L.V. Gasparov, W. Qiu, J.C. Nino, C.H. Patterson, D.B. Tanner, Phys. Rev. B 82, 214302 (2010)
H.C. Gupta, S. Brown, N. Rani, V.B. Gohel, J. Raman Spectrosc. 32, 41 (2001)
A. Garbout, S. Bouattour, A.W. Kolsi, J. Alloys Compd. 469, 229 (2009)
M. Mączka, J. Hanuza, K. Hermanowicz, A.F. Fuentes, K. Matsuhira, Z. Hiroi, J. Raman Spectrosc. 39, 537 (2008)
F. Rosi, V. Manuali, C. Miliani, B.G. Brunetti, A. Sgamellotti, T. Grygar, D. Hradil, J. Raman Spectrosc. 40, 107 (2009)
M. Mączka, M.L. Sanjuán, A.F. Fuentes, L. Macalik, J. Hanuza, K. Matsuhira, Z. Hiroi, Phys. Rev. B 79, 214437 (2009)
T. Hahn, in International Tables of Crystallography, Vol. A (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1996)
I. Levin, T.G. Amos, J.C. Nino, T.A. Vanderah, C.A. Randall, M.T. Lanagan, J. Solid State Chem. 69, 168 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 10874065, 11174122, and 11134004), key projects from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant Nos. 2009CB929503 and 2009ZX02101-4), and Analysis & Test Fund of Nanjing University. T. Al-Kassab acknowledges the generous support of the KAUST baseline funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhu, X. et al. Dielectric properties and microstructural characterization of cubic pyrochlored bismuth magnesium niobates. Appl. Phys. A 115, 661–666 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7843-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7843-8