Abstract
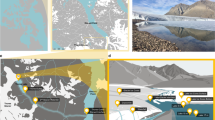
Wind is a major transporter of biotic and abiotic material in coastal Antarctica. Sulfate-depleted sea salts delivered by wind to the Antarctic interior are thought to derive from sea ice, signifying a connection between Antarctic coastal environments and the interior. We hypothesized that bacteria, known to concentrate in salt-rich environments on the surface of sea ice, may also be subject to wind-driven transport. To test this hypothesis, we undertook a comparative evaluation of the composition and structure of bacterial communities, determined by deep sequencing of the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene, in samples of frost flowers, young sea ice, and seawater from two coastal sites north of Ross Island, Antarctica, and in fresh snow over land and in surface ice of the Wilson Piedmont and Taylor Glaciers. Contrary to expectation, sequence reads that were consistently found in frost flowers, presumed to be the most mobile element of the sea ice environment, were rarely found in the terrestrial samples. Instead, cyanobacterial reads associated with the genus Pseudanabaena and found in abundance in the glacial ice and snow samples comprised up to 14.1 % of frost flower communities at one of our sites. Although this clade had not previously been reported in the Ross Sea region, wind patterns and other published data suggest that a likely source may be terrestrial aquatic environments on nearby Ross Island, including Mt. Erebus. One member of a sulfur-oxidizing, halophilic clade of the Gammaproteobacteria previously associated with hydrothermal sites was more abundant in frost flowers than in any other sample type. We hypothesize that these bacteria originated from hydrothermally influenced environments on Mt. Erebus. Overall, these findings suggest that wind is an important mechanism of microbial transport between the terrestrial and marine environments in coastal Antarctica, and may facilitate the exchange of taxa and genetic material between isolated habitats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Sáez L, Galand PE, Casamayor EO, Pedrós-Alió C, Bertilsson S (2010) High bicarbonate assimilation in the dark by Arctic bacteria. ISME J 4:1581–1590. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.69
Atkins CB, Dunbar GB (2009) Aeolian sediment flux from sea ice into Southern McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Glob Planet Change 69:133–141. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.04.006
Austin DA, Moss MO (1986) Numerical taxonomy of red-pigmented bacteria isolated from a lowland river, with the description of a new taxon, Rugamonas rubra gen. nov., sp. nov. Microbiology 132:1899–1909. doi:10.1099/00221287-132-7-1899
Barber DG, Ehn JK, Pućko M, Rysgaard S, Deming JW, Bowman JS, Papakyriakou T, Galley RJ, Søgaard DH (2014) Frost flowers on young Arctic sea ice: the climatic, chemical and microbial significance of an emerging ice type. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:11593–11612. doi:10.1002/2014JD021736
Beaudon E, Moore J (2009) Frost flower chemical signature in winter snow on Vestfonna ice cap (Nordaustlandet, Svalbard). Cryosphere Discuss 3:159–180. doi:10.5194/tcd-3-159-2009
Berger SA, Krompass D, Stamatakis A (2011) Performance, accuracy, and web server for evolutionary placement of short sequence reads under maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 60:291–302. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syr010
Bottos EM, Woo AC, Zawar-Reza P, Pointing SB, Cary SC (2014) Airborne bacterial populations above desert soils of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Microb Ecol 67:120–128. doi:10.1007/s00248-013-0296-y
Bowman JS, Deming JW (2010) Elevated bacterial abundance and exopolymers in saline frost flowers and implications for atmospheric chemistry and microbial dispersal. Geophys Res Lett 37:1–5. doi:10.1029/2010GL043020
Bowman JS, Ducklow HW (2015) Microbial communities can be described by metabolic structure: a general framework and application to a seasonally variable, depth-stratified microbial community from the coastal West Antarctic Peninsula. PLoS One 10:e0135868. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135868
Bowman JS, Larose C, Vogel TM, Deming JW (2013) Selective occurrence of Rhizobiales in frost flowers on the surface of young sea ice near Barrow, Alaska and distribution in the polar marine rare biosphere. Environ Microbiol Rep 5:575–582. doi:10.1111/1758-2229.12047
Bowman JS, Berthiaume CT, Armbrust EV, Deming JW (2014) The genetic potential for key biogeochemical processes in Arctic frost flowers and young sea ice revealed by metagenomic analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:376–387. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12331
Breezee J, Cady N, Staley JT (2004) Subfreezing growth of the sea ice bacterium Psychromonas ingrahamii. Microb Ecol 47:300–304. doi:10.1007/s00248-003-1040-9
Broady PA, Kibblewhite AL (1991) Morphological characterization of Oscillatoriales (Cyanobacteria) from Ross Island and southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 3:35–45. doi:10.1017/S095410209100007X
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. doi:10.1073/pnas.1000080107
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M, Gormley N, Gilbert JA, Smith G, Knight R (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624. doi:10.1038/ismej.2012.8
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2007) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:169–172. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl889
Cox MP, Peterson DA, Biggs PJ (2010) SolexaQA: at-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform 11:485. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-485
de los Ríos A, Ascaso C, Wierzchos J, Fernández-valiente E, Quesada A (2004) Microstructural characterization of cyanobacterial mats from the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microb 70:569–580. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.1.569
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microb 72:5069–5072. doi:10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Douglas TA, Domine F, Barret M, Anastasio C, Beine HJ, Bottenheim J, Grannas A, Houdier S, Netcheva S, Rowland G, Staebler R, Steffen A (2012) Frost flowers growing in the Arctic ocean–atmosphere–sea ice–snow interface: 1. Chemical composition. J Geophys Res 117:1–15. doi:10.1029/2011JD016460
Eronen-Rasimus E, Kaartokallio H, Lyra C, Autio R, Kuosa H, Dieckmann GS, Thomas DN (2014) Bacterial community dynamics and activity in relation to dissolved organic matter availability during sea-ice formation in a mesocosm experiment. MicrobiologyOpen 3:139–156. doi:10.1002/mbo3.157
Ewert M, Carpenter SD, Colangelo-Lillis J, Deming JW (2013) Bacterial and extracellular polysaccharide content of brine-wetted snow over Arctic winter first-year sea ice. J Geophys Res Ocean 118:726–735. doi:10.1002/jgrc.20055
Grzymski JJ, Riesenfeld CS, Williams TJ, Dussaq AM, Ducklow H, Erickson M, Cavicchioli R, Murray AE (2012) A metagenomic assessment of winter and summer bacterioplankton from Antarctica Peninsula coastal surface waters. ISME J 6:1901–1915. doi:10.1038/ismej.2012.31
Han MV, Zmasek CM (2009) phyloXML: XML for evolutionary biology and comparative genomics. BMC Bioinform 10:356. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-356
Herbold CW, Lee CK, McDonald IR, Cary SC (2014) Evidence of global-scale aeolian dispersal and endemism in isolated geothermal microbial communities of Antarctica. Nat Commun 5:3875. doi:10.1038/ncomms4875
Hughes KA, McCartney HA, Lachlan-Cope TA, Pearce DA (2004) A preliminary study of airborne microbial biodiversity over Peninsular Antarctica. Cell Mol Biol 50:537–542
Jungblut A, Hawes I, Mountfort D, Hitzfeld B, Dietrich DR, Burns BP, Neilan BA (2005) Diversity within cyanobacterial mat communities in variable salinity meltwater ponds of McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 7:519–529. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00717.x
Kellogg CTE, Deming JW (2009) Comparison of free-living, suspended particle, and aggregate-associated Bacterial and Archaeal communities in the Laptev Sea. Aquat Microb Ecol 57:1–18. doi:10.3354/ame01317
Kim J-G, Park S-J, Quan Z-X, Jung M-Y, Cha I-T, Kim S-J, Kim K-H, Yang E-J, Kim Y-N, Lee S-H, Rhee S-K (2013) Unveiling abundance and distribution of planktonic Bacteria and Archaea in a polynya in Amundsen Sea, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 16:1566–1578. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12287
Luria C, Ducklow H, Amaral-Zettler L (2014) Marine Bacterial, Archaeal and Eukaryotic diversity and community structure on the continental shelf of the western Antarctic Peninsula. Aquat Microb Ecol 73:107–121. doi:10.3354/ame01703
Marion GM, Farren RE, Komrowski AJ (1999) Alternative pathways for seawater freezing. Cold Reg Sci Technol 29:259–266. doi:10.1016/S0165-232X(99)00033-6
Marshall KT, Morris RM (2013) Isolation of an aerobic sulfur oxidizer from the SUP05/Arctic96BD-19 clade. ISME J 7:452–455. doi:10.1038/ismej.2012.78
Matsen FA, Kodner RB, Armbrust EV (2010) pplacer: linear time maximum-likelihood and Bayesian phylogenetic placement of sequences onto a fixed reference tree. BMC Bioinform 11:538. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-538
Michaud AB, Marie S, Priscu JC (2012) Cyanobacterial diversity across landscape units in a polar desert: Taylor Valley, Antarctica. FEMS Microb Ecol 82:268–278. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01297.x
Miller LA, Fripiat F, Else BGT, Bowman JS, Brown KA, Collins RE, Ewert M, Fransson A, Gosselin M (2015) Methods for biogeochemical studies of sea ice: the state of the art, caveats, and recommendations. Elem Sci Anth 3:1–53. doi:10.12952/journal.elementa.000038
Minikin A, Wagenbach D, Ducroz F, Mulvaney R, Keck L, Legrand M, Hall JS, Wolff EW (1998) Sea-salt aerosol in coastal Antarctic regions at three coastal. J Geophys Res 103:10961–10974
Mykytczuk NC, Foote SJ, Omelon CR, Southam G, Greer CW, Whyte LG (2013) Bacterial growth at −15 °C; molecular insights from the permafrost bacterium Planococcus halocryophilus Or1. ISME J 7:1211–1226. doi:10.1038/ismej.2013.8
Nadeau T, Castenholz RW (2000) Characterization of psychrophilic Oscillatorians (cyanobacteria) from Antarctic meltwater ponds. J Phycol 923:914–923
Nadeau T-L, Milbrandt EC, Castenholz RW (2001) Evolutionary relationships of cultivated Antarctic Oscllatorians (Cyanobacteria). J Phycol 37:650–654
Nawrocki EP, Eddy SR (2013) Computational identification of functional RNA homologs in metagenomic data. RNA Biol 10:1170–1179. doi:10.4161/rna.25038
Nawrocki EP, Burge SW, Bateman A, Daub J, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Floden EW, Gardner PP, Jones TA, Tate J, Finn RD (2015) Rfam 12.0: updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D130–D137. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1063
Nkem JN, Wall DH, Virginia RA, Barrett JE, Broos EJ, Porazinska DL, Adams BJ (2006) Wind dispersal of soil invertebrates in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Polar Biol 29:346–352. doi:10.1007/s00300-005-0061-x
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2016) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.3-4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Parker BC, Simmons GM, Wharton RA Jr, Seaburg KG, Love FG (1982) Removal of organic and inorganic matter from Antarctic lakes by aerial escape of bluegreen algal mats. J Phycol 18:72–78
Pasteris DR, McConnell JR, Das SB, Criscitiello AS, Evans MJ, Maselli OJ, Sigl M, Layman L (2014) Seasonally resolved ice core records from West Antarctica indicate a sea ice source of sea salt aerosol and a biomass burning source of ammonium. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:9168–9182. doi:10.1002/2013JD020720
Pearce DA, Hughes KA, Lachlan-Cope T, Harangozo SA, Jones AE (2010) Biodiversity of air-borne microorganisms at Halley station, Antarctica. Extremophiles 14:145–159. doi:10.1007/s00792-009-0293-8
Porazinska DL, Fountain AG, Nylen TH, Tranter M, Virginia RA, Wall DH (2004) The biodiversity and biogeochemistry of cryoconite holes from McMurdo Dry Valley glaciers, Antarctica. Arct Antarct Alp Res 36:84–91
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35:7188–7196. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm864
Rankin AM (2002) Frost flowers: implications for tropospheric chemistry and ice core interpretation. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2002JD002492
Rankin AM, Auld V, Wolff EW (2000) Frost flowers as a source of fractionated sea salt aerosol in the polar regions. Geophys Res Lett 27:3469–3472
Šabacká M, Priscu JC, Basagic HJ, Fountain AG, Wall DH, Virginia RA, Greenwood MC (2012) Aeolian flux of biotic and abiotic material in Taylor Valley, Antarctica. Geomorphology 155–156:102–111. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.12.009
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 75:7537–7541. doi:10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Shi Y, Tyson GW, Eppley JM, Delong EF (2010) Integrated metatranscriptomic and metagenomic analyses of stratified microbial assemblages in the open ocean. ISME J 5:999–1013. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.189
Sievert SM, Heidorn T, Kuever J (2000) Halothiobacillus kellyi sp. nov., a mesophilic, obligately chemolithoautotrophic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a shallow- water hydrothermal vent in the Aegean Sea, and emended description of the genus Halothiobacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1229–1237. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-3-1229
Soo RM, Wood SA, Grzymski JJ, McDonald IR, Cary SC (2009) Microbial biodiversity of thermophilic communities in hot mineral soils of Tramway Ridge, Mount Erebus, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 11:715–728. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01859.x
Sorokin DY, Kovaleva OL, Tourova TP, Muyzer G (2010) Thiohalobacter thiocyanaticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, sulfur-oxidizing gammaproteobacterium from hypersaline lakes, that utilizes thiocyanate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:444–450. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.012880-0
Tang EPY, Tremblay R, Vincent WF (1997) Cyanobacterial dominance of polar freshwater ecosystems: are high-latitude mat-formers adapted to low temperature? J Phycol 181:171–181
Team RC (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.r-project.org/. Accessed 1 Dec 2012
Tebo BM, Davis RE, Anitori RP, Connell LB, Schiffman P, Staudigel H (2015) Microbial communities in dark oligotrophic volcanic ice cave ecosystems of Mt. Erebus, Antarctica. Front Microbiol 6:1–14. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00179
Wells LE, Deming JW (2006) Characterization of a cold-active bacteriophage on two psychrophilic marine hosts. Aquat Microb Ecol 45:15–29. doi:10.3354/ame045015
Whitaker D, Christman M (2014) clustsig: significant cluster analysis. http://cran.r-project.org/package=clustsig. Accessed 1 Mar 2016
Wolff EW (2003) An ice core indicator of Antarctic sea ice production? Geophys Res Lett 30:2–5. doi:10.1029/2003GL018454
Wright JJ, Konwar KM, Hallam SJ (2012) Microbial ecology of expanding oxygen minimum zones. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:381–394. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2778
Zmasek C (2014) Archaeopteryx. https://sites.google.com/site/cmzmasek/home/software/archaeopteryx. Accessed 1 Mar 2016
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSF PLR award 1043265 to J.W.D. and the Walters Endowed Professorship. J.S.B. was supported by an NSF IGERT Fellowship through the University of Washington’s Astrobiology Program and an EPA STAR Fellowship. We are grateful to Shelly Carpenter for her stalwart assistance with sample collections and processing in the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowman, J.S., Deming, J.W. Wind-driven distribution of bacteria in coastal Antarctica: evidence from the Ross Sea region. Polar Biol 40, 25–35 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-1921-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-1921-2