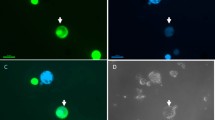
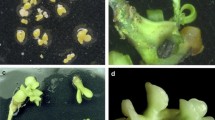
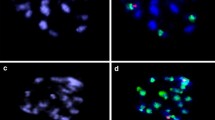
Abstract
CMS (cytoplasmic male sterility) can be controlled by the mitochondrion genome in higher plants, including Satsuma mandarin. Somatic fusion experiments in citrus combining embryogenic callus protoplasts of one parent with leaf protoplasts of a second parent often produce cybrid plants of the leaf parent, a phenomenon occurring most often with interspecific fusion combinations. In an attempt to practically exploit this cybridization phenomenon, we conducted somatic fusion experiments combining embryogenic suspension-derived protoplasts of Satsuma mandarin, Citrus unshiu Marc. cv. Guoqing No. 1 (G1), a male-sterile cultivar, with leaf protoplasts of other seedy types—Hirado Buntan Pink pummelo (HBP) [Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck], Sunburst mandarin (C. reticulata Blanco), Orie Lee hybrid (C. reticulata cv. Clementine × Murcott tangor), and Murcott tangor [C. reticulata × C. sinensis (L.) Osbeck], respectively—in an attempt to generate seedless cybrids by the targeted transfer of CMS. The genetic identities of regenerated plants from all four parental combinations were determined by flow cytometry, SSR, CAPS (or PCR-RFLP), RFLP, and chloroplast-SSR analyses. Regenerated plants from the first three parental combinations were diploids, and the cybrid nature of G1 + HBP with the mitochondrion genome from G1 and the chloroplast genome from HBP was confirmed, whereas the cybrid nature of the remaining two combinations was difficult to confirm because of the close phylogenetic relatedness of both fusion parents, as expected. Plants from G1 + Murcott were confirmed as tetraploid somatic hybrids. This is the first report of targeted citrus cybrid production by symmetric fusion with male-sterile Satsuma as the callus parent and other seedy cultivars as the leaf parents.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAPS::
-
Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence
- CMS::
-
Cytoplasmic male sterility
- cp-SSR::
-
Chloroplast simple sequence repeat
- PEG::
-
Polyethylene glycol
- SSR::
-
Simple sequence repeat
- RFLP::
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
References
Akagi H (2001) Cybridization in Oryza sativa L. (rice). In: Nagata T, Bajaj YPS (eds) Somatic hybridization in crop improvement II, vol 49. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 17–36
Akagi H, Taguchi T, Fujimura T (1995) Stable inheritance and expression of the CMS traits introduced by asymmetric protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 91:563–567
Al-Janabi SM, McClelland M, Petersen C, Sobral BWS (1994) Phylogenetic analysis of organellar DNA sequences in the Andropogoneae: Saccharinea. Theor Appl Genet 88:933–944
Atanassov II, Atanassova SA, Dragoeva AI, Atanassov AI (1998) A new CMS source in Nicotiana developed via somatic cybridization between N. tabacum and N. alata. Theor Appl Genet 97:982–985
Bastia T, Scotti N, Cardi T (2001) Organelle DNA analysis of Solanum and Brassica somatic hybrids by PCR with ‘universal primers’. Theor Appl Genet 102:1265–1272
Bhattacharjee B, Sane AP, Gupta HS (1999) Transfer of wild abortive cytoplasmic male sterility through protoplast fusion in rice. Mol Breed 5:319–327
Bryan GJ, McNicoll J, Ramsay G, Meyer RC, De Jong WS (1999) Polymorphic simple sequence repeat markers in chloroplast genomes of Solanaceous plants. Theor Appl Genet 99:859–867
Cabasson CM, Luro F, Ollitrault P, Grosser JW (2001) Non-random inheritance of mitochondrial genomes in Citrus hybrids produced by protoplast fusion. Plant Cell Rep 20:604–609
Cardi T, Earle ED (1997) Production of new CMS Brassica oleracea by transfer of ‘Anand’ cytoplasm from B. rapa through protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 94:204–212
Cheng YJ, Guo WW, Deng XX (2003a) Molecular characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear genomes in phenotypically abnormal Valencia orange (Citrus sinensis) + Meiwa kumquat (Fortunella crassifolia) intergeneric somatic hybrids. Plant Cell Rep 21:445–451
Cheng YJ, Guo WW, Deng XX (2003b) cpSSR: a new tool to analyze chloroplast genome of citrus somatic hybrids. Acta Bot Sin 45:906–909
Creemers-Molenaar J, Hall RD, Krens FA (1992) Asymmetric protoplast fusion aimed at intraspecific transfer of cytoplasmic male-sterility (CMS) in Lolium perenne L. Theor Appl Genet 84:763–770
Demesure B, Sodzi N, Petit RJ (1995) A set of universal primers for amplification of polymorphic non-coding regions of mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA in plants. Mol Ecol 4:129–131
Deng XX, Guo WW, Yu GH (2000a) Citrus somatic hybrids regenerated from protoplast electrofusion. Acta Hortic 535:163–168
Deng XX, Guo WW, Yu GH (2000b) Diploid mesophyll parent type plants regenerated from nine symmetrical protoplast fusion combinations in Citrus (in Chinese). Acta Hortic Sin 27:1–5
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Gleba YY, Sytnik KM (1984) Protoplast fusion. In: Shoeman R (ed) Genetic engineering in higher plants. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, pp 63–114
Grosser JW, Gmitter FG Jr (1990) Protoplast fusion and citrus improvement. Plant Breed Rev 8:339–374
Grosser JW, Gmitter FG Jr, Tusa N, Reforgiato Recupero G, Cucinotta P (1996) Further evidence of a cybridization requirements for plant regeneration from citrus leaf protoplasts following somatic fusion. Plant Cell Rep 15:672–676
Grosser JW, Ollitrault P, Olivares-Fuster O (2000) Somatic hybridization in citrus: an effective tool to facilitate variety improvement. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36:434–449
Guo WW, Deng XX (2000) Citrus cybrids and their cytoplasmic genetic recombination (in Chinese). Acta Hortic Sin 27:487–491
Guo WW, Deng XX (2001) Wide somatic hybrids of Citrus with its related genera and their potential in genetic improvement. Euphytica 118:175–183
Guo WW, Cheng YJ, Deng XX (2002) Regeneration and molecular characterization of intergeneric somatic hybrids between Citrus reticulata and Poncirus trifoliata. Plant Cell Rep 20:829–834
Huo HQ, Hao YJ, Deng XX (1999) Induction of embryogenic callus of loose skin mandarins (in Chinese). Acta Biol Exp Sin 32:289–295
Kijas JMH, Thomas MR, Fowler JCS, Roose ML (1997) Integration of trinucleotide microsatellite into a linkage map of Citrus. Theor Appl Genet 94:701–708
Kirti PB, Banga SS, Prakash S, Chopra VL (1995) Transfer of Ogu cytoplasmic male-sterility to Brassica juncea and improvement of the male-sterile line through somatic-cell fusion. Theor Appl Genet 91:517–521
Kobayashi S, Ohgawara T, Fujiwara K, Oiyama I (1991) Analysis of cytoplasmic genomes in somatic hybrids between navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osb) and ‘Murcott’ tangor. Theor Appl Genet 82:6–10
Kumar A, Cocking EC (1987) Protoplast fusion—a novel-approach to organelle genetics in higher plants. Am J Bot 74:1289–1303
Liu JH, Landgren M, Glimelius K (1996) Transfer of the Brassica tournefortii cytoplasm to B. napus for the production of cytoplasmic male sterile B. napus. Physiol Plant 96:123–129
Liu JH, Pang XM, Cheng YJ, Meng HJ, Deng XX (2002) Molecular characterization of the nuclear and cytoplasmic genomes of intergeneric diploid plants from cell fusion between Microcitrus papuana and Rough lemon. Plant Cell Rep 21:327–332
Lotfy S, Luro F, Carreel F, Froelicher Y, Rist D, Ollitrault P (2003) Application of cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence method for analysis of cytoplasmic genome among Aurantioideae intergeneric somatic hybrids. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 128:225–230
Louzada ES, del Rio HS, Xia D, Moran-Mirabal JM (2002) Preparation and fusion of citrus sp. microprotoplasts. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 127:484–488
Melchers G, Mohri Y, Watanabe K, Wakabayashi S, Harada K (1992) One-step generation of cytoplasmic male-sterility by fusion of mitochondrial-inactivated tomato protoplasts with nuclear-inactivated Solanum protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6832–6836
Miranda M, Motomura T, Ikeda F, Ohgawara T, Saito W, Endo T, Omura M, Moriguchi T (1997) Somatic hybrids obtained by fusion between Poncirus trifoliata (2x) and Fortunella hindsii (4x) protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 16:401–405
Moreira CD, Chase CD, Gmitter FG Jr, Grosser JW (2000a) Inheritance of organelle genomes in citrus somatic cybrids. Mol Breed 6:401–405
Moreira CD, Chase CD, Gmitter FG Jr, Grosser JW (2000b) Transmission of organelle genomes in citrus somatic hybrids. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 61:165–168
Moriguchi T, Hidaka T, Omura M, Motomura T, Akihama T (1996) Genotypes and parental combination influence efficiency of cybrid induction in Citrus by electrofusion. HortScience 31:275–278
Moriguchi T, Motomura T, Hidaka T, Akihama T, Omura M (1997) Analysis of mitochondrial genomes among Citrus plants produced by the interspecific somatic hybrids of ‘Seminole’ tangelo with rough lemon. Plant Cell Rep 16:397-400
Morton BR, Clegg MT (1993) A chloroplast DNA mutational hotspot and gene conversion in a noncoding region near rbcL in the grass family (Poaceae). Curr Genet 24:357–365
Motegi T, Nou IS, Zhou J, Kanno A, Kameya T, Hirata Y (2003) Obtaining an Ogura-type CMS line from asymmetrical protoplast fusion between cabbage (fertile) and radish (fertile). Euphytica 129:319–323
Murashige T, Tucker DPH (1969) Growth factor requirements of citrus tissue culture. In: Chapman HD (ed) Proc 1st Citrus Symp, vol 3. University of California Press, Riverside, pp 1155–1161
Nicolosi E, Deng ZN, Gentile A, La Malfa S (2000) Citrus phylogeny and genetic origin of important species as investigated by molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:1155–1166
Niedz RP, Hyndman SE, Wynn ET, Bausher MG (2002) Normalizing sweet orange [C. sinensis (L.) Osbeck] somatic embryogenesis with semi-permeable membranes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 38:552–557
Ohgawara T, Uchimiya H, Ishii S, Kobayashi S (1994) Somatic hybridization between Citrus sinensis and Poncirus trifoliata. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Somatic hybridization in crop improvement I, vol 27. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 439–454
Perez RM, Galiana AM, Navarro L, Duran-Vila N (1998) Embryogenesis in vitro of several Citrus species and cultivars. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 73:796–802
Provan J, Powell W, Hollingsworth PM (2001) Chloroplast microsatellites: new tools for studies in plant ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 16:142–147
Saito W, Ohgawara T, Shimizu J, Kobayashi S (1993) Citrus cybrid regeneration following cell fusion between nucellar cells and mesophyll cells. Plant Sci 88:195–201
Saito W, Ohgawara T, Shimizu J, Kobayashi S (1994) Somatic hybridization in Citrus using embryogenic cybrid callus. Plant Sci 99:89–95
Sakai T, Imamura J (1990) Intergeneric transfer of cytoplasmic male-sterility between Raphanus sativus (CMS line) and Brassica napus through cytoplast-protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 80:421–427
Sigareva MA, Earle ED (1997) Direct transfer of a cold-tolerant Ogura male sterile cytoplasm into cabbage (Brassica oleracea ssp capitata) via protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 94:213–220
Spangenberg G, Freydl E, Osusky M, Nagel J, Potrykus I (1991) Organelle transfer by microfusion of defined protoplast-cytoplast pairs. Theor Appl Genet 81:477–486
Yamamoto M, Kobayashi SA (1995) Cybrid plant produced by electrofusion between Citrus unshiu (Satsuma mandarin) and C. sinensis (sweet orange). Plant Tissue Cult Lett 12:131–137
Yamamoto M, Matsumoto R, Yamada Y (1995) Relationship between sterility and seedlessness in Citrus. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 64:23-29
Yamamoto M, Matsumoto R, Okudai N, Yamada Y (1997) Aborted anthers of Citrus result from gene-cytoplasmic male sterility. Sci Hortic 70:9–14
Yamamoto M, Kobayashi S, Yoshioka T, Matsumoto R (2001) Cybridization in Citrus unshiu Marc. (Satsuma mandarin) and C. sinensis (L.) Osbeck (Sweet orange). In: Nagata T, Bajaj YPS (eds) Somatic hybridization in crop improvement II, vol 49. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 124–138
Zelcer A, Aviv D, Galun E (1978) Interspecific transfer of cytoplasmic male-sterility by fusion between protoplasts of normal Nicotiana sylvestris and x-ray-irradiated protoplasts of male-sterile N. tabacum. Z Pflanzenphysiol 90:397–407
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Florida Agricultural Experiment Station and approved for publication as Journal Series No. R-09483. The authors also thank the Florida Citrus Production Research Advisory Council, the 863 High-Tech Project of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), the International Foundation for Science (IFS) in Stockholm, Sweden, and the Chengguang Youth Project of Wuhan City of China for partial financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G.C. Phillips
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W.W., Prasad, D., Cheng, Y.J. et al. Targeted cybridization in citrus: transfer of Satsuma cytoplasm to seedy cultivars for potential seedlessness. Plant Cell Rep 22, 752–758 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0747-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0747-x