Abstract
Background
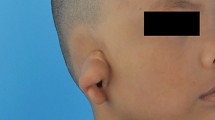
In contrast to prominent ear, lying ear can be defined when the antihelix of the ear is excessively folded, i.e., the conchoscaphal angle is much less than 90°. In such case, ears may look smaller than the face. These patients want their ears to be exposed more. In Asia, there is also a tendency to prefer large and long ears. The objective of this study was to present a surgical method for correcting lying ear deformities.
Methods
From August 2017 to June 2018, 37 patients (72 ears) underwent surgery using our surgical method for lying ear deformities. After the cartilage was exposed on the posterior auricular surface, the fibrous band present at the conchoscaphal angle was released. Two longitudinal cartilage incisions were performed along the border of the antihelix. Horizontal mattress sutures were performed on the cartilage until the conchoscaphal angle was close to 90°. Onlay cartilage grafting was performed for the most severe portion of the deformity.
Results
We performed reoperation for four patients due to recurrence (n = 2), under-correction (n = 1), and cartilage exposure (n = 1). Most patients obtained satisfactory aesthetic results.
Conclusions
There have been few reports of the surgical method for lying ear deformities. Our surgical method can provide satisfactory clinical outcomes for correcting lying ear deformities.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janis JE, Rohrich RJ, Gutowski KA (2005) Otoplasty (review). Plast Reconstr Surg 115:60e–72e
Sinno S, Chang JB, Thorne CH (2015) Precision in otoplasty: combining reduction otoplasty with traditional otoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 135:1342–1348
Kim SE, Yeo CH, Kim T, Kim YH, Lee JH, Chung KJ (2017) Correction of lying ears by augmentation of the conchoscaphal angle. J Craniofac Surg 28:254–255
Woo PN, Lip PL (1996) Why do old men have big ears? The Chinese believe that thick ears signify greater wealth. BMJ 312:582
Hoehn JG, Ashruf S (2005) Otoplasty: sequencing the operation for improved results. Plast Reconstr Surg 115:5e–16e
Foda HM (1999) Otoplasty: A graduated approach. Aesthet Plast Surg 23:407–412
Liaw J, Patel VA, Carr MM (2017) Congenital anomalies of the external ear. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 28:72–76
Janz BA, Cole P, Hollier LH Jr, Stal S (2009) Treatment of prominent and constricted ear anomalies. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:27e–37e
Choe KS, Sclafani AP, Litner JA, Yu GP, Romo T 3rd (2004) The Korean American woman’s face: anthropometric measurements and quantitative analysis of facial aesthetics. Arch Facial Plast Surg 6:244–252
Ely ET (1881) An operation for prominence of the auricles. Arch Otolaryngol 10:97
Luckett WH (1910) A new operation for prominent ears based on the anatomy of the deformity. Surg Gynaecol Obstet 10:635–637
Mustardé JC (1963) The correction of prominent ears by using simple mattress sutures. Br J Plast Surg 16:170–178
Kaye BL (1967) A simplified method for correcting the prominent ear. Plast Reconstr Surg 40:44–48
Furnas DW (1968) Correction of prominent ears by conchomastoid sutures. Plast Reconstr Surg 42:189–193
Elliott RA (1990) Otoplasty: a combined approach. Clin Plast Surg 17:373–381
Szychta P, Orfaniotis G, Stewart KJ (2012) Revision otoplasty: an algorithm. Plast Reconstr Surg 130:907–916
Lentz AK, Plikaitis CM, Bauer BS (2011) Understanding the unfavorable result after otoplasty: an integrated approach to correction. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:536–544
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article to declare.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All patients provided written informed consent for the publication and the use of their images.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video 1. This video demonstrates the surgical method of using horizontal mattress suture to correct the lying ear deformity
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, T.K., Kim, Y.M. & Min, K.H. Surgical Correction of the Lying Ear Deformities. Aesth Plast Surg 43, 1228–1232 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01365-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01365-x