Abstract
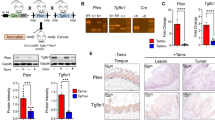
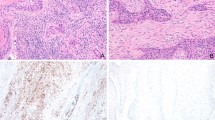
The objective of this study was to observe the distribution of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the development of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and to determine the role of Tregs in the progression of tongue SCC. A mouse model of 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4NQO)-induced-tongue SCC was established. The expression of Forkhead box P3 (Foxp3), interleukin 10, transforming growth factor-β, chemokine CC motif ligands 17, 20, and CC chemokine receptor 4 was determined using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Foxp3 expression was also analyzed using immunohistochemistry. The results were compared with those of control mice and of 4NQO-treated mice treated with a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor. Well to moderately differentiated tongue SCC was induced in all of the experimental mice. The amount of Tregs of the experimental mice was over 10 times as much as control mice at the early stage of tumor progression. COX-2 inhibitor did not prevent the progression of tongue SCC and did not reduce the total amount of Tregs. Tregs function at the early stage of the development of tongue SCC, and it may be effective to suppress Tregs at the early stage of tumor progression for the treatment and/or prevention of tongue SCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 4NQO:
-
4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide
- CCL:
-
Chemokine CC motif ligand(s)
- CCR:
-
CC chemokine receptor
- CI:
-
Confidence interval(s)
- PG:
-
Prostaglandin
- PGE2:
-
Prostaglandin E2
- RT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- Th3:
-
T helper 3
- Tr1(17):
-
Type 1(17) T regulatory
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory T cells
References
Roncarolo MG, Bacchetta R, Bordignon C, Narula S, Levings MK (2001) Type 1 T regulatory cells. Immunol Rev 182:68–79
Weiner HL (2001) Induction and mechanism of action of thransforming growth factor-beta-secreting Th3 reglatory cells. Immunol Rev 182:207–214
Shevach EM (2002) CD4 + CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol 2:389–400
Larmonier N, Marron M, Zeng Y, Cantrell J, Romanoski A, Sepassi M, Thompson S, Chen X, Andreansky S, Katsanis E (2007) Tumor-derived CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell suppression of dendritic cell function involves TGF-beta and IL-10. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:48–59
Yu P, Lee Y, Liu W, Krausz T, Chong A, Schreiber H, Fu YX (2005) Intratumor depletion of CD4+ cells unmasks tumor immunogenicity leading to the rejection of late-stage tumors. J Exp Med 201:779–791
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Gracia JR, Zhang L, Burow M, Zhu Y, Wei S, Kryczek I, Daniel B, Gordon A, Myers L, Lackner A, Disis ML, Knutson KL, Chen L, Zou W (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10:942–949
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S (2006) Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res 12:5423–5434
Katz SC, Bamboat ZM, Maker AV, Shia J, Pillarisetty VG, Yopp AC, Hedvat CV, Gonen M, Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, D’Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP (2013) Regulatory T cell infiltration predicts outcome following resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol 20:946–955
Viguier M, Lemaitre F, Verola O, Cho MS, Gorochov G, Dubertret L, Bachelez H, Kourilsky P, Ferradini L (2004) Foxp3 expressing CD4+ CD25(high) regulatory T cells are overexpressed in human metastatic melanoma lymph nodes and inhibit the function of infiltrating T cells. J Immunol 173:1444–1453
Bron L, Jandus C, Andrejevic-Blant S, Speiser DE, Monnier P, Romero P, Rivals JP (2012) Prognostic value of arginase-II expression and regulatory T-cell infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 132:E85–E93
Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, Peyrard S, Klein C, Agueznay Nel H, Mosseri V, Laccourreye O, Bruneval P, Fridman WH, Brasnu DF, Tartour E (2006) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res 12:465–472
Shang B, Liu Y, Jiang SJ, Liu Y (2015) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 5:15179
Albers AE, Ferris RL, Kim GG, Chikamatsu K, DeLeo AB, Whiteside TL (2005) Immune responses to p53 in patients with cancer: enrichment in tetramer+ p53 peptide-specific T cells and regulatory T cells at tumor sites. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54:1072–1081
Strauss L, Bergmann C, Szczepanski M, Gooding W, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (2007) A unique subset of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells secreting interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-β1 mediates suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res 13:4345–4354
Hanakawa H, Orita Y, Sato Y, Takeuchi M, Ohno K, Gion Y, Tsukahara K, Tamamura R, Ito T, Nagatsuka H, Nishizaki K, Yoshino T (2014) Regulatory T-cell infiltration in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Otolaryngol 134:859–864
Vitale-Cross L, Czerninski R, Amornphimoltham P, Patel V, Molinolo AA, Gutkind JS (2009) Chemical carcinogenesis models for evaluating molecular-targeted prevention and treatment of oral cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2:419–422
Tang XH, Knudsen B, Bemis D, Tickoo S, Gudas LJ (2004) Oral cavity and esophageal carcinogenesis modeled in carcinogen-treated mice. Clin Cancer Res 10:301–313
Crofford LJ (1997) COX-1 and COX-2 tissue expression: implications and predictions. J Rheumatol 24(Suppl 49):15–19
Hla T, Neilson K (1992) Human cyclooxygenase-2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7384–7388
Baratelli F, Lin Y, Zhu L, Yang SC, Heuze-Vourc’h N, Zeng G, Reckamp K, Dohadwala M, Sharma S, Dubinett SM (2005) Prostaglandin E2 induces FOXP3 gene expression and T regulatory cell function in human CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 175:1483–1490
Mahic M, Yaqub S, Johansson CC, Tasken K, Aandahl EM (2006) FOXP3 + CD4 + CD25+ adaptive regulatory T cells express cyclooxygenase-2 and suppress effector T cells by a prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 177:246–254
Sun DS, Zhaq MQ, Xia M, Li L, Jiang YH (2012) The correlation between tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and cyclooxygenase-2 expression and their association with recurrence in resected head and neck cancers. Med Oncol 29:707–713
Yuan XL, Chen L, Li MX, Dong P, Xue J, Wang J, Zhang TT, Wang XA, Zhang FM, Ge HL, Shen LS, Xu D (2010) Elevated expression of Foxp3 in tumor-infiltrating Treg cells suppresses T-cell proliferation and contributes to gastric cancer progression in a COX-2-dependent manner. Clin Immunol 134:277–288
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S (2003) Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299:1057–1061
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330
Nicholson IC, Mavrangelos C, Bird DR, Bresatz-Atkins S, Eastaff-Leung NG, Grose RH, Gundsambuu B, Hill D, Millard DJ, Sadlon TJ, To S, Zola H, Barry SC, Krumbiegel D (2012) PI16 is expressed by a subset of human memory Treg with enhanced migration to CCL17 and CCL20. Cell Immunol 275:12–18
Li J, Liang F, Yu D, Qing H, Yang Y (2013) Development of a 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide model of lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 49:299–305
Chu M, Su YX, Wang L, Zhang TH, Liang YJ, Liang LZ, Liao GQ (2012) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells contribute to oral cancer progression in 4NQO-treated mice. Oral Dis 18:67–73
Gasparoto TH, de Souza Malaspina TS, Benevides L, de Melo EJ, Jr Costa MR, Damante JH, Ikoma MR, Garlet GP, Cavassani KA, da Silva JS, Campanelli AP (2010) Patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma are characterized by increased frequency of suppressive regulatory T cells in the blood and tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59:819–828
Mannino MH, Zhu Z, Xiao H, Bai Q, Wakefield MR, Fang Y (2015) The paradoxical role of IL-10 in immunity and cancer. Cancer Lett 367:103–107
Massagué J, Blain SW, Lo RS (2000) TGF-beta signaling in growth control, cancer and heritable disorders. Cell 103:295–309
Han G, Wang XJ (2011) Roles of TGF-β signaling Smads in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Biosci 1:41
Oshimori N, Oristian D, Fuchs E (2015) TGF-β promotes heterogeneity and drug resistance in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell 160:963–976
Wang YH, Wu MW, Yang AK, Zhang WD, Sun J, Liu TR, Chen YF (2011) COX-2 gene increases tongue cancer cell proliferation and invasion through VEGF-C pathway. Med Oncol 28(Suppl 1):S360–S366
Edelman MJ, Watson D, Wang X, Morrison C, Kratzke RA, Jewell S, Hodgson L, Mauer AM, Gajra A, Masters GA, Bedor M, Vokes EE, Green MJ (2008) Eicosanoid modulation in advanced lung cancer: cyclooxugenase-2 expression is a positive predictive factor for celecoxib + chemotherapy-Cancer and Leukemia Group B Trial 30203. J Clin Oncol 26:848–855
Iellem A, Mariani M, Lang R, Recalde H, Panina-Bordignon P, Sinigaglia F, D’Ambrosio D (2001) Unique chemotactic response profile and specific expression of chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 194:847–853
Li WM, Liu HR (2016) CCL20-CCR6 cytokine network facilitate Treg activity in advanced grades and metastatic variants of hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand J Immunol 83:33–37
Yu Q, Lou XM, He Y (2015) Preferential recruitment of Th17 cells to cervical cancer via CCR6-CCL20 pathway. PLoS One 10:e0120855
Kawai O, Ishii G, Kubota K, Murata Y, Naito Y, Mizuno T, Aokage K, Saijo N, Nishikawa Y, Gemma A, Kudoh S, Ochiai A (2008) Predominant infiltration of macrophages and CD8+ T cells in cancer nests is a significant predictor of survival in stage IV nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 113:1387–1395
Naito Y, Saito K, Shiiba K, Ohuchi A, Saigenji K, Nagura H, Ohtani H (1998) CD8+ T cells infiltrated within cancer cell nests as a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 58:3491–3494
Schumacher K, Haensch W, Röefzaad C, Schlag PM (2001) Prognostic significance of activated CD8+ T cell infiltrations within esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res 61:3932–3936
Knoechel B, Lohr J, Kahn E, Bluestone JA, Abbas AK (2005) Sequential development of interleukin 2-dependent effector and regulatory T cells in response to endogenous systemic antigen. J Exp Med 202:1375–1386
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research C from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan [Grant No. 25462684 to Orita Y ] and by Wesco Scientific Promotion Foundation [to Orita Y].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miki, K., Orita, Y., Gion, Y. et al. Regulatory T cells function at the early stage of tumor progression in a mouse model of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 65, 1401–1410 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1902-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1902-x