Abstract
Purpose
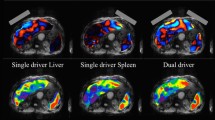
To assess how different driver power amplitudes affect the measurement of liver stiffness in pediatric liver magnetic resonance elastography (MRE).
Methods
From January 2018 to May 2018, pediatric patients (≤ 18 years) who underwent liver MRE with 20% and 56% driver power amplitudes were included in this retrospective study. Region-of-interests (ROIs) were drawn on four stiffness maps to include the largest area of the liver parenchyma. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were used to assess agreements for the area, mean, maximum, minimum and standard deviation of liver stiffness between the driver power amplitudes.
Results
128 MRE stiffness maps from 16 patients (M:F = 10:6, median 12.5 years old) were included. On MRE, median ROI areas of liver were 83.1 cm2 (range, 46.9–144.1 cm2) and 63.0 cm2 (range, 5.4–123.4 cm2) for the driver power amplitudes of 20% and 56%, respectively. Median liver stiffness values were 2.3 kPa (range, 1.7–8.0 kPa) and 2.8 kPa (range, 1.7–8.5 kPa). Maximum and minimum liver stiffness values were 5.3 kPa and 1.0 kPa for 20% and 7.8 kPa and 1.1 kPa for 56%. Standard deviation was 0.6 kPa for 20% and 1.0 kPa for 56%. ICC values between the two power amplitudes were 0.33–0.51 for the ROI area and the maximum, minimum and standard deviation values of liver stiffness. The ICC value for liver stiffness was 0.857 (95% confidence interval, 0.760–0.915).
Conclusion
Liver stiffness with two driver power amplitudes on MRE showed good reliability in pediatric patients. Driver power amplitudes need to be optimized according to the pediatric liver size.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Available on demands.
References
Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D (2008) Autoimmune pediatric liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 14(21):3360–3367
Mavis AM, Alonso EM (2015) Liver disease in the adolescent. Clin Liver Dis 19(1):171–185
Friedman SL (2010) Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(8):425–436
Bortolotti F, Guido M (2007) Reversal of liver cirrhosis: a desirable clinical outcome and its pathogenic background. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 44(4):401–406
Castera L, Pinzani M (2010) Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango? Gut 59:861–866
Etchell E, Jugé L, Hatt A, Sinkus R, Bilston LE (2017) Liver Stiffness Values Are Lower in Pediatric Subjects than in Adults and Increase with Age: A Multifrequency MR Elastography Study. Radiology 283(1):222–230
Joshi M, Dillman JR, Towbin AJ, Serai SD, Trout AT (2017) MR elastography: high rate of technical success in pediatric and young adult patients. Pediatr Radiol 47(7):838–843
Trout AT, Sheridan RM, Serai SD, Xanthakos SA, Su W, Zhang B, Wallihan DB (2018) Diagnostic Performance of MR Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Children and Young Adults with a Spectrum of Liver Diseases. Radiology 287(3):824–832
Shinagawa Y, Mitsufuji T, Morimoto S, Nakamuta R, Urakawa H, Morita A, Fujimitsu R, Takano K, Yoshimitsu K (2014) Optimization of scanning parameters for MR elastography at 3.0 T clinical unit: volunteer study. Jpn J Radiol 32(7):441–446
Serai SD, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ (2012) Pediatric liver MR elastography. Dig Dis Sci 57(10):2713–2719
Binkovitz LA, El-Youssef M, Glaser KJ, Yin M, Binkovitz AK, Ehman RL (2012) Pediatric MR elastography of hepatic fibrosis: principles, technique and early clinical experience. Pediatr Radiol 42(4):402–409
Kim JK, Yoon H, Lee M-J, Kim M-J, Han K, Koh H, Kim S, Han SJ, Shin HJ (2019) Feasibility of Spin-Echo Echo-Planar Imaging MR Elastography in Livers of Children and Young Adults. Investig Magn Reson Imaging 23(3):251–258
Calle-Toro JS, Serai SD, Hartung EA, Goldberg DJ, Bolster BD, Jr., Darge K, Anupindi SA (2019) Magnetic resonance elastography SE-EPI vs GRE sequences at 3T in a pediatric population with liver disease. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44(3):894–902
JM B, D A (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 327(8476):307–310
Siegel MJ, Priatna A, Bolster Jr BD, Kotyk JJ (2012) Pediatric MR elastography of the liver. Clin Pediatr Imaging:108–111
Guglielmo FF, Venkatesh SK, Mitchell DG (2019) Liver MR elastography technique and image interpretation: pearls and pitfalls. Radiographics 39(7):1983–2002
Funding
We have no financial relationships to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approved this single-center retrospective study and waived the requirement for informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DK., Yoon, H., Han, K. et al. Effect of different driver power amplitudes on liver stiffness measurement in pediatric liver MR elastography. Abdom Radiol 46, 4729–4735 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03197-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03197-3