Abstract
Purpose
MR elastography (MRE) can serve as an accurate surrogate marker of liver fibrosis. For any diagnostic test that is to replace the current reference standard, interobserver agreement should be at least as good and preferably better. The objective of this study was to perform a head-to-head comparison of the interobserver agreements of MRE and liver fibrosis staging on biopsy in a single cohort of hepatitis patients.
Methods
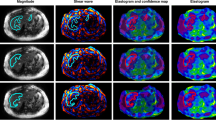
One hundred and three patients with viral hepatitis B or C who had a liver biopsy underwent MRE. Two readers independently selected a region-of-interest (ROI) in the liver to derive elasticity values. Two pathologists first independently staged fibrosis on biopsies using the METAVIR classification and subsequently held a consensus meeting. Interobserver agreements of elasticity values and fibrosis stages were assessed with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC).
Results
MRE and biopsy data were available for 85/103 patients. ICC of pathologists staging fibrosis was almost perfect at 0.91 (95% CI 0.86–0.94). ICC for MRE readers was significantly (P < 0.0001) higher at 0.99 (95% CI 0.98–1.00).
Conclusions
Interobserver agreement for liver fibrosis staging was almost perfect for both histopathology and MRE, with a significant higher agreement for MRE. Its high interobserver agreement and reliable accuracy support the use of MRE as a non-invasive screening tool for liver fibrosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TE:
-
Transient elastography
- MRE:
-
Magnetic resonance elastography
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- ROI:
-
Region-of-interest
References
Ly KN, Xing J, Klevens RM, et al. (2012) The increasing burden of mortality from viral hepatitis in the United States between 1999 and 2007. Ann Intern Med 156(4):271–278. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-156-4-201202210-00004
Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM (2011) Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34(3):274–285. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04724.x
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2012) EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 57(1):167–185. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.010
Rustogi R, Horowitz J, Harmath C, et al. (2012) Accuracy of MR elastography and anatomic MR imaging features in the diagnosis of severe hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(6):1356–1364. doi:10.1002/jmri.23585
Huwart L, Peeters F, Sinkus R, et al. (2006) Liver fibrosis: non-invasive assessment with MR elastography. NMR Biomed 19(2):173–179. doi:10.1002/nbm.1030
Lee DH, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI (2012) MR elastography of healthy liver parenchyma: Normal value and reliability of the liver stiffness value measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging 38(5):1215–1223. doi:10.1002/jmri.23958
Venkatesh SK, Wang G, Lim SG, Wee A (2014) Magnetic resonance elastography for the detection and staging of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Eur Radiol 24(1):70–78. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-2978-8
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, et al. (2012) Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Magn Reson Med Sci 11(4):291–297. doi:10.2463/mrms.11.291
Kim D, Kim WR, Talwalkar JA, Kim HJ, Ehman RL (2013) Advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography. Radiology 268(2):411–419. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121193
Kim BH, Lee JM, Lee YJ, et al. (2011) MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: experience from a tertiary center in Asia. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(5):1110–1116. doi:10.1002/jmri.22723
Bohte AE, de Niet A, Jansen L, et al. (2013) Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis: a comparison of ultrasound-based transient elastography and MR elastography in patients with viral hepatitis B and C. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-3046-0
Hines CD, Bley TA, Lindstrom MJ, Reeder SB (2010) Repeatability of magnetic resonance elastography for quantification of hepatic stiffness. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(3):725–731. doi:10.1002/jmri.22066
The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group (1994) Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 20(1 Pt 1):15–20
Cholongitas E, Senzolo M, Standish R, et al. (2006) A systematic review of the quality of liver biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol 125(5):710–721. doi:10.1309/W3XC-NT4H-KFBN-2G0B
Rousselet MC, Michalak S, Dupre F, et al. (2005) Sources of variability in histological scoring of chronic viral hepatitis. Hepatology 41(2):257–264. doi:10.1002/hep.20535
Robert M, Sofair AN, Thomas A, et al. (2009) A comparison of hepatopathologists’ and community pathologists’ review of liver biopsy specimens from patients with hepatitis C. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(3):335–338. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2008.11.029
Bohte AE, Garteiser P, de Niet A, et al. (2013) MR Elastography of the liver: defining thresholds for detecting viscoelastic changes. Radiology 269(3):768–776. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122669
Bedossa P, Poynard T (1996) An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 24(2):289–293. doi:10.1002/hep.510240201
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al. (1995) Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22:696–699
Sinkus R, Siegmann K, Xydeas T, et al. (2007) MR elastography of breast lesions: understanding the solid/liquid duality can improve the specificity of contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Magn Reson Med 58(6):1135–1144. doi:10.1002/mrm.21404
Norman GR, Streiner DL (2008) Biostatistics: the bare essentials. Shelton: People’s Medical Pub. House
Donner A, Zou GY (2002) Testing the equality of dependent intraclass correlation coefficients. J R Stat Soc D 51:367–379. doi:10.1111/1467-9884.00324
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, et al. (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135(1):32–40. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076
Bedossa P, Dargere D, Paradis V (2003) Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 38(6):1449–1457. doi:10.1016/j.hep.2003.09.022
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ, et al. (2007) Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(10):1207.e2–1213.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.06.012
Sturm N, Marlu A, Arvers P, Zarski JP, Leroy V (2013) Comparative assessment of liver fibrosis by computerized morphometry in naive patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. Liver Int 33(3):428–438. doi:10.1111/liv.12092
Acknowledgements
This study was presented at the European Society of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Radiology annual meeting 2013 and was funded by the NutsOhra Foundation, The Netherlands. NutsOhra was not involved in designing and conducting this study, did not have access to the data, and was not involved in data analysis or preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have potential relevant conflicts of interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Runge, J.H., Bohte, A.E., Verheij, J. et al. Comparison of interobserver agreement of magnetic resonance elastography with histopathological staging of liver fibrosis. Abdom Imaging 39, 283–290 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-013-0063-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-013-0063-z