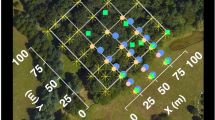
Abstract
The forest gap crucially influences forest environments, but its effects on local fungal community assembly are not fully understood. In this study, the fungal community in a weeping cypress forest was investigated as a function of forest gap locations based on forest clearing, using amplicon sequencing of the ITS2 region. The results showed that the fungal community significantly varied with the variations in soil properties related to gap location. Deterministic processes played pivotal roles in fungal community assembly, which was mainly driven by the temperature, moisture, available nitrogen, and microbial carbon in soil. Beta diversity of the fungal community increased from the gap center to the closed canopy. The relative abundances of dominant orders such as Microascales, Sordariales, and Chaetothyriales regularly varied as a function of gap location, and they were potential indicators for different gap locations. Based on network analysis, gap locations caused distinct co-occurrence patterns of fungal communities. This study shed light on the roles of forest gaps in the assembly of local fungal communities and provided additional strategies to manage forest ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, McDowell N, Vennetier M, Kitzberger T, Rigling A, Breshears DD, Hogg EH, Gonzalez P, Fensham R, Zhang Z, Castro J, Demidova N, Lim JH, Allard G, Running SW, Semerci A, Cobb N (2010) A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag 259(4):660–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001
Al-Yasiri MH, Normand A-C, Mauffrey J-F, Ranque S (2017) Anthropogenic impact on environmental filamentous fungi communities along the Mediterranean littoral. Mycoses 60(7):477–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/myc.12612
Baldrian P (2017) Forest microbiome: diversity, complexity and dynamics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 41(2):109–130. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuw040
Banerjee S, Kirkby CA, Schmutter D, Bissett A, Kirkegaada JA, Richardson AE (2016) Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and keystone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol Biochem 97:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.03.017
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc B 57(1):289–300
Boer WD, Folman LB, Summerbell RC, Boddy L (2005) Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol 29(4):795–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2004.11.005
Buee M, Reich M, Murat C, Morin E, Nilsson RH, Uroz S, Martin F (2009) 454 Pyrosequencing analyses of forest soils reveal an unexpectedly high fungal diversity. New Phytol 184(2):449–456. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03003.x
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Met 7(5):335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chase JM, Myers JA (2011) Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos T R Soc B 366(1576):2351–2363. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0063
Clemmensen KE, Finlay RD, Dahlberg A, Stenlid J, Wardle DA, Lindahl BD (2015) Carbon sequestration is related to mycorrhizal fungal community shifts during long-term succession in boreal forests. New Phytol 205(4):1525–1536. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13208
Cooley L, Spelman D, Thursky K, Slavin M (2007) Infection with Scedosporium apiospermum and S.prolificans Australia. Emerg Infect Dis 13(8):1170–1177. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1308.060576
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Erdos P, Rényi A (1960) On the evolution of random graphs. Publ Math Inst Hung Acad Sci 5(1):17–60
Gray AN, Spies TA, Easter MJ (2002) Microclimatic and soil moisture responses to gap formation in coastal Douglas-fir forests. Can J For Res 32(2):332–343. https://doi.org/10.1139/X01-200
Gray AN, Spies TA, Pabst RJ (2012) Canopy gaps affect long-term patterns of tree growth and mortality in mature and old-growth forests in the Pacific Northwest. For Ecol Manag 281:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.06.035
Harantová L, Mudrák O, Kohout P, Elhottová D, Frouz J, Baldrian P (2017) Development of microbial community during primary succession in areas degraded by mining activities. Land Degrad Dev 28(8):2574–2584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2817
Hart S, Stark J, Davidson E, Firestone M, Weaver R, Angle S, Bottomley P, Bezdiecek D, Smith S, Tabatabai A (1994) Microbiological and biochemical properties. In: Hart S (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 985–1017
He W, Wu FZ, Yang WQ, Tan B, Zhao YY, Wu QQ, He M (2016a) Lignin degradation in foliar litter of two shrub species from the gap center to the closed canopy in an alpine fir forest. Ecosystems 19(1):115–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-015-9921-6
He W, Wu FZ, Yang WQ, Zhang DJ, Xu ZF, Tan B, Zhao YY, Justine MF (2016b) Gap locations influence the release of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in two shrub foliar litter in an alpine fir forest. Sci Rep UK 6:11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22014
Jackson ML (1958) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River Inc,Englewood Cliffs
Kivlin SN, Winston GC, Goulden ML, Treseder KK (2014) Environmental filtering affects soil fungal community composition more than dispersal limitation at regional scales. Fungal Ecol 12:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2014.04.004
Langarica-Fuentes A, Zafar U, Heyworth A, Brown T, Fox G, Robson GD (2014) Fungal succession in an in-vessel composting system characterized using 454 pyrosequencing. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 88(2):296–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12293
Mallik AU, Kreutzweiser DP, Spalvieri CM (2014) Forest regeneration in gaps seven years after partial harvesting in riparian buffers of boreal mixedwood streams. For Ecol Manag 312:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.10.015
Mandarano AH, Giloteaux L, Keller BA, Levine SM, Hanson MR (2018) Eukaryotes in the gut microbiota in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. PeerJ 6:18. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4282
Muscolo A, Sidari M, Mercurio R (2007) Influence of gap size on organic matter decomposition, microbial biomass and nutrient cycle in Calabrian pine (Pinus laricio, Poiret) stands. For Ecol Manag 242(2-3):412–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2007.01.058
Muscolo A, Bagnato S, Sidari M, Mercurio R (2014) A review of the roles of forest canopy gaps. J For Res 25(4):725–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-014-0521-7
Newman MEJ (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103(23):8577–8582. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601602103
Nguyen NH, Song Z, Bates ST, Branco S, Tedersoo L, Menke J, Schilling JS, Kennedy PG (2016) FUNGuild: an open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol 20:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.06.006
Peltoniemi K, Laiho R, Juottonen H, Kiikkila O, Makiranta P, Minkkinen K, Pennanen T, Penttila T, Sarjala T, Tuittila ES, Tuomivirta T, Fritze H (2015) Microbial ecology in a future climate: effects of temperature and moisture on microbial communities of two boreal fens. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiv062
Ritter E, Dalsgaard L, Einhorn KS (2005) Light, temperature and soil moisture regimes following gap formation in a semi-natural beech-dominated forest in Denmark. For Ecol Manag 206(1-3):15–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.08.011
Sariyildiz T (2008) Effects of gap-size classes on long-term litter decomposition rates of beech, oak and chestnut species at high elevations in Northeast Turkey. Ecosystems 11(6):841–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-008-9164-x
Schliemann SA, Bockheim JG (2014) Influence of gap size on carbon and nitrogen biogeochemical cycling in Northern hardwood forests of the Upper Peninsula, Michigan. Plant Soil 377(1-2):323–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-2005-5
Schoch CL, Sung GH, Lopez-Giraldez F, Townsend JP, Miadlikowska J, Hofstetter V, Robbertse B, Matheny PB, Kauff F, Wang Z, Gueidan C, Andrie RM, Trippe K, Ciufetti LM, Wynns A, Fraker E, Hodkinson BP, Bonito G, Groenewald JZ, Arzanlou M, de Hoog GS, Crous PW, Hewitt D, Pfister DH, Peterson K, Gryzenhout M, Wingfield MJ, Aptroot A, Suh SO, Blackwell M, Hillis DM, Griffith GW, Castlebury LA, Rossman AY, Lumbsch HT, Lucking R, Budel B, Rauhut A, Diederich P, Ertz D, Geiser DM, Hosaka K, Inderbitzin P, Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B, Mostert L, O’Donnell K, Sipman H, Rogers JD, Shoemaker RA, Sugiyama J, Summerbell RC, Untereiner W, Johnston PR, Stenroos S, Zuccaro A, Dyer PS, Crittenden PD, Cole MS, Hansen K, Trappe JM, Yahr R, Lutzoni F, Spatafora JW (2009) The Ascomycota tree of life: a phylum-wide phylogeny clarifies the origin and evolution of fundamental reproductive and ecological traits. Syst Biol 58(2):224-239 https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syp020
She W, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Qin S, Feng W, Sun Y, Zheng J, Wu B (2018) Resource availability drives responses of soil microbial communities to short-term precipitation and nitrogen addition in a desert shrubland. Front Microbiol 9:186. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00186
Singh J, Raghubanshi A, Singh R, Srivastava S (1989) Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna. Nature 338(6215):499–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/338499a0
Stanford G, Carter JN, Simpson EC, Schwaninger DE (1973) Nitrate determination by a modified conway microdiffusion method. J Assoc Offic Ana Chem 56(6):1365–1368
Urbanová M, Šnajdr J, Baldrian P (2015) Composition of fungal and bacterial communities in forest litter and soil is largely determined by dominant trees. Soil Biol Biochem 84:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.02.011
Watkinson SC, Boddy L, Money N (2015) The fungi. In: Academic Press,Cambriadge,Massachusetts,UK
Xu JX, Xue L, Su ZY (2016) Impacts of forest gaps on soil properties after a severe ice storm in a Cunninghamia lanceolata stand. Pedosphere 26(3):408–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1002-0160(15)60053-4
Yang YG, Geng YQ, Zhou HJ, Zhao GL, Wang L (2017) Effects of gaps in the forest canopy on soil microbial communities and enzyme activity in a Chinese pine forest. Pedobiologia 61:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2017.03.001
Yulin Y, Xianwei L, Yigui Z, Yunke L (2014) Effects of gap thinning on growth and diversity of a cypress plantation in the hilly region of central Sichuan. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 19(19):922–928 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1145.2014.05004
Zhang Q, Zak JC (1995) Effects of gap size on litter decomposition and microbial activity in a subtropical forest. Ecology 76(7):2196–2204
Zhang ZQ, Zhou X, Tian L, Ma LN, Luo SS, Zhang JF, Li XJ, Tian CJ (2017) Fungal communities in ancient peatlands developed from different periods in the Sanjiang Plain. China PLoS One 12(12):16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187575
Zhang HF, Wang LL, Liu HM, Zhao JN, Li G, Wang H, Lai X, Li J, Xiu WM, Yang DL (2018) Nitrogen deposition combined with elevated precipitation is conducive to maintaining the stability of the soil fungal diversity on the Stipa baicalensis steppe. Soil Biol Biochem 117:135–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.11.004
Zhou JZ, Deng Y, Zhang P, Xue K, Liang YT, Van Nostrand JD, Yang YF, He ZL, Wu LY, Stahl DA, Hazen TC, Tiedje JM, Arkin AP (2014) Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. P Natl Acad Sci USA 111(9):E836–E845. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1324044111
Zhu J-j, Matsuzaki T, Lee F-q, Gonda Y (2003) Effect of gap size created by thinning on seedling emergency, survival and establishment in a coastal pine forest. For Ecol Manag 182(1-3):339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(3)00094-X
Žifčáková L, Větrovský T, Howe A, Baldrian P (2016) Microbial activity in forest soil reflects the changes in ecosystem properties between summer and winter. Environ Microbiol 18(1):288–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13026
Funding
This study was funded by German Government Loans for Sichuan Forestry Sustainable Management (G1403083), a Pillar Project of the “12th” Five-Year Plan for China (2011BAC09B05), and a Project of the Sichuan Provincial Education Department (No. 18ZB305)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL and XwL designed the study. YS, HY, XL, MG, and YH performed the experiments. DL, YS, HY, XjL, and MG analyzed the data. XzL improved the manuscript, and DL wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 584 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Li, X., Su, Y. et al. Forest gaps influence fungal community assembly in a weeping cypress forest. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 3215–3224 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-09582-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-09582-1