Abstract
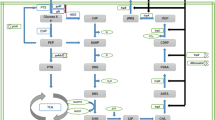
L-tryptophan (L-trp) is a biosynthetic precursor of various bioactive components with pharmaceutical interest. The development of an efficient L-trp production strain using targeted molecular engineering approaches is challenging due to the requirement of several precursors and the complex regulations of the pathways involved. In this study, we present a rationally engineered and genetically stable L-trp overproducing Escherichia coli strain. The streamlined strain E. coli S028 is able to efficiently produce 34–40 g/L of L-trp with a yield of 0.15 g L-trp/g glucose and a productivity of 0.60 g/L/h in fed-batch fermentations. The titer and productivity of L-trp achieved are over twice as much as those reported so far for rationally developed L-trp producers. In addition, for the first time, both intracellular and extracellular concentrations of L-trp and the key metabolites in a L-trp hyperproducer strain were measured with an automated fast-sampling unit which is connected to a well-controlled bioreactor. The time series metabolic analysis gives valuable information about the regulation of L-trp synthesis in a highly productive strain and reveals targets for further improvement. Among others, it was found that L-trp and the byproduct glutamate (L-glu) accumulated to an extremely high level in the cell initially whereas the intracellular concentrations of glutamine (L-gln) stayed at a relatively low level throughout the fermentation. The metabolic analysis suggests that (a) the engineered serine biosynthesis pathway was able to effectively synthesize the substrate serine (intracellular concentration > 8 mM) for L-trp production, while (b) the substrate L-gln with an intracellular concentration of 0.8–1.2 mM seems to limit the biosynthesis of L-trp, even though L-glu was overproduced intra- and extracellularly. Thus, an increased availability of glutamine synthetase which catalyzes L-glu conversion to L-gln and an overexpression of the L-trp exporter gene could be important targets for further strain improvement.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba S, Imanaka T, Tsunekawa H (1980) Enhancement of tryptophan production by Escherichia coli as an application of genetic engineering. Biotechnol Lett 2:525–530
Al-Rabiee R, Lee EJ, Grant GA (1996) The mechanism of velocity modulated allosteric regulation in D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. Cross-linking adjacent regulatory domains with engineered disulfides mimics effector binding. J Biol Chem 271:13013–13017
Azuma S, Tsunekawa H, Okabe M, Okamoto R, Aiba S (1993) Hyper-production of L-tryptophan via fermentation with crystallization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:471–476
Baker TI, Crawford IP (1966) Anthranilate synthetase. Partial purification and some kinetic studies on the enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 241:5577–5584
Bennett BD, Yuan J, Kimball EH, Rabinowitz JD (2008) Absolute quantitation of intracellular metabolite concentrations by an isotope ratio-based approach. Nat Protoc 3:1299–1311
Bennett BD, Kimball EH, Gao M, Osterhout R, Van Dien SJ, Rabinowitz JD (2009) Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli. Nat Chem Biol 5:593–599
Berry A (1996) Improving production of aromatic compounds in Escherichia coli by metabolic engineering. Trends Biotechnol 14:250–256
Bertrand K, Yanofsky C (1976) Regulation of transcription termination in leader region of tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli involves tryptophan or its metabolic product. J Mol Biol 103:339–349
Bommareddy RR, Chen Z, Rappert S, Zeng A-P (2014) A de novo NADPH generation pathway for improving lysine production of Corynebacterium glutamicum by rational design of the coenzyme specificity of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Metab Eng 25:30–37
Caligiuri MG, Bauerle R (1991a) Identification of amino acid residues involved in feedback regulation of the anthranilate synthase complex from Salmonella typhimurium. Evidence for an amino-terminal regulatory site*. J Biol Chem 266:8328–8335
Caligiuri MG, Bauerle R (1991b) Subunit communication in the anthranilate synthase complex from Salmonella typhimurium. Science 252:1845–1848
Chan EC, Tsai HL, Chen SL, Mou DG (1993) Amplification of the tryptophan operon gene in Escherichia coli chromosome to increase L-tryptophan biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:301–305
Cheng L, Wang J, Xu Q, Xie X, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Chen N (2012) Effect of feeding strategy on l-tryptophan production by recombinant Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol:1–10
Cheng L, Wang J, Xu Q, Zhao C, Shen Z, Xie X, Chen N (2013) Strategy for pH control and pH feedback-controlled substrate feeding for high-level production of L-tryptophan by Escherichia coli. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:883–890
da Luz JA, Hans E, Zeng A (2014) Automated fast filtration and on-filter quenching improve the intracellular metabolite analysis of microorganisms. Eng Life Sci 14:135–142
DeFeyter RC, Pittard J (1986) Purification and properties of shikimate kinase II from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 165:331–333
Dodge TC, Gerstner JM (2002) Optimization of the glucose feed rate profile for the production of tryptophan from recombinant E coli. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77:1238–1245
Fang M, Zhang C, Yang S, Cui J, Jiang P, Lou K, Wachi M, Xing X (2015) High crude violacein production from glucose by Escherichia coli engineered with interactive control of tryptophan pathway and violacein biosynthetic pathway. Microb Cell Factories 14:8
Fang M, Wang T, Zhang C, Bai J, Zheng X, Zhao X, Lou C, Xing X (2016) Intermediate-sensor assisted push-pull strategy and its application in heterologous deoxyviolacein production in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 33:41–51
Ger YM, Chen SL, Chiang HJ, Shiuan D (1994) A single ser-180 mutation desensitizes feedback inhibition of the phenylalanine-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Biochem 116:986–990
Grant GA, Schuller DJ, Banaszak LJ (1996) A model for the regulation of D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, a Vmax-type allosteric enzyme. Protein Sci 5:34–41
Gu P, Yang F, Kang J, Wang Q, Qi Q (2012) One-step of tryptophan attenuator inactivation and promoter swapping to improve the production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Factories 11:30
Gu P, Yang F, Li F, Liang Q, Qi Q (2013) Knocking out analysis of tryptophan permeases in Escherichia coli for improving L-tryptophan production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:6677–6683
Hasegawa S, Suda M, Uematsu K, Natsuma Y, Hiraga K, Jojima T, Inui M, Yukawa H (2013) Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for high-yield L-valine production under oxygen deprivation conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1250–1257
Heermann R, Zeppenfeld T, Jung K (2008) Simple generation of site-directed point mutations in the Escherichia coli chromosome using red®/ET® recombination. Microb Cell Factories 7:14
Ikeda M (2006) Towards bacterial strains overproducing L-tryptophan and other aromatics by metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:615–626
Ikeda M, Katsumata R (1999) Hyperproduction of tryptophan by Corynebacterium glutamicum with the modified pentose phosphate pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2497–2502
Ikeda M, Nakanishi K, Kino K, Katsumata R (1994) Fermentative production of tryptophan by a stable recombinant strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum with a modified serine-biosynthetic pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:674–678
Kind S, Neubauer S, Becker J, Yamamoto M, Völkert M, Gv A, Zelder O, Wittmann C (2014) From zero to hero - production of bio-based nylon from renewable resources using engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Metab Eng 25:113–123
Kumamoto AA, Miller WG, Gunsalus RP (1987) Escherichia coli Tryptophan repressor binds multiple sites within the aroH and trp operators. Genes Dev 1:556–564
Kwak JH, Hong KW, Lee SH, Hong JH, Lee SY (1999) Identification of amino acid residues involved in feedback inhibition of the anthranilate synthase in Escherichia coli. J Biochem Mol Biol 32:20–24
Lawley B, Pittard AJ (1994) Regulation of aroL expression by TyrR protein and trp repressor in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 176:6921–6930
Lee KH, Park JH, Kim TY, Kim HU, Lee SY (2007) Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for L-threonine production. Mol Syst Biol 3:149
Liu Q, Cheng Y, Xie X, Xu Q, Chen N (2012a) Modification of tryptophan transport system and its impact on production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 114:549–554
Liu Q, Cheng Y, Xu Q, Xie X, Chen N (2012b) Effects of aroP gene disruption on L-tryptophan fermentation. Front Chem Sci Eng 6:158–162
Luo W, Huang J, Zhu X, Huang L, Cai J, Xu Z (2013) Enhanced production of l-tryptophan with glucose feeding and surfactant addition and related metabolic flux redistribution in the recombinant Escherichia coli. Food Sci Biotechnol 22:207–214
McCandliss RJ, Poling MD, Herrmann KM (1978) 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase. Purification and molecular characterization of the phenylalanine-sensitive isoenzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 253:4259–4265
Nagaraja P, Yathirajan HS, Vasantha RA (2003) Highly sensitive reaction of tryptophan with p-phenylenediamine. Anal Biochem 312:157–161
O’Neil MJ (2006) The Merck index. An encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals, 14th edn. Merck, Whitehouse Station, p 1682
Park JH, Lee KH, Kim TY, Lee SY (2007) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of L-valine based on transcriptome analysis and in silico gene knockout simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:7797–7802
Park JH, Oh JE, Lee KH, Kim JY, Lee SY (2012) Rational Design of Escherichia coli for L -isoleucine production. ACS Synth Biol 1:532–540
Pearson JT, Dabrowski MJ, Kung I, Atkins WM (2005) The central loop of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase is flexible and functionally passive. Arch Biochem Biophys 436:397–405
Platt T (1981) Termination of transcription and its regulation in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Cell 24:10–23
Porter RJ, Mulder RT, Joyce PR, Luty SE (2005) Tryptophan and tyrosine availability and response to antidepressant treatment in major depression. J Affect Disord 86:129–134
Ray JM, Yanofsky C, Bauerle R (1988) Mutational analysis of the catalytic and feedback sites of the tryptophan-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:5500–5506
Rodrigues AL, Trachtmann N, Becker J, Lohanatha AF, Blotenberg J, Bolten CJ, Korneli C, de Souza L, André O, Porto LM, Sprenger GA, Wittmann C (2013) Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of the antitumor drugs violacein and deoxyviolacein. Metab Eng 20:29–41
Rodriguez A, Martínez JA, Flores N, Escalante A, Gosset G, Bolivar F (2014) Engineering Escherichia coli to overproduce aromatic amino acids and derived compounds. Microb Cell Factories 13:126
Schoner R, Herrmann KM (1976) 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase. Purification, properties, and kinetics of the tyrosine-sensitive isoenzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 251:5440–5447
Schuster S (1999) Detection of elementary flux modes in biochemical networks: a promising tool for pathway analysis and metabolic engineering. Trends Biotechnol 17:53–60
Shen T, Liu Q, Xie X, Xu Q, Chen N (2012) Improved production of tryptophan in genetically engineered Escherichia coli with TktA and PpsA overexpression. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:605219
Wang J, Cheng L, Wang J, Liu Q, Shen T, Chen N (2013) Genetic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance production of l-tryptophan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7587–7596
Yu D, Ellis HM, Lee E, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Court DL (2000) An efficient recombination system for chromosome engineering in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:5978–5983
Zhang Y, Muyrers JPP, Rientjes J, Stewart AF (2003) Phage annealing proteins promote oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis in Escherichia coli and mouse ES cells. BMC Mol Biol 4:1
Zhao ZJ, Zou C, Zhu YX, Dai J, Chen S, Wu D, Wu J, Chen J (2011) Development of L-tryptophan production strains by defined genetic modification in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1921–1929
Zhao Z, Chen S, Wu D, Wu J, Chen J (2012) Effect of gene knockouts of L-tryptophan uptake system on the production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 47:340–344
Zurawski G, Elseviers D, Stauffer GV, Yanofsky C (1978) Translational control of transcription termination at the attenuator of the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 75:5988–5992
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Donald L. Court for providing us with the strain DY330 and helpful information. We also thank Mr. Wen Liu for helping with sample analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 882 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Zeng, AP. Rational design and metabolic analysis of Escherichia coli for effective production of L-tryptophan at high concentration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 559–568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7772-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7772-5