Abstract
Background
The clinical presentation of congenital portosystemic shunt is variable and gastrointestinal bleeding is an uncommon presentation.
Objective
To describe the imaging features of congenital portosystemic shunt as it presented in 11 children with (n = 6) and without gastrointestinal bleeding (n = 5).
Materials and methods
We performed a retrospective study on a clinical and imaging dataset of 11 children diagnosed with congenital portosystemic shunt.
Results
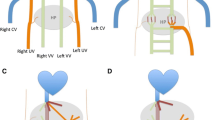
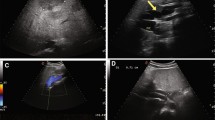
A total of 11 children with congenital portosystemic shunt were included in this study, 7 with extrahepatic portosystemic shunts and 4 with intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Six patients with gastrointestinal bleeding had an extrahepatic portosystemic shunt, and the imaging results showed that the shunts originated from the splenomesenteric junction (n = 5) or splenic vein (n = 1) and connected to the internal iliac vein. Among the five cases of congenital portosystemic shunt without gastrointestinal bleeding, one case was an extrahepatic portosystemic shunt and the other four were intrahepatic portosystemic shunts.
Conclusion
Most congenital portosystemic shunt patients with gastrointestinal bleeding had a shunt that drained portal blood into the iliac vein via an inferior mesenteric vein. This type of shunt was uncommon, but the concomitant rate of gastrointestinal bleeding with this type of shunt was high.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guerin F, Blanc T, Gauthier F et al (2012) Congenital portosystemic vascular malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg 21:233–244
Abernethy J, Banks J (1793) Account of two instances of uncommon formation, in the viscera of the human body. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 83:59–66
Lautz TB, Tantemsapya N, Rowell E et al (2011) Management and classification of type II congenital portosystemic shunts. J Pediatr Surg 46:308–314
Morgan G, Superina R (1994) Congenital absence of the portal vein: two cases and a proposed classification system for portasystemic vascular anomalies. J Pediatr Surg 29:1239–1241
Park JH, Cha SH, Han JK et al (1990) Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt. AJR Am J Roentgenol 155:527–528
Kobayashi N, Niwa T, Kirikoshi H et al (2010) Clinical classification of congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatol Res 40:585–593
Alonso-Gamarra E, Parron M, Perez A et al (2011) Clinical and radiologic manifestations of congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts: a comprehensive review. Radiographics 31:707–722
Kasahara M, Nakagawa A, Sakamoto S et al (2009) Living donor liver transplantation for congenital absence of the portal vein with situs inversus. Liver Transpl 15:1641–1643
McElhinney DB, Marx GR, Newburger JW (2011) Congenital portosystemic venous connections and other abdominal venous abnormalities in patients with polysplenia and functionally univentricular heart disease: a case series and literature review. Congenit Heart Dis 6:28–40
Singhal A, Srivastava A, Goyal N et al (2009) Successful living donor liver transplant in a child with Abernethy malformation with biliary atresia, ventricular septal defect and intrapulmonary shunting. Pediatr Transplant 13:1041–1047
Sokollik C, Bandsma RH, Gana JC et al (2013) Congenital portosystemic shunt: characterization of a multisystem disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 56:675–681
Niwa T, Aida N, Tachibana K et al (2002) Congenital absence of the portal vein: clinical and radiologic findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:681–686
Grazioli L, Alberti D, Olivetti L et al (2000) Congenital absence of portal vein with nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Eur Radiol 10:820–825
Gadodia A, Sharma R, Kandpal H et al (2011) Congenital absence of portal vein with large inferior mesenteric-caval shunt. Trop Gastroenterol 32:223–226
Arana E, Marti-Bonmati L, Martinez V et al (1997) Portal vein absence and nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver with giant inferior mesenteric vein. Abdom Imaging 22:506–508
Horiguchi Y, Kitano T, Takagawa H et al (1988) A large inferior mesenteric-caval shunt via the internal iliac vein. Gastroenterol Jpn 23:684–687
Charre L, Roggen F, Lemaire J et al (2004) Hematochezia and congenital extrahepatic portocaval shunt with absent portal vein: successful treatment by liver transplantation. Transplantation 78:1404–1406
Alomari AI, Chaudry G, Fox VL et al (2009) Atypical manifestation of patent ductus venosus in a child: intervening against a paradoxical presentation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:537–542
Komatsu S, Nagino M, Hayakawa N et al (1995) Congenital absence of portal venous system associated with a large inferior mesenteric-caval shunt: a case report. Hepatogastroenterology 42:286–290
Kim MJ, Ko JS, Seo JK et al (2012) Clinical features of congenital portosystemic shunt in children. Eur J Pediatr 171:395–400
Scalabre A, Gorincour G, Hery G et al (2012) Evolution of congenital malformations of the umbilical-portal-hepatic venous system. J Pediatr Surg 47:1490–1495
Franchi-Abella S, Branchereau S, Lambert V et al (2010) Complications of congenital portosystemic shunts in children: therapeutic options and outcomes. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 51:322–330
Blanc T, Guerin F, Franchi-Abella S et al (2014) Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: a new anatomical classification correlated with surgical strategy. Ann Surg 260:188–198
Bernard O, Franchi-Abella S, Branchereau S et al (2012) Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: recognition, evaluation, and management. Semin Liver Dis 32:273–287
Bruckheimer E, Dagan T, Atar E et al (2013) Staged transcatheter treatment of portal hypoplasia and congenital portosystemic shunts in children. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36:1580–1585
Barsky MF, Rankin RN, Wall WJ et al (1989) Patent ductus venosus: problems in assessment and management. Can J Surg 32:271–275
Lv Z, Xiao X, Zheng J et al (2009) Modified Soave procedure for the treatment of vascular malformations involving anorectum and sigmoid colon. J Pediatr Surg 44:2359–2363
Konstas AA, Digumarthy SR, Avery LL et al (2011) Congenital portosystemic shunts: imaging findings and clinical presentations in 11 patients. Eur J Radiol 80:175–181
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Medical Guide Project, Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology, China (Grant No. 134119a4100 to Z. Qiao), and the National Key Clinical Specialty Construction Programs of China (2014-2016).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Y., Zhu, H., Chen, J. et al. Congenital portosystemic shunts with and without gastrointestinal bleeding – case series. Pediatr Radiol 45, 1964–1971 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-015-3417-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-015-3417-6