Abstract
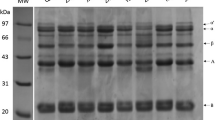
The gel properties and secondary structures of soybean protein isolate/egg white composite gels with different blend ratios and protein concentrations were investigated in this paper. The hardness, springiness and water-holding capacity of composite gels were all increased with the increase in the protein concentrations. When total protein concentration was above 0.03 g mL−1, the soybean protein isolate/egg white proteins blended in ratio of 1:1 showed higher enhancement in springiness and water-holding capacity. The hardness and storage modulus of gels increased gradually with the increase in egg white in the composite gels. The content of α-helical structures of the gels were increased firstly and then decreased, whereas the content of β-sheet was increased gradually with the increase in egg white ratio. The tendencies of α-helical and β-sheet were in accordance with springiness and hardness of gels, respectively. The microstructure investigations showed that gels formed an even structure with less large particles at the soybean protein isolate/egg white ratio of 1:1, which was related to the higher springiness and water-holding capacity. The relationship between changes in the protein structure and the texture properties could be used to design product systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mine Y (1995) Recent advances in the understanding of egg white protein functionality. Trends Food Sci Technol 6(7):225–232
Badii F, Howell N (2006) Fish gelatin: structure, gelling properties and interaction with egg albumen proteins. Food Hydrocoll 20(5):630–640
Dawson P, Sheldon B, Ball H (1990) Effect of washing and adding spray-dried egg white to mechanically deboned chicken meat on the quality of cooked gels. Poult Sci 69(2):307–312
Kinsella JE (1979) Functional properties of soy proteins. J Am Oil Chem Soc 56(3):242–258
Gujral HS, Kaur A, Singh N, Sodhi NS (2002) Effect of liquid whole egg, fat and textured soy protein on the textural and cooking properties of raw and baked patties from goat meat. J Food Eng 53(4):377–385
Luo Y, Shen H, Pan D, Bu G (2008) Gel properties of surimi from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) as affected by heat treatment and soy protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll 22(8):1513–1519
Nielsen N (1985) Structure of soy proteins. New protein food 5:27–64
Catsimpoolas N, Meyer E (1970) Gelation phenomena of soybean globulins I. Protein–protein interactions. Cereal Chem 47:559–570
Hermansson A (1978) Physico-chemical aspects of soy prodeins structure formation. J Texture Stud 9(1–2):33–58
Utsumi S, Kinsella JE (1985) Forces involved in soy protein gelation: effects of various reagents on the formation, hardness and solubility of heat-induced gels made from 7S, 11S, and soy isolate. J Food Sci 50(5):1278–1282
Ma CY, Yiu S, Harwalkar V (1990) Rheological and structural properties of egg white/oat globulin co-gels. J Food Sci 55(1):99–102
Chronakis IS, Kasapis S (1993) Structural properties of single and mixed milk/soya proteins systems. Food Hydrocoll 7(6):459–478
Comfort S, Howell NK (2002) Gelation properties of soya and whey protein isolate mixtures. Food Hydrocoll 16(6):661–672
Matulis RJ, Mckeith FK, Sutherland JW, Brewer MS (1995) Sensory characteristics of frankfurters as affected by salt, fat, soy protein and carrageenan. J Food Sci 60(1):48–54
Jafarpour A, Hajiduon HA (2012) A comparative study on effect of egg white, soy protein isolate and potato starch on functional properties of common carp (cyprinus carpio) surimi gel. J Food process Technol 3(11):1–6
Liao A, Wu W (2013) Functional properties of soybean-egg white protein composite blends. Mod Food Sci Technol 29(7):1606–1610
Li F, Kong X, Zhang C, Hua Y (2011) Rheological properties and permeability of soy protein-stabilised emulsion gels made by acidification with glucono-δ-lactone. J Sci Food Agric 91(12):2186–2191
Tabilo-Munizaga G, Barbosa-Cánovas GV (2004) Color and textural parameters of pressurized and heat-treated surimi gels as affected by potato starch and egg white. Food Res Int 37(8):767–775
Salvador P, Toldrà M, Saguer E, Carretero C, Parés D (2009) Microstructure–function relationships of heat-induced gels of porcine haemoglobin. Food Hydrocoll 23(7):1654–1659
Maltais A, Remondetto GE, Subirade M (2008) Mechanisms involved in the formation and structure of soya protein cold-set gels: a molecular and supramolecular investigation. Food Hydrocoll 22(4):550–559
Creusot N, Wierenga PA, Laus MC, Giuseppin ML, Gruppen H (2011) Rheological properties of patatin gels compared with β-lactoglobulin, ovalbumin, and glycinin. J Sci Food Agric 91(2):253–261
Byler DM, Susi H (1986) Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers 25(3):469–487
Yamamoto F, Cunha R (2007) Acid gelation of gellan: effect of final pH and heat treatment conditions. Carbohydr polym 68(3):517–527
Renkema J, Lakemond CM, de Jongh HH, Gruppen H, van Vliet T (2000) The effect of pH on heat denaturation and gel forming properties of soy proteins. J Biotechnol 79(3):223–230
Renkema JM, van Vliet T (2002) Heat-induced gel formation by soy proteins at neutral pH. J Agric Food Chem 50(6):1569–1573
Hatta H, Kitabatake N, Doi E (1986) Turbidity and Hardness of a Heat-induced Gel of Hen Egg Ovalbumin (Food & Nutrition). Agric Biol Chem 50(8):2083–2089
Ziegler GR, Foegeding EA (1990) The gelation of proteins. Adv Food Nutr Res 34:203–298
Van Kleef F (1986) Thermally induced protein gelation: gelation and rheological characterization of highly concentrated ovalbumin and soybean protein gels. Biopolymers 25(1):31–59
Hashizume K, Nakamura N, Watanabe T (1975) Influence of ionic strength on conformation changes of soybean proteins caused by heating, and relationship of its conformation changes to gel formation. Agric Biol Chem 39:1339–1347
Liu ZS, Chang SK, Li LT, Tatsumi E (2004) Effect of selective thermal denaturation of soybean proteins on soymilk viscosity and tofu’s physical properties. Food Res Int 37(8):815–822
Powrie W, Nakai S (1985) Characteristics of edible fluids of animal origin: eggs. Food Chem 2:829–855
Powrie W, Nakai S, Stadelman W, Cotterill O (1986) Egg science and technology. Macmillan, London, pp 61–65
Clark A, Kavanagh G, Ross-Murphy S (2001) Globular protein gelation—theory and experiment. Food Hydrocoll 15(4):383–400
Petruccelli S, Anon M (1995) Thermal aggregation of soy protein isolates. J Agric Food Chem 43(12):3035–3041
Britten M, Giroux HJ (2001) Acid-induced gelation of whey protein polymers: effects of pH and calcium concentration during polymerization. Food Hydrocoll 15(4):609–617
Kohyama K, Murata M, Tani F, Sano Y, Doi E (1995) Effects of protein composition on gelation of mixtures containing soybean 7S and 11S globulins. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59(2):240–245
Utsumi S, Maruyama N, Satoh R, Adachi M (2002) Structure-function relationships of soybean proteins revealed by using recombinant systems. Enzyme Microb Technol 30(3):284–288
Margoshes B (1990) Correlation of protein sulfhydryls with the strength of heat-formed egg white gels. J Food Sci 55(6):1753
Furukawa T, Ohta S, Yamamoto A (1980) Texture-structure relationships in heat-induced soy protein gels. J Texture Stud 10(4):333–346
Yoo B, Figueiredo A, Rao M (1994) Rheological properties of mesquite seed gum in steady and dynamic shear. LWT-Food Sci Technol 27(2):151–157
Gu L, Wang M, zhou J (2013) Effects of protein interactions on properties and microstructure of zein–gliadin composite films. J Food Eng 119(2):288–298
Surewicz WK, Mantsch HH, Chapman D (1993) Determination of protein secondary structure by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: a critical assessment. Biochemistry 32(2):389–394
Herrero A, Cambero M, Ordóñez J, De la Hoz L, Carmona P (2008) Raman spectroscopy study of the structural effect of microbial transglutaminase on meat systems and its relationship with textural characteristics. Food Chem 109(1):25–32
Herrero AM, Carmona P, Cofrades S, Jiménez-Colmenero F (2008) Raman spectroscopic determination of structural changes in meat batters upon soy protein addition and heat treatment. Food Res Int 41(7):765–772
Turgeon SL, Beaulieu M (2001) Improvement and modification of whey protein gel texture using polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll 15(4):583–591
Alvarez MD, Fernández C, Olivares MD, Canet W (2012) A rheological characterisation of mashed potatoes enriched with soy protein isolate. Food Chem 133(4):1274–1282
Acknowledgments
This experimental study was financially supported by the National 863 Programs of China (2013AA102207), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP11222) and Excellent Doctoral Cultivation Foundation of Jiangnan University (JUDCF12001).
Conflict of interest
None.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Dong, Y., Niu, F. et al. Study on the gel properties and secondary structure of soybean protein isolate/egg white composite gels. Eur Food Res Technol 240, 367–378 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2336-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2336-3