Abstract
Rationale
Cocaine base paste (CBP) is an illegal drug of abuse usually consumed by adolescents in a socio-economically vulnerable situation. Repeated drug use targets key brain circuits disrupting the processes that underlie emotions and cognition. At the basis of such neuroadaptations lie changes in the expression of immediate-early genes (IEGs). Nevertheless, changes in transcriptional regulation associated with CBP consumption remain unknown.
Objectives
We aimed to describe behavioral phenotype related to locomotion, anxiety-like behavior, and memory of CBP-injected mice and to study IEGs expression after an abstinence period.
Methods
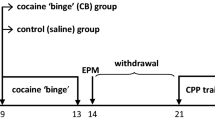
Five-week-old female CF-1 mice were i.p. injected daily with vehicle or CBP (40 mg/kg) for 10 days and subjected to a 10-day period of abstinence. Open field and novel object recognition tests were used to evaluate locomotion and anxiety-like behaviors and recognition memory, respectively, during chronic administration and after abstinence. After abstinence, prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAc) were isolated and gene expression analysis performed through real-time PCR.
Results
We found an increase in locomotion and anxiety-like behavior during CBP administration and after the abstinence period. Furthermore, the CBP group showed impaired recognition memory after abstinence. Egr1, FosB, ΔFosB, Arc, Bdnf, and TrkB expression was upregulated in CBP-injected mice in NAc and FosB, ΔFosB, Arc, and Npas4 expression was downregulated in mPFC. We generated an anxiety score and found positive and negative correlations with IEGs expression in NAc and mPFC, respectively.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that chronic CBP exposure induced alterations in anxiety-like behavior and recognition memory. These changes were accompanied by altered IEGs expression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen SL (2003) Trajectories of brain development: point of vulnerability or window of opportunity? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(03)00005-8
Barat SA, Abdel-Rahman MS (1998) Kinetics and rat locomotor activity following cocaine and lidocaine administration. J Appl Toxicol 18:227–232
Barry DN, Coogan AN, Commins S (2016) The time course of systems consolidation of spatial memory from recent to remote retention: a comparison of the immediate early genes Zif268, c-Fos and Arc. Neurobiol Learn Mem 128:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2015.12.010
Belluscio LM, Berardino BG, Ferroni NM, Ceruti JM, Cánepa ET (2014) Early protein malnutrition negatively impacts physical growth and neurological reflexes and evokes anxiety and depressive-like behaviors. Physiol Behav 129:237–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.02.051
Berardino BG, Fesser EA, Cánepa ET (2017) Perinatal protein malnutrition alters expression of miRNA biogenesis genes Xpo5 and Ago2 in mice brain. Neurosci Lett 647:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.03.012
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2006) Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study “recognition memory”. Nat Protoc 1:1306–1311. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.205
Brasesco M, Canay R, Legisa AC de Psen A-G (2010) Consumo de Paco y otras sustancias psicoactivas en niños y niñas en situación de calle
Briand LA, Gross JP, Robinson TE (2008) Impaired object recognition following prolonged withdrawal from extended-access cocaine self-administration. Neuroscience 155:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.004
Buffalari DM, Baldwin CK, See RE (2012) Treatment of cocaine withdrawal anxiety with guanfacine: relationships to cocaine intake and reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 223:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2705-1
Caffino L, Giannotti G, Mottarlini F, Racagni G, Fumagalli F (2017) Developmental exposure to cocaine dynamically dysregulates cortical Arc/Arg3.1 modulation in response to a challenge. Neurotox Res 31:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9683-8
Casey BJ, Jones RM (2010) Neurobiology of the adolescent brain and behavior: implications for substance use disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49:1189–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.08.017
Chambers RA, Taylor JR, Potenza MN (2003) Developmental neurocircuitry of motivation in adolescence: a critical period of addiction vulnerability. Am J Psychiatry 160:1041–1052. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.160.6.1041
Cheval H, Chagneau C, Levasseur G, Veyrac A, Faucon-Biguet N, Laroche S, Davis S (2012) Distinctive features of Egr transcription factor regulation and DNA binding activity in CA1 of the hippocampus in synaptic plasticity and consolidation and reconsolidation of fear memory. Hippocampus 22:631–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20926
Coffey SF, Dansky BS, Carrigan MH, Brady KT (2000) Acute and protracted cocaine abstinence in an outpatient population: a prospective study of mood, sleep and withdrawal symptoms. Drug Alcohol Depend 59:277–286
Comisión Interamericana para el Control del Abuso de Drogas OEA (2019) Informe del consumo de drogas en las Américas
Craige CP, Lewandowski S, Kirby LG, Unterwald EM (2015) Dorsal raphe 5-HT2C receptor and GABA networks regulate anxiety produced by cocaine withdrawal. Neuropharmacology 93:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.01.021
Crombag HS, Jedynak JP, Redmond K, Robinson TE, Hope BT (2002) Locomotor sensitization to cocaine is associated with increased Fos expression in the accumbens, but not in the caudate. Behav Brain Res 136:455–462
Dalley JW, Lääne K, Pena Y, Theobald DEH, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Attentional and motivational deficits in rats withdrawn from intravenous self-administration of cocaine or heroin. Psychopharmacology 182:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0107-3
de Drogas-Sedronar OA (2014) El consumo de pasta base-paco en la Argentina
de Oliveira Citó Mdo C , da Silva FCC, Silva MIG, et al (2012) Reversal of cocaine withdrawal-induced anxiety by ondansetron, buspirone and propranolol. Behav Brain Res 231:116–123. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.01.056
El Rawas R, Klement S, Kummer KK et al (2012) Brain regions associated with the acquisition of conditioned place preference for cocaine vs. social interaction. Front Behav Neurosci 6:63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00063
Ennaceur A (2010) One-trial object recognition in rats and mice: methodological and theoretical issues. Behav Brain Res 215:244–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.12.036
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59
Epele ME (2010) Memory, forgetting, and economic crisis: drug use and social fragmentation in an Argentine shantytown. Med Anthropol Q 24:22–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1548-1387.2010.01083.x
Epele ME (2011) New toxics, new poverty: a social understanding of the freebase cocaine/paco in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Subst Use Misuse 46:1468–1476. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2011.576745
Ferrando R, Bocchino S, Barrachina A et al (2009) Alteraciones de la perfusión cerebral en consumidores activos de pasta base de cocaína *. Rev Psiquiatr Urug 2009;73(1)51-62. Alteraciones 73:51–62
Ferrando R, Barrachina A, Silveira A et al (2011) Cambios del flujo sanguíneo cerebral en consumidores activos de pasta base y chorhidrato de cocaína. Alasbimn J 14
Franklin, Keith BJ and Paxinos G (2007) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd Editio. Academic Press, London
Gao P, Limpens JHW, Spijker S, Vanderschuren LJMJ, Voorn P (2015) Stable immediate early gene expression patterns in medial prefrontal cortex and striatum after long-term cocaine self-administration. Addict Biol n/a-n/a 22:354–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12330
Garavan H, Hester R (2007) The role of cognitive control in cocaine dependence. Neuropsychol Rev 17:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-007-9034-x
García-Pardo MP, De la Rubia Ortí JE, Aguilar Calpe MA (2017) Differential effects of MDMA and cocaine on inhibitory avoidance and object recognition tests in rodents. Neurobiol Learn Mem 146:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2017.10.013
Ghasemzadeh MB, Windham LK, Lake RW, Acker CJ, Kalivas PW (2009) Cocaine activates Homer1 immediate early gene transcription in the mesocorticolimbic circuit: differential regulation by dopamine and glutamate signaling. Synapse 63:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20577
Gräff J, Woldemichael BT, Berchtold D, Dewarrat G, Mansuy IM (2012) Dynamic histone marks in the hippocampus and cortex facilitate memory consolidation. Nat Commun 3:991. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1997
Grubbs F (1969) Procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples. Technometrics 11:1–21
Hall C, Ballachey E (1932) A study of the rat’s behavior in a field. A contribution to method in comparative psychology. Univ Calif Publ Psychol 6:1–12
Hulvershorn LA, Hummer TA, Fukunaga R et al (2015) Neural activation during risky decision-making in youth at high risk for substance use disorders. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 233:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.05.007
Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (2006) Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:565–598. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.113009
Jeri FR, Sanchez C, Del Pozo T, Fernandez M (1992) The syndrome of coca paste. J Psychoactive Drugs 24:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.1992.10471637
Jovanovski D, Erb S, Zakzanis KK (2005) Neurocognitive deficits in cocaine users: a quantitative review of the evidence. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 27:189–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803390490515694
Junta Internacional de Fiscalización de Estupefacientes. UN (2018) Informe anual
Kim D, Kim S-K (2012) Comparing patterns of component loadings: principal component analysis (PCA) versus independent component analysis (ICA) in analyzing multivariate non-normal data. Behav Res Methods 44:1239–1243. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-012-0193-1
Li X, Wolf ME (2015) Multiple faces of BDNF in cocaine addiction. Behav Brain Res 279:240–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.11.018
Li Y, Ge S, Li N, Chen L, Zhang S, Wang J, Wu H, Wang X, Wang X (2016) NMDA and dopamine D1 receptors within NAc-shell regulate IEG proteins expression in reward circuit during cocaine memory reconsolidation. Neuroscience 315:45–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.11.063
Lizasoain I, Moro M, Lorenzo P (2002) Cocaína, aspectos farmacológicos. Adicciones 14:57–64
López-Hill X, Prieto JP, Meikle MN, Urbanavicius J, Abin-Carriquiry JA, Prunell G, Umpiérrez E, Scorza MC (2011) Coca-paste seized samples characterization: chemical analysis, stimulating effect in rats and relevance of caffeine as a major adulterant. Behav Brain Res 221:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.005
Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR, Heim C (2009) Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:434–445. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2639
Manning CE, Williams ES, Robison AJ (2017) Reward network immediate early gene expression in mood disorders. Front Behav Neurosci 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00077
Meikle MN, Urbanavicius G, Prunell J et al (2009) Primer estudio pre-clínico de la acción de pasta base de cocaína en el sistema nervioso central. Rev Psiquiatr Urug 76:26–36
Meikle MN, Prieto JP, Urbanavicius J, López X, Abin-Carriquiry JA, Prunell G, Scorza MC (2013) Anti-aggressive effect elicited by coca-paste in isolation-induced aggression of male rats: influence of accumbal dopamine and cortical serotonin. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 110:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2013.07.010
Minatohara K, Akiyoshi M, Okuno H (2015) Role of immediate-early genes in synaptic plasticity and neuronal ensembles underlying the memory trace. Front Mol Neurosci 8:78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00078
Muñiz JA, Prieto JP, González B, Sosa MH, Cadet JL, Scorza C, Urbano FJ, Bisagno V (2017) Cocaine and caffeine effects on the conditioned place preference test: concomitant changes on early genes within the mouse prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. Front Behav Neurosci 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00200
Nestler EJ (2001) Molecular basis of long-term plasticity underlying addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/35053570
Pascale A, Hynes M, Cumsille F, Bares C (2014) Use of cocaine base paste in South America: a review of epidemiological, medical and toxicological issues
Paus T, Keshavan M, Giedd JN (2008) Why do many psychiatric disorders emerge during adolescence? Nat Rev Neurosci 9:947–957. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2513
Pedraz M, Araos P, García-Marchena N et al (2015) Sex differences in psychiatric comorbidity and plasma biomarkers for cocaine addiction in abstinent cocaine-addicted subjects in outpatient settings. Front Psychiatry 6:17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00017
Pelloux Y, Costentin J, Duterte-Boucher D (2009) Anxiety increases the place conditioning induced by cocaine in rats. Behav Brain Res 197:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.08.029
Pérez J (2003) Clínica de la adicción a pasta base de cocaína. Rev Chil Neuropsiq 41:55–63
Perrine SA, Sheikh IS, Nwaneshiudu CA, Schroeder JA, Unterwald EM (2008) Withdrawal from chronic administration of cocaine decreases delta opioid receptor signaling and increases anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in the rat. Neuropharmacology 54:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.10.007
Placenza FM, Rajabi H, Stewart J (2008) Effects of chronic buprenorphine treatment on levels of nucleus accumbens glutamate and on the expression of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats. Psychopharmacology 200:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1210-z
Prieto JP, Galvalisi M, López-Hill X, Meikle MN, Abin-Carriquiry JA, Scorza C (2015) Caffeine enhances and accelerates the expression of sensitization induced by coca paste indicating its relevance as a main adulterant. Am J Addict 24:475–481. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12245
Romo-Avilés N, Camarotti AC, Tarragona A, Touris C (2015) Doing gender in a toxic world. Women and freebase cocaine in the City of Buenos Aires (Argentina). Subst Use Misuse 50:557–565. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2014.991404
Roy É, Jutras-Aswad D, Bertrand K, Dufour M, Perreault M, Laverdière É, Bene-Tchaleu F, Bruneau J (2015) Anxiety, mood disorders and injection risk behaviors among cocaine users: results from the COSMO study. Am J Addict 24:654–660. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12286
Ruijter JM, Ramakers C, Hoogaars WMH, Karlen Y, Bakker O, van den Hoff MJB, Moorman AFM (2009) Amplification efficiency: linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp045
Salas-Ramirez KY, Frankfurt M, Alexander A, Luine VN, Friedman E (2010) Prenatal cocaine exposure increases anxiety, impairs cognitive function and increases dendritic spine density in adult rats: influence of sex. Neuroscience 169:1287–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.04.067
Simon P, Dupuis R, Costentin J (1994) Thigmotaxis as an index of anxiety in mice. Influence of dopaminergic transmissions. Behav Brain Res 61:59–64
Slaker M, Churchill L, Todd RP, Blacktop JM, Zuloaga DG, Raber J, Darling RA, Brown TE, Sorg BA (2015) Removal of perineuronal nets in the medial prefrontal cortex impairs the acquisition and reconsolidation of a cocaine-induced conditioned place preference memory. J Neurosci 35:4190–4202. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3592-14.2015
Spronk DB, van Wel JHP, Ramaekers JG, Verkes RJ (2013) Characterizing the cognitive effects of cocaine: a comprehensive review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1838–1859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.07.003
Thomas GM, Huganir RL (2004) MAPK cascade signalling and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1346
Triaca J, Cardeillac V, Idiarte Borda C (2009) Características de los primeros usuarios que consultaron en el Centro de Referencia Nacional de la Red Drogas “ Portal Amarillo .” Rev Psiquiatr del Uruguay 73:37–48
Valzachi MC, Teodorov E, Marcourakis T, Bailey A, Camarini R (2013) Enhancement of behavioral sensitization, anxiety-like behavior, and hippocampal and frontal cortical CREB levels following cocaine abstinence in mice exposed to cocaine during adolescence. PLoS One 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078317
Veyrac A, Besnard A, Caboche J, et al (2014) The transcription factor Zif268/Egr1, brain plasticity, and memory. In: Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 1st edn. Academic Press London, pp 89–129
Volkow ND, Morales M (2015) The brain on drugs: from reward to addiction. Cell 162:712–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.046
Volkow ND, Wang G-J, Fowler JS, Tomasi D (2012) Addiction circuitry in the human brain. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 52:321–336. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134625
Vonmoos M, Hulka LM, Preller KH, Jenni D, Baumgartner MR, Stohler R, Bolla KI, Quednow BB (2013) Cognitive dysfunctions in recreational and dependent cocaine users: role of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, craving and early age at onset. Br J Psychiatry 203:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.112.118091
Vonmoos M, Hulka LM, Preller KH, Minder F, Baumgartner MR, Quednow BB (2014) Cognitive impairment in cocaine users is drug-induced but partially reversible: evidence from a longitudinal study. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:2200–2210. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.71
Wei W, Coelho CM, Li X, Marek R, Yan S, Anderson S, Meyers D, Mukherjee C, Sbardella G, Castellano S, Milite C, Rotili D, Mai A, Cole PA, Sah P, Kobor MS, Bredy TW (2012) p300/CBP-associated factor selectively regulates the extinction of conditioned fear. J Neurosci 32:11930–11941. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0178-12.2012
Yamamoto DJ, Nelson AM, Mandt BH, Larson GA, Rorabaugh JM, Ng CMC, Barcomb KM, Richards TL, Allen RM, Zahniser NR (2013) Rats classified as low or high cocaine locomotor responders: a unique model involving striatal dopamine transporters that predicts cocaine addiction-like behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1738–1753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.07.002
Ye L, Allen WE, Thompson KR, Tian Q, Hsueh B, Ramakrishnan C, Wang AC, Jennings JH, Adhikari A, Halpern CH, Witten IB, Barth AL, Luo L, McNab JA, Deisseroth K (2016) Wiring and molecular features of prefrontal ensembles representing distinct experiences. Cell 165:1776–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.010
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Secretaría de Programación para la Prevención de la Drogadicción (SEDRONAR, Argentina) for supplying CBP seized samples. We would also like to thank the staff at the Bioterio Central, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, UBA, for their assistance with mice.
Conflict of interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was supported by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, Argentina (Grant PICT-2013-0653), and Universidad de Buenos Aires (Grant UBACYT20020130100011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors BB, EF, and LB undertook all behavioral and biochemical studies and assisted in the interpretation of the results. OG designed the statistical analysis and prepared the figures and tables. EC initiated and designed the study, collected and analyzed the experimental results, and wrote the final draft of the manuscript. NP provided critical revision of the manuscript. BB and NP contributed to the final manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experiments were performed in accordance with local regulations and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide of the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH publication 80-23/96) and were previously approved by the Ethical Committee (CICUAL) of the Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires (Protocol No 0054/16).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1243 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berardino, B.G., Fesser, E.A., Belluscio, L.M. et al. Effects of cocaine base paste on anxiety-like behavior and immediate-early gene expression in nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex of female mice. Psychopharmacology 236, 3525–3539 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05321-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05321-0