Abstract
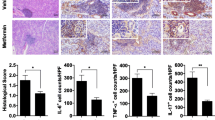
Chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is characterized by the reduced secretion of exocrine glands, suggesting strategies targeting inflammation to be a potential option for SS therapy. Bufotalin, an active constituent of Bufadienolides, exerts potent antitumor effects with unknown effects on autoimmune diseases including SS. This study aims to investigate whether bufotalin possesses therapeutic potentials to SS and the underlying mechanisms. The experimental Sjögren’s syndrome (ESS) murine model was constructed by SG-immunization and murine naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured under Th17 polarization conditions with or without low doses of bufotalin treatment. Saliva flow rate was measured, and flow cytometry was applied to analyze T cell subpopulations. ELISA was conducted to determine the levels of targeted inflammatory cytokines. Bufotalin-treated ESS mice showed higher saliva flow rates, lower serum levels of autoantibodies (anti-M3R and anti-SSA IgG), lower serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as lower Th17 cell population from spleens and cervical lymph nodes. Additionally, in vitro study showed that bufotalin inhibits Th17 polarization and secretion of cytokines IL-17 and IFN-γ. Bufotalin at a low dose significantly ameliorates ESS development, possibly via inhibiting pro-inflammatory Th17 population and secretion of inflammatory cytokines during ESS pathogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson TC 3rd, Fox RI, Frisman DM, Howell FV (1983) Immunohistologic analysis of lymphoid infiltrates in primary Sjogren's syndrome using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 130:203–208
Alunno A, Carubbi F, Bartoloni E, Bistoni O, Caterbi S, Cipriani P, Giacomelli R, Gerli R (2014) Unmasking the pathogenic role of IL-17 axis in primary Sjogren's syndrome: a new era for therapeutic targeting? Autoimmun Rev 13:1167–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.022
Blokland SLM, Flessa CM, van Roon JAG, Mavragani CP (2019) Emerging roles for chemokines and cytokines as orchestrators of immunopathology in Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key438
Casciola-Rosen LA, Anhalt G, Rosen A (1994) Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med 179:1317–1330. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.179.4.1317
Cheng CS, Wang J, Chen J, Kuo KT, Tang J, Gao H, Chen L, Chen Z, Meng Z (2019) New therapeutic aspects of steroidal cardiac glycosides: the anticancer properties of Huachansu and its main active constituent Bufalin. Cancer Cell Int 19:92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0806-1
Christodoulou MI, Kapsogeorgou EK, Moutsopoulos HM (2010) Characteristics of the minor salivary gland infiltrates in Sjogren's syndrome. J Autoimmun 34:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.10.004
Ciccia F, Guggino G, Rizzo A, Ferrante A, Raimondo S, Giardina A, Dieli F, Campisi G, Alessandro R, Triolo G (2012) Potential involvement of IL-22 and IL-22-producing cells in the inflamed salivary glands of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 71:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2011.154013
de Paiva CS, Rocha EM (2015) Sjogren syndrome: what and where are we looking for? Curr Opin Ophthalmol 26:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1097/ICU.0000000000000208
Eriksson P, Andersson C, Ekerfelt C, Ernerudh J, Skogh T (2004) Relationship between serum levels of IL-18 and IgG1 in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and healthy controls. Clin Exp Immunol 137:617–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02562.x
Fox RI, Adamson TC 3rd, Fong S, Young C, Howell FV (1983) Characterization of the phenotype and function of lymphocytes infiltrating the salivary gland in patients with primary Sjogren syndrome. Diagn Immunol 1:233–239
Fox RI, Robinson CA, Curd JG, Kozin F, Howell FV (1986) Sjogren's syndrome. Proposed criteria for classification. Arthritis Rheum 29:577–585
Gowda RM, Cohen RA, Khan IA (2003) Toad venom poisoning: resemblance to digoxin toxicity and therapeutic implications. Heart 89:e14. https://doi.org/10.1136/heart.89.4.e14
Haneji N, Nakamura T, Takio K, Yanagi K, Higashiyama H, Saito I, Noji S, Sugino H, Hayashi Y (1997) Identification of alpha-fodrin as a candidate autoantigen in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Science 276:604–607
Johnson AC, Davison LM, Giltiay NV, Vareechon C, Li X, Jorgensen TN (2012) Lack of T cells in Act1-deficient mice results in elevated IgM-specific autoantibodies but reduced lupus-like disease. Eur J Immunol 42:1695–1705. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201142238
Jonsson R, Vogelsang P, Volchenkov R, Espinosa A, Wahren-Herlenius M, Appel S (2011) The complexity of Sjogren's syndrome: novel aspects on pathogenesis. Immunol Lett 141:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2011.06.007
Karabiyik A, Peck AB, Nguyen CQ (2013) The important role of T cells and receptor expression in Sjogren's syndrome. Scand J Immunol 78:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.12079
Katsifis GE, Rekka S, Moutsopoulos NM, Pillemer S, Wahl SM (2009) Systemic and local interleukin-17 and linked cytokines associated with Sjogren's syndrome immunopathogenesis. Am J Pathol 175:1167–1177. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2009.090319
Lin X, Song JX, Shaw PC, Ng TB, Wong RN, Sze SC, Tong Y, Lee KF, Zhang KY (2011) An autoimmunized mouse model recapitulates key features in the pathogenesis of Sjogren's syndrome. Int Immunol 23:613–624. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxr066
Lin X et al (2015) Th17 cells play a critical role in the development of experimental Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204584
Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B (2012) CD4(+)T cells: differentiation and functions. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:925135. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/925135
Ma XC, Zhang BJ, Xin XL, Huang SS, Deng S, Zhang HL, Shu XH, Diao YP, Cui J (2009) Simultaneous quantification of seven major bufadienolides in three traditional Chinese medicinal preparations of Chansu by HPLC-DAD. Nat Prod Commun 4:179–184
Nguyen CQ, Yin H, Lee BH, Carcamo WC, Chiorini JA, Peck AB (2010) Pathogenic effect of interleukin-17A in induction of Sjogren's syndrome-like disease using adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R220. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3207
Pan Z et al (2019) Bufotalin induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in human malignant melanoma A375 cells. Oncol Rep. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7032
Sandhya P, Kurien BT, Danda D, Scofield RH (2017) Update on pathogenesis of Sjogren's syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rev 13:5–22. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573397112666160714164149
Singh N, Cohen PL (2012) The T cell in Sjogren's syndrome: force majeure, not spectateur. J Autoimmun 39:229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2012.05.019
Tsuboi H, Matsumoto I, Hagiwara S, Hirota T, Takahashi H, Ebe H, Yokosawa M, Hagiya C, Asashima H, Takai C, Miki H, Umeda N, Kondo Y, Ogishima H, Suzuki T, Hirata S, Saito K, Tanaka Y, Horai Y, Nakamura H, Kawakami A, Sumida T (2015) Efficacy and safety of abatacept for patients with Sjogren's syndrome associated with rheumatoid arthritis: rheumatoid arthritis with orencia trial toward Sjogren's syndrome Endocrinopathy (ROSE) trial-an open-label, one-year, prospective study-interim analysis of 32 patients for 24 weeks. Mod Rheumatol 25:187–193. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2014.951144
Verstappen GM, Kroese FGM, Bootsma H (2019) T cells in primary Sjogren's syndrome: targets for early intervention. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez004
Vivino FB (2017) Sjogren's syndrome: clinical aspects. Clin Immunol 182:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2017.04.005
Waiwut P, Inujima A, Inoue H, Saiki I, Sakurai H (2012) Bufotalin sensitizes death receptor-induced apoptosis via bid- and STAT1-dependent pathways. Int J Oncol 40:203–208. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2011.1182
Wei WL, Hou JJ, Wang X, Yu Y, Li HJ, Li ZW, Feng ZJ, Qu H, Wu WY, Guo DA (2019) Venenum bufonis: an overview of its traditional use, natural product chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology. J Ethnopharmacol 237:215–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.042
Xiao F, Lin X, Tian J, Wang X, Chen Q, Rui K, Ma J, Wang S, Wang Q, Wang X, Liu D, Sun L, Lu L (2017) Proteasome inhibition suppresses Th17 cell generation and ameliorates autoimmune development in experimental Sjogren's syndrome. Cell Mol Immunol 14:924–934. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.8
Yang M et al (2010) Novel function of B cell-activating factor in the induction of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells. J Immunol 184:3321–3325. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0902551
Yang M, Deng J, Liu Y, Ko KH, Wang X, Jiao Z, Wang S, Hua Z, Sun L, Srivastava G, Lau CS, Cao X, Lu L (2012) IL-10-producing regulatory B10 cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing Th17 cell generation. Am J Pathol 180:2375–2385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.03.010
Yoshimi R, Ueda A, Ozato K, Ishigatsubo Y (2012) Clinical and pathological roles of Ro/SSA autoantibody system. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:606195. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/606195
Zhang Y, Liu RB, Cao Q, Fan KQ, Huang LJ, Yu JS, Gao ZJ, Huang T, Zhong JY, Mao XT, Wang F, Xiao P, Zhao Y, Feng XH, Li YY, Jin J (2019) USP16-mediated deubiquitination of calcineurin a controls peripheral T cell maintenance. J Clin Invest 129:2856–2871. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI123801
Zhu YR, Xu Y, Fang JF, Zhou F, Deng XW, Zhang YQ (2014) Bufotalin-induced apoptosis in osteoblastoma cells is associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.077
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Huang and Guangxia Yang contributed equally to this work. Guangxia Yang, Jing Fei, and Yingyi Wu conceptualized the study and conducted the literature review for all databases. Yang Huang, Guangxia Yang, Jing Fei, and Yingyi Wu performed all statistical analyses. Juzhen Yan drafted the paper. Juzhen Yan provided useful additional intellectual content into the draft and contributed to the writing of the final version of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Yang, G., Fei, J. et al. Bufotalin ameliorates experimental Sjögren’s syndrome development by inhibiting Th17 generation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 1977–1985 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01817-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01817-1