Abstract
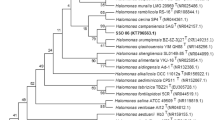
A short-rod-shaped moderately halophilic bacterium, designated CUG 00002T, was isolated from the sediment of Xiaochaidan salt lake in Qinghai Province, China by using R2A medium. The cells were Gram-staining negative, aerobic, forming creamy and circular colonies with diameters of 2–3 mm on R2A agar when incubated at 30 °C for 3 days. 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic analysis indicated that strain CUG 00002T belonged to the genus Halomonas in the class Gammaproteobacteria, showing highest sequence similarity of 97.1 and 96.7 % to Halomonas mongoliensis Z-7009T (=DSM 17332=VKM B2353) and Halomonas shengliensis SL014B-85T (=CGMCC 1.6444T=LMG 23897T), respectively. The predominant isoprenoid quinone was ubiquinone-9 (Q9), and the major fatty acids were C16:0, summed feature 3 (comprising C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c) and summed feature 8 (comprising C18:1 ω7c or C18:1 ω6c). The genomic DNA G+C content of strain CUG 00002T was 61.8 mol%. The above characteristics were consistent with the placement of the organism in the genus Halomonas. The level of DNA–DNA relatedness between CUG 00002T and its most closely related strain H. mongoliensis Z-7009T was 41.0 ± 1.6 %. Based on the results of phenotypic, phylogenetic and biochemical analyses, strain CUG 00002T represents a novel species of the genus Halomonas, for which the name Halomonas xiaochaidanensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is CUG 00002T (=CCTCC AB 2014152T=KCTC 42685T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow G, Feltham RKA (2004) Cowan and Steel’s manual for the identification of medical bacteria. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Berendes F, Gottschalk G, Heine-Dobbernack E, Moore E, Tindall B (1996) Halomonas desiderata sp. nov, a new alkaliphilic, halotolerant and denitrifying bacterium isolated from a municipal sewage works. Syst Appl Microbiol 19:158–167
Collins M, Jones D (1980) Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycans based on 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid. J Appl Bacteriol 48:459–470
Deng S, Dong H, Lv G, Jiang H, Yu B, Bishop ME (2010) Microbial dolomite precipitation using sulfate reducing and halophilic bacteria: results from Qinghai Lake, Tibetan Plateau, NW China. Chem Geol 278:151–159
Dong H, Zhang G, Jiang H, Yu B, Chapman LR, Lucas CR, Fields MW (2006) Microbial diversity in sediments of saline Qinghai Lake, China: linking geochemical controls to microbial ecology. Microbial Ecol 51:65–82
Dussault H (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70:484
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Franzmann P, Burton H, McMeekin T (1987) Halomonas subglaciescola, a new species of halotolerant bacteria isolated from Antarctica. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:27–34
Franzmann PD, Wehmeyer U, Stackebrandt E (1988) Halomonadaceae fam. nov., a new family of the class Proteobacteria to accommodate the genera Halomonas and Deleya. Syst Appl Microbiol 11:16–19
Fredrickson JK et al (2008) Protein oxidation: key to bacterial desiccation resistance? ISME J 2:393–403
Guan T-W, Xiao J, Zhao K, Luo X-X, Zhang X-P, Zhang L-L (2010) Halomonas xinjiangensis sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:349–352
Jiang H, Dong H, Zhang G, Yu B, Chapman LR, Fields MW (2006) Microbial diversity in water and sediment of Lake Chaka, an athalassohaline lake in northwestern China. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3832–3845
Jiang H, Dong H, Yu B, Liu X, Li Y, Ji S, Zhang CL (2007) Microbial response to salinity change in Lake Chaka, a hypersaline lake on Tibetan plateau. Environ Microbiol 9:2603–2621
Jiang H, Dong H, Yu B, Lv G, Deng S, Berzins N, Dai M (2009) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in Qinghai Lake, Northwestern China. Geomicrobiol J 26:199–211
Kaye JZ, Márquez MC, Ventosa A, Baross JA (2004) Halomonas neptunia sp. nov., Halomonas sulfidaeris sp. nov., Halomonas axialensis sp. nov. and Halomonas hydrothermalis sp. nov.: halophilic bacteria isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal-vent environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:499–511
Kaye JZ, Sylvan JB, Edwards KJ, Baross JA (2011) Halomonas and Marinobacter ecotypes from hydrothermal vent, subseafloor and deep-sea environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 75:123–133
Kim JM, Le NT, Chung BS, Park JH, Bae J-W, Madsen EL, Jeon CO (2008) Influence of soil components on the biodegradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and o-, m-, and p-xylenes by the newly isolated bacterium Pseudoxanthomonas spadix BD-a59. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7313–7320
Kim O-S et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Komagata K, Suzuki K-I (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:1
Lim J-M, Yoon J-H, Lee J-C, Jeon CO, Park D-J, Sung C, Kim C-J (2004) Halomonas koreensis sp. nov., a novel moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a solar saltern in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2037–2042
Liu W-Y, Wang J, Yuan M (2011) Halomonas aidingensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from Aiding salt lake in Xinjiang, China. Anton Leeuw Int J G 99:663–670
Liu B-B et al (2013) Halalkalicoccus paucihalophilus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from Lop Nur region in Xinjiang, northwest of China. Antonie Leeuw Int J G 103:1007–1014
Llamas I, Del Moral A, Martínez-Checa F, Arco Y, Arias S, Quesada E (2006) Halomonas maura is a physiologically versatile bacterium of both ecological and biotechnological interest. Anton Leeuw Int J G 89:395–403
Martínez-Cánovas MJ, Quesada E, Llamas I, Béjar V (2004) Halomonas ventosae sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, denitrifying, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:733–737
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin D, Collins M, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Nguyen HTT, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2012) ‘Candidatus Halomonas phosphatis’, a novel polyphosphate-accumulating organism in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Environ Microbiol 14:2826–2837
Peng Y-L, He P-Q, Huang X-H, Cong B-L, Lin X-Z, Liu C-L, Tang X-X (2009) Isolation, identification and study of Halomonas sp. YD-7 from deep-sea hydrothermal vent in Indian Ocean. Adv Mar Sci 3:009
Quillaguamán J, Hatti-Kaul R, Mattiasson B, Alvarez MT, Delgado O (2004) Halomonas boliviensis sp. nov., an alkalitolerant, moderate halophile isolated from soil around a Bolivian hypersaline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:721–725
Raina J-B, Tapiolas D, Willis BL, Bourne DG (2009) Coral-associated bacteria and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3492–3501
Reasoner D, Geldreich E (1985) A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1–7
Romano I, Lama L, Orlando P, Nicolaus B, Giordano A, Gambacorta A (2007) Halomonas sinaiensis sp. nov., a novel halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake inside Ras Muhammad Park, Egypt. Extremophiles 11:789–796
Sabet S, Diallo L, Hays L, Jung W, Dillon JG (2009) Characterization of halophiles isolated from solar salterns in Baja California, Mexico. Extremophiles 13:643–656
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI technical note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Sorokin DY, Berben T, Melton ED, Overmars L, Vavourakis CD, Muyzer G (2014) Microbial diversity and biogeochemical cycling in soda lakes. Extremophiles 18:791–809
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Vreeland R, Litchfield C, Martin E, Elliot E (1980) Halomonas elongata, a new genus and species of extremely salt-tolerant bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:485–495
Wang Y-N, Cai H, Chi C-Q, Lu A-H, Lin X-G, Jiang Z-F, Wu X-L (2007a) Halomonas shengliensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, denitrifying, crude-oil-utilizing bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1222–1226
Wang Y-N, Cai H, Yu S-L, Wang Z-Y, Liu J, Wu X-L (2007b) Halomonas gudaonensis sp. nov., isolated from a saline soil contaminated by crude oil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:911–915
Williams S, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington E, Sneath P, Sackin M (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129:1743–1813
Williams S, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, (1989) Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943. In: Holt JG (ed) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 1st edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 2452–2492
Wu QL, Zwart G, Schauer M, Kamst-van Agterveld MP, Hahn MW (2006) Bacterioplankton community composition along a salinity gradient of sixteen high-mountain lakes located on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5478–5485
Wu QL, Chatzinotas A, Wang J, Boenigk J (2009) Genetic diversity of eukaryotic plankton assemblages in eastern Tibetan lakes differing by their salinity and altitude. Microbiol Ecol 58:569–581
Xu P et al (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family ‘Oxalobacteraceae’isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153
Yan L-J, Zheng M-P, Yuan Z-J (2014) Influence of climate change on salt lakes in Qinghai Province and their mineral resources exploitation in the past forty years: a case study of Xiao Qaidam Lake. Miner Depos 33:921–929
Yoon J-H, Lee K-C, Kho YH, Kang KH, Kim C-J, Park Y-H (2002) Halomonas alimentaria sp. nov., isolated from jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:123–130
Zhang G, Tian J, Jiang N, Guo X, Wang Y, Dong X (2008) Methanogen community in Zoige wetland of Tibetan plateau and phenotypic characterization of a dominant uncultured methanogen cluster ZC-I. Environ Microbiol 10:1850–1860
Zheng M (1997) An introduction to saline Lakes on the Qinghai—Tibet plateau, vol 76. Springer, New York
Zumft WG (1992) The denitrifying bacteria. In: Balows A, Truper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes: a handbook on the biology of bacteria: ecophysiology, isolation, identification, applications, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 554–582
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Rüdiger Pukall (DSMZ, Germany) and Dr. Yuguang Zhou_(CGMCC, China) for their kind providing reference type strains. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41422208), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M582298), State Key Laboratory of Biogeology and Environmental Geology, China University of Geosciences (No. GBL11201), and the Fundamental Research Funds for National University, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). W-J Li was also supported by the Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Guangdong Province Higher Vocational Colleges and Schools Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain CUG 00002T is KU221020.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Zhang, G., Xian, W. et al. Halomonas xiaochaidanensis sp. nov., isolated from a salt lake sediment. Arch Microbiol 198, 761–766 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1235-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1235-3