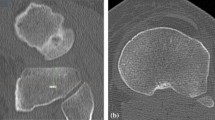
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the suitability of positioning an asymmetrical tibial tray relative to the posterior tibial edge and to analyse the relationship between the posterior fit and tibial rotation after computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty (TKA). It was hypothesised that an asymmetrical tray would adjust to the posterior border of the tibial plateau with proper tibial rotation.
Methods
Ninety-three consecutive knees underwent total knee arthroplasty using a Persona fixed-bearing system (63 varus deformities and 30 valgus deformities) and a 3-month follow-up CT scan. An independent examiner measured different variables: the femoral angle between the clinical epicondylar axis and the posterior condylar line of the femoral component, the tibial angle between the posterior borders of the tibial tray and the tibial plateau, and the tibial rotation with respect to the femoral component. These measurements were also compared between varus and valgus subgroups.
Results
For the varus and valgus subgroups, the mean postoperative femoral angle was 2.1º ± 1.2º and 2.5º ± 1.0º, respectively (n.s.). The mean posterior fitting angle of the tibial tray was 0.1º ± 2.4º and 1.4º ± 3.2º for the varus and valgus subgroups, respectively, with a significant difference between groups (p = 0.03). The tibial rotations with respect to the femoral component for the varus and valgus groups were 0.9º ± 3.3º and 2.2º ± 3.1º of external rotation, respectively (n.s.).
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that fitting an asymmetrical tibial tray to the posterior border of the tibial plateau could optimise tibial rotation. The posterior border was considered to be a reliable and easily identifiable landmark for proper tibial rotation and coverage during a primary TKA.
Level of evidence
IV


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelnasser MK, Adi MM, Elnaggar AA, Tarabichi S (2019) Internal rotation of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty can lead to extension deficit. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05695-w
Aglietti P, Sensi L, Cuomo P, Ciardullo A (2008) Rotational position of femoral and tibial components in TKA using the femoral transepicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(11):2751–2755
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Baldini A, Indelli PF, De Luca L, Cerulli Mariani PP, Marcucci M (2013) Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty: the anterior tibial cortex is a reliable landmark. Joints 1(4):155–160
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:46–55
Bellemans J, Robijns F et al (2005) The influence of tibial slope on maximal flexion after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(3):193–196
Beranger JS, Dujardin D, Taburet JF, Boisrenoult P, Steltzlen C, Beaufils P, Pujol N (2018) Is distal femoral torsion the same in both of a patient’s legs? Morphometric CT study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 104(4):481–484
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Berhouet J, Beaufils P, Boisrenoult P, Frasca D, Pujol N (2011) Rotational positioning of the tibial tray in total knee arthroplasty: a CT evaluation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97(7):699–704
Bizzozero P, Bulaid Y, Flecher X, Ollivier M, Parratte S, Argenson JN (2018) Morphometric tibial implant decreases posterior overhang rate and improves clinical outcomes: results of a prospective, matched controlled study. J Arthroplasty 33(9):2804–2809
Bonnin MP, Saffarini M, Shepherd D, Bossard N, Dantony E (2016) Oversizing the tibial component in TKAs: incidence, consequences and risk factors. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(8):2532–2540
Bourne RB, Finlay JB (1986) The influence of tibial component intramedullary stems and implant-cortex contact on the strain distribution of the proximal tibia following total knee arthroplasty. An in vitro study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 208:95–99
Clary C, Aram L, Deffenbaugh D, Heldreth M (2014) Tibial base design and patient morphology affecting tibial coverage and rotational alignment after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):3012–3018
Cobb JP, Dixon H, Dandachli W, Iranpour F (2008) The anatomical tibial axis: reliable rotational orientation in knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(8):1032–1038
Coughlin KM, Incavo SJ, Churchill DL, Beynnon BD (2003) Tibial axis and patellar position relative to the femoral epicondylar axis during squatting. J Arthroplasty 18(8):1048–1055
Dai Y, Scuderi GR, Bischoff JE, Bertin K, Tarabichi S, Rajgopal A (2014) Anatomic tibial component design can increase tibial coverage and rotational alignment accuracy: a comparison of six contemporary designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):2911–2923
Engh GA (2003) The difficult knee: severe varus and valgus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 416:58–63
Hartel MJ, Loosli Y, Delfosse D, Diel P, Thali M, Ross S, Kohl S, Eggli S (2014) The influence of tibial morphology on the design of an anatomical tibial baseplate for TKA. Knee 21(2):415–419
Hernandez-Vaquero D, Noriega-Fernandez A, Fernandez-Carreira JM, Fernandez-Simon JM, Llorens de los Rios J (2014) Computer-assisted surgery improves rotational positioning of the femoral component but not the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):3127–3134
Heyse TJ, El-Zayat BF, De Corte R, Chevalier Y, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Labey L (2018) Internal femoral component malrotation in TKA significantly alters tibiofemoral kinematics. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26(6):1767–1775
Huddleston JI, Scott RD, Wimberley DW (2005) Determination of neutral tibial rotational alignment in rotating platform TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:101–106
Indelli PF, Graceffa A, Baldini A, Payne B, Pipino G, Marcucci M (2015) Relationship between tibial baseplate design and rotational alignment landmarks in primary total knee arthroplasty. Arthritis 2015:189294
Indelli PF, Graceffa A, Marcucci M, Baldini A (2016) Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Ann Transl Med 4(1):3
Kang KT, Kwon SK, Son J, Kwon OR, Lee JS, Koh YG (2018) The increase in posterior tibial slope provides a positive biomechanical effect in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26(10):3188–3195
Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS (2017) Clinical outcome of medial pivot compared with press-fit condylar sigma cruciate-retaining mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 32(10):3016–3023
Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS, Park SD (2014) The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop 38(2):379–385
Kuriyama S, Ishikawa M, Furu M, Ito H, Matsuda S (2014) Malrotated tibial component increases medial collateral ligament tension in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res 32(12):1658–1666
Martin S, Saurez A, Ismaily S, Ashfaq K, Noble P, Incavo SJ (2014) Maximizing tibial coverage is detrimental to proper rotational alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(1):121–125
Matziolis G, Krocker D, Weiss U, Tohtz S, Perka C (2007) A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Three-dimensional evaluation of implant alignment and rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(2):236–243
Michaut M, Beaufils P, Galaud B, Abadie P, Boisrenoult P, Fallet L (2008) Rotational alignment of femoral component with computed-assisted surgery (CAS) during total knee arthroplasty. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 94(6):580–584
Saffarini M, Nover L, Tandogan R, Becker R, Moser LB, Hirschmann MT, Indelli PF (2019) The original Akagi line is the most reliable: a systematic review of landmarks for rotational alignment of the tibial component in TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(4):1018–1027
Staats K, Wannmacher T, Weihs V, Koller U, Kubista B, Windhager R (2019) Modern cemented total knee arthroplasty design shows a higher incidence of radiolucent lines compared to its predecessor. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(4):1148–1155
Stulberg SD, Goyal N (2015) Which tibial tray design achieves maximum coverage and ideal rotation: anatomic, symmetric, or asymmetric? An MRI-based study. J Arthroplasty 30(10):1839–1841
Wernecke GC, Harris IA, Houang MT, Seeto BG, Chen DB, MacDessi SJ (2012) Comparison of tibial bone coverage of 6 knee prostheses: a magnetic resonance imaging study with controlled rotation. J Orthop Surg 20(2):143–147
Whiteside LA, Saeki K, Mihalko WM (2000) Functional medial ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 380(11):45–57
Woiczinski M, Kistler M, Schröder C, Braun C, Weber P, Müller PE, Jansson V, Steinbrück A (2019) TKA design-integrated trochlea groove rotation reduces patellofemoral pressure. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(5):1680–1692
Yoshioka Y, Siu D, Cooke DV (1987) The anatomical and functional axis of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:873–880
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Centre Hospitalier de Versailles (No. 12014).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okazaki, Y., Pujol, N. The use of an asymmetrical tibial tray in TKA optimises tibial rotation when fitted to the posterior tibial plateau border. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28, 3821–3826 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-05858-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-05858-0