Abstract
Purpose
Blood blister-like aneurysms (BBAs) are rare vascular lesions and a therapeutic challenge. Although endovascular treatment of BBA is a promising approach, the optimal treatment remains controversial. The purpose of this study was to compare the safety and efficacy of stent-assisted coiling (SAC) and flow diverter (FD) in the management of BBAs.
Methods
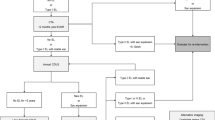
A proportion meta-analysis including a published series of BBAs treated with endovascular approaches from 2009 to 2020 including SAC and FD was performed by searching English language studies via MEDLINE and EMBASE.
Results
The 32 studies included 16 based on SAC and 16 involving FD. The long-term complete occlusion rate was higher in FD (89.26%, 95% confidence interval, CI 82.93–94.26%, I2 = 14.42%) than in SAC (70.26%, 95% CI 56.79–82.13%, I2 = 70.60%). The rate of aneurysm recanalization was lower in FD (4.54%, 95% CI 1.72–8.16%, I2 = 0%) than in SAC (25.38%, 95% CI 14.44–38.19%, I2 = 67.31%). Rates of mortality, favorable functional outcome, procedural complications, and rebleeding showed no differences between the two procedures.
Conclusion
In a proportion meta-analysis comparing FD with SAC, the FD was associated with more favorable angiographic outcomes but similar complications and clinical outcomes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakagawa F, Kobayashi S, Takemae T, Sugita K. Aneurysms protruding from the dorsal wall of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 1986;65:303–8.
Peitz GW, Sy CA, Grandhi R. Endovascular treatment of blister aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42:E12.
Lee BH, Kim BM, Park MS, Park SI, Chung EC, Suh SH, Choi CS, Won YS, Yu IK. Reconstructive endovascular treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 2009;110:431–6.
Ishikawa T, Nakamura N, Houkin K, Nomura M. Pathological consideration of a “blister-like” aneurysm at the superior wall of the internal carotid artery: case report. Neurosurgery. 1997;40:403–5; discussion 405-6.
Scanarini M, Mingrino S, Giordano R, Baroni A. Histological and ultrastructural study of intracranial saccular aneurysmal wall. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1978;43:171–82.
El Dib R, Nascimento Junior P, Kapoor A. An alternative approach to deal with the absence of clinical trials: a proportional meta-analysis of case series studies. Acta Cir Bras. 2013;28:870–6.
Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, Bazerbachi F. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2018;23:60–3.
Murad MH. Clinical Practice Guidelines: A Primer on Development and Dissemination. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92:423–33.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1.
Park JH, Jang W, Kim SW, Lee J, Lim YS, Cho CG, Park SW, Kim BH. The Clinical Manifestations and Chest Computed Tomography Findings of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients in China: A Proportion Meta-Analysis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;13:95–105.
Abu-Zidan FM, Abbas AK, Hefny AF. Clinical “case series”: a concept analysis. Afr Health Sci. 2012;12:557–62.
Roy D, Milot G, Raymond J. Endovascular treatment of unruptured aneurysms. Stroke. 2001;32:1998–2004.
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke. 1988;19:604–7.
Jennett B, Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet. 1975;1:480–4.
NHLBI. Quality assessment tool for case series studies.. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools. Accessed 28 Apr 2021.
Neyeloff JL, Fuchs SC, Moreira LB. Meta-analyses and Forest plots using a microsoft excel spreadsheet: step-by-step guide focusing on descriptive data analysis. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:52.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Zhang X, Shen R, Zhao J, Sun J, Zhang Q, Chen Z. Using overlapping low-profile visualized intraluminal support stent-assisted coil embolization for treating blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Neurosurg Rev. 2021;44:1053–60.
Wu YQ, Li LZ, Wang ZY, Zhang T, Xu M, Cheng MX. Endovascular Intervention with a Low-profile Visualized Intraluminal Support Stent Versus Surgical Clipping for Blood Blister-like Aneurysms : A Retrospective Study. Clin Neuroradiol. 2021;31:417–24.
Fang Y, Zhu D, Peng Y, Zhong M, Xu J, Li Q, Liang G, Wang Y, Feng W, Wang D, Zhang Y, Chen D, Guo Q, Li T, Xie X, Zhu G, Guan S, Gu Z, Li G, Yang H, He X, Zhu Q, Wan J, Li Q, Yang P, Zhao R, Huang Q, Hong B, Xu Y, Liu J. Treatment of Blood Blister-like Aneurysms with Stent-Assisted Coiling: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e486–91.
Yan Z, Zheng K, Xiong Y, Lan F, Wang Y, Tan X, Zhong M, Li Z. Intracranial Complex Ruptured Aneurysms Coiled with Overlapping Low-Profile Visualized Intraluminal Support Stents: Another Available Option for Complex Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2019;125:e22–8.
Hao X, Li G, Ren J, Li J, He C, Zhang HQ. Endovascular Patch Embolization for Blood Blister-Like Aneurysms in Dorsal Segment of Internal Carotid Artery. World Neurosurg. 2018;113:26–32.
Xu D, Zhang C, Wang T, Wang C, Kallmes DF, Lanzino G, You C, Xie X. Evaluation of Enterprise Stent-Assisted Coiling and Telescoping Stent Technique as Treatment of Supraclinoid Blister Aneurysms of the Internal Carotid Artery. World Neurosurg. 2018;110:e890–6.
Ren Y, Liu L, Sun H, Liu Y, Li H, Ma L, Zhang CW, Xie XD, He M, You C, Li J. Microsurgical versus Endovascular Treatments for Blood-Blister Aneurysms of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Retrospective Study of 83 Patients in a Single Center. World Neurosurg. 2018;109:e615–24.
Zhu D, Fang Y, Yang P, Zhang P, Chen L, Xu Y, Hong B, Huang Q, Liu JM. Overlapped Stenting Combined with Coiling for Blood Blister-Like Aneurysms: Comparison of Low-Profile Visualized Intraluminal Support (LVIS) Stent and Non-LVIS Stent. World Neurosurg. 2017;104:729–35.
Yu B, Zheng J, Hong Y, Chen L, Xi Z, Yu M, Que Z, Liu Y. Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization of Ruptured Supraclinoid Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery. Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26:219–22.
Chinchure SD, Gupta V, Goel G, Gupta A, Jha A. Subarachnoid hemorrhage with blister aneurysms: Endovascular management. Neurol India. 2014;62:393–9.
Fang YB, Li Q, Wu YN, Zhang Q, Yang PF, Zhao WY, Huang QH, Hong B, Xu Y, Liu JM. Overlapping stents for blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014;123:34–9.
Lim YC, Kim BM, Suh SH, Jeon P, Kim SH, Ihn YK, Lee YJ, Sim SY, Chung J, Kim DJ, Kim DI. Reconstructive treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms with stent and coil. Neurosurgery. 2013;73:480–8.
Fang YB, Li Q, Yang PF, Huang QH, Zhao WY, Xu Y, Hong B, Liu JM. Treatment of blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery with stent-assisted coil embolization. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115:920–5.
Ihn YK, Kim SH, Sung JH, Kim TG. The efficacy of endovascular treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms using stent-assisted coil embolization. Interv Neuroradiol. 2012;18:432–41.
Meckel S, Singh TP, Undrén P, Ramgren B, Nilsson OG, Phatouros C, McAuliffe W, Cronqvist M. Endovascular treatment using predominantly stent-assisted coil embolization and antiplatelet and anticoagulation management of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:764–71.
Capocci R, Shotar E, Di Maria F, Rolla-Bigliani C, Al Raaisi A, André A, Mahtout J, Boch AL, Degos V, Sourour N, Clarençon F. Delayed Treatment (≥5 Days) by Flow Diversion of Ruptured Blister-Like Cerebral Aneurysms: Case Series of 8 Consecutive Patients. Clin Neuroradiol. 2020;30:287–96.
Ghorbani M, Griessenauer CJ, Wipplinger C, Azar M, Shojaei H, Bavand K, Khosravi D. Flow diverter embolization device for endovascular treatment of ruptured blister and wide necked very small aneurysms. Heliyon. 2019;5:e02241.
Griffin A, Reese V, Hüseyinoglu Z, Niedzwiecki D, Yang L, Cutler A, Gonzalez LF, Zomorodi A, Smith T, Hauck EF. Predictors of Clinical Outcome After Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with the Pipeline Embolization Device. World Neurosurg. 2019;130:e666–71.
Parthasarathy R, Gupta V, Gupta A. Safety of Prasugrel loading in ruptured blister like aneurysm treated with a Pipeline device. Br J Radiol. 2018;91:20170476.
Mokin M, Chinea A, Primiani CT, Ren Z, Kan P, Srinivasan VM, Hanel R, Aguilar-Salinas P, Turk AS, Turner RD, Chaudry MI, Ringer AJ, Welch BG, Mendes Pereira V, Renieri L, Piano M, Elijovich L, Arthur AS, Cheema A, Lopes DK, Saied A, Baxter BW, Hawk H, Puri AS, Wakhloo AK, Shallwani H, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Dabus G, Linfante I. Treatment of blood blister aneurysms of the internal carotid artery with flow diversion. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018;10:1074–8.
Cerejo R, Bain M, John S, Hardman J, Moore N, Hussain MS, Toth G. Flow diverter treatment of cerebral blister aneurysms. Neuroradiology. 2017;59:1285–90.
Yang C, Vadasz A, Szikora I. Treatment of ruptured blood blister aneurysms using primary flow-diverter stenting with considerations for adjunctive coiling: A single-centre experience and literature review. Interv Neuroradiol. 2017;23:465–76.
Ryan RW, Khan AS, Barco R, Choulakian A. Pipeline flow diversion of ruptured blister aneurysms of the supraclinoid carotid artery using a single-device strategy. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42:E11.
Lozupone E, Piano M, Valvassori L, Quilici L, Pero G, Visconti E, Boccardi E. Flow diverter devices in ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a single-center experience. J Neurosurg. 2018;128:1037–43.
Luecking H, Engelhorn T, Lang S, Goelitz P, Kloska S, Roessler K, Doerfler A. FRED Flow Diverter: A Study on Safety and Efficacy in a Consecutive Group of 50 Patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38:596–602.
Linfante I, Mayich M, Sonig A, Fujimoto J, Siddiqui A, Dabus G. Flow diversion with Pipeline Embolic Device as treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage secondary to blister aneurysms: dual-center experience and review of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017;9:29–33.
Kumar D, Rahul KR, Santhosh P, Mehta P, Cherian M, Kheradia D. Flow diversion in ruptured blood blister aneurysms: single centre experience. J Clin Interv Radiol ISVIR. 2017;1:77–84.
Aydin K, Arat A, Sencer S, Hakyemez B, Barburoglu M, Sencer A, İzgi N. Treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms with flow diverter SILK stents. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7:202–9.
Lin N, Brouillard AM, Keigher KM, Lopes DK, Binning MJ, Liebman KM, Veznedaroglu E, Magarik JA, Mocco J, Duckworth EA, Arthur AS, Ringer AJ, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH. Utilization of Pipeline embolization device for treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms: US multicenter experience. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7:808–15.
Yoon JW, Siddiqui AH, Dumont TM, Levy EI, Hopkins LN, Lanzino G, Lopes DK, Moftakhar R, Billingsley JT, Welch BG, Boulos AS, Yamamoto J, Tawk RG, Ringer AJ, Hanel RA; Endovascular Neurosurgery Research Group. Feasibility and safety of pipeline embolization device in patients with ruptured carotid blister aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2014;75:419–29; discussion 429.
Chalouhi N, Zanaty M, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, Hasan D, Kung D, Rosenwasser RH, Jabbour P. Treatment of blister-like aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery. 2014;74:527–32; discussion 532.
Algra AM, Lindgren A, Vergouwen MDI, Greving JP, van der Schaaf IC, van Doormaal TPC, Rinkel GJE. Procedural Clinical Complications, Case-Fatality Risks, and Risk Factors in Endovascular and Neurosurgical Treatment of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76:282–93.
Bodily KD, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G, Fiorella DJ, White PM, Kallmes DF. Stent-assisted coiling in acutely ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a qualitative, systematic review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:1232–6.
Zhang X, Zuo Q, Tang H, Xue G, Yang P, Zhao R, Li Q, Fang Y, Xu Y, Hong B, Huang Q, Liu J. Stent assisted coiling versus non-stent assisted coiling for the management of ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019;11:489–96.
Bsat S, Bsat A, Tamim H, Chanbour H, Alomari SO, Houshiemy MNE, Moussalem C, Omeis I. Safety of stent-assisted coiling for the treatment of wide-necked ruptured aneurysm: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of prevalence. Interv Neuroradiol. 2020;26:547–56.
Peschillo S, Cannizzaro D, Caporlingua A, Missori P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Treatment and Outcome of Blister-Like Aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37:856–61.
Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, Sandercock P; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005;366:809–17.
Zhu D, Yan Y, Zhao P, Duan G, Zhao R, Liu J, Huang Q. Safety and Efficacy of Flow Diverter Treatment for Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;118:e79–86.
Shah SS, Gersey ZC, Nuh M, Ghonim HT, Elhammady MS, Peterson EC. Microsurgical versus endovascular interventions for blood-blister aneurysms of the internal carotid artery: systematic review of literature and meta-analysis on safety and efficacy. J Neurosurg. 2017;127:1361–73.
Scerrati A, Visani J, Flacco ME, Ricciardi L, Trungu S, Raco A, Dones F, De Bonis P, Sturiale CL. Endovascular Treatment of Ruptured Intracranial Blister Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42:538–45.
Murad MH, Asi N, Alsawas M, Alahdab F. New evidence pyramid. Evid Based Med. 2016;21:125–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. Lee, D. H. Kim, S. H. Lee, J. H. Moon, S.-Y. Yang, K.-T. Cho and B. H. Kim, declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
B. H. Kim and K.-T. Cho contributed equally to this report as corresponding authors.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Fig. 3
Funnel plots for estimates in the proportion meta-analysis involving blood-blister like aneurysms treated with SAC or FD according to complete occlusion rate at follow-up. In the funnel plot, the X‑axis represent the mean results and the Y-axis shows the sample size. SAC stent-assisted coiling, FD flow diverter.
Supplementary Fig. 4
Funnel plots for estimates in the proportion meta-analysis involving blood-blister like aneurysms treated with SAC or FD according to recanalization rate. In the funnel plot, the X‑axis represent the mean results and the Y-axis shows the sample size. SAC stent-assisted coiling, FD flow diverter
Supplementary Fig. 5
Funnel plots for estimates in the proportion meta-analysis involving blood-blister like aneurysms treated with SAC or FD according to mortality rate. In the funnel plot, the X‑axis represent the mean results and the Y-axis shows the sample size. SAC stent-assisted coiling, FD flow diverter
Supplementary Fig. 6
Funnel plots for estimates in the proportion meta-analysis involving blood-blister like aneurysms treated with SAC or FD according to rate of favorable outcome. In the funnel plot, the X‑axis represent the mean results and the Y-axis shows the sample size. SAC stent-assisted coiling, FD flow diverter
Supplementary Fig. 7
Funnel plots for estimates in the proportion meta-analysis involving blood-blister like aneurysms treated with SAC or FD according to rate of procedural complication. In the funnel plot, the X‑axis represent the mean results and the Y-axis shows the sample size. SAC stent-assisted coiling, FD flow diverter
Supplementary Fig. 8
Funnel plots for estimates in the proportion meta-analysis involving blood-blister like aneurysms treated with SAC or FD according to rebleeding rate. In the funnel plot, the X‑axis represent the mean results and the Y-axis shows the sample size. SAC stent-assisted coiling, FD flow diverter
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Kim, D.H., Lee, S.H. et al. Stent-assisted Coiling vs. Flow Diverter for Treating Blood Blister-like Aneurysms. Clin Neuroradiol 32, 889–902 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-022-01160-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-022-01160-3