Abstract
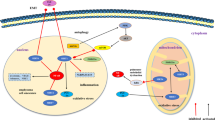
Apelin is an endogenous ligand of G protein-coupled receptor APJ. It is extensively expressed in many tissues such as heart, liver, and kidney, especially in lung tissue. A growing body of evidence suggests that apelin/APJ system is closely related to the development of respiratory diseases. Therefore, in this review, we focus on the role of apelin/APJ system in respiratory diseases, including pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), pulmonary embolism (PE), acute lung injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome (OSAS), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), pulmonary edema, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. In detail, apelin/APJ system attenuates PAH by activating AMPK-KLF2-eNOS-NO signaling and miR424/503-FGF axis. Also, apelin protects against ALI/ARDS by reducing mitochondrial ROS-triggered oxidative damage, mitochondria apoptosis, and inflammatory responses induced by the activation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. Apelin/APJ system also prevents the occurrence of pulmonary edema via activating AKT-NOS3-NO pathway. Moreover, apelin/APJ system accelerates NSCLC cells’ proliferation and migration via triggering ERK1/2–cyclin D1 and PAK1–cofilin signaling, respectively. Additionally, apelin/APJ system may act as a predictor in the development of OSAS and PE. Considering the pleiotropic actions of apelin/APJ system, targeting apelin/APJ system may be a potent therapeutic avenue for respiratory diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A, Heng HH, Tsui LC, Kennedy JL, Shi X, Petronis A, George SR, Nguyen T (1993) A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene 136(1–2):355–360
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Fujino M (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251(2):471–476. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.9489
Medhurst AD, Jennings CA, Robbins MJ, Davis RP, Ellis C, Winborn KY, Lawrie KW, Hervieu G, Riley G, Bolaky JE, Herrity NC, Murdock P, Darker JG (2003) Pharmacological and immunohistochemical characterization of the APJ receptor and its endogenous ligand apelin. J Neurochem 84(5):1162–1172
Cano Martinez LJ, Coral Vazquez RM, Mendez JP, Trejo S, Perez Razo JC, Canto P (2018) Serum concentrations of apelin-17 isoform vary in accordance to blood pressure categories in individuals with obesity class 3. Clin Exp Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2018.1462374
Xie F, Lv D, Chen L (2014) ELABELA: a novel hormone in cardiac development acting as a new endogenous ligand for the APJ receptor. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 46(7):620–622. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmu032
Pauli A, Norris ML, Valen E, Chew GL, Gagnon JA, Zimmerman S, Mitchell A, Ma J, Dubrulle J, Reyon D, Tsai SQ, Joung JK, Saghatelian A, Schier AF (2014) Toddler: an embryonic signal that promotes cell movement via Apelin receptors. Science 343(6172):1248636. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1248636
Lu L, Wu D, Li L, Chen L (2017) Apelin/APJ system: a bifunctional target for cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Cardiol 230:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.215
O'Carroll AM, Lolait SJ, Harris LE, Pope GR (2013) The apelin receptor APJ: journey from an orphan to a multifaceted regulator of homeostasis. J Endocrinol 219(1):R13–35. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0227
Bai B, Tang J, Liu H, Chen J, Li Y, Song W (2008) Apelin-13 induces ERK1/2 but not p38 MAPK activation through coupling of the human apelin receptor to the Gi2 pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 40(4):311–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00403.x
D'Aniello C, Lonardo E, Iaconis S, Guardiola O, Liguoro AM, Liguori GL, Autiero M, Carmeliet P, Minchiotti G (2009) G protein-coupled receptor APJ and its ligand apelin act downstream of Cripto to specify embryonic stem cells toward the cardiac lineage through extracellular signal-regulated kinase/p70S6 kinase signaling pathway. Circ Res 105(3):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.201186
Scimia MC, Hurtado C, Ray S, Metzler S, Wei K, Wang J, Woods CE, Purcell NH, Catalucci D, Akasaka T, Bueno OF, Vlasuk GP, Kaliman P, Bodmer R, Smith LH, Ashley E, Mercola M, Brown JH, Ruiz-Lozano P (2012) APJ acts as a dual receptor in cardiac hypertrophy. Nature 488(7411):394–398. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11263
Bai B, Jiang Y, Cai X, Chen J (2014) Dynamics of apelin receptor/G protein coupling in living cells. Exp Cell Res 328(2):401–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.08.035
Zhou Q, Xu J, Liu M, He L, Zhang K, Yang Y, Yang X, Zhou H, Tang M, Lu L, Chen Z, Chen L, Li L (2019) Warburg effect is involved in apelin-13-induced human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28218
Xie F, Liu W, Feng F, Li X, He L, Lv D, Qin X, Li L, Li L, Chen L (2015) Apelin-13 promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via PI3K-Akt-ERK1/2-p70S6K and PI3K-induced autophagy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 47(12):969–980. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmv111
Liu MQ, Chen Z, Chen LX (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel mechanism and therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37(4):425–443. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.145
Zhang H, Chen S, Zeng M, Lin D, Wang Y, Wen X, Xu C, Yang L, Fan X, Gong Y, Zhang H, Kong X (2018) Apelin-13 administration protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Physiol Biochem 49(5):1918–1932. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493653
Liu M, Li H, Zhou Q, Zhao H, Lv D, Cao J, Jiang J, Tang M, Wu D, Liu J, Wu L, Hu H, He L, Huang S, Chen Z, Li L, Chen L (2018) ROS-Autophagy pathway mediates monocytes-human umbilical vein endothelial cells adhesion induced by apelin-13. J Cell Physiol 233(10):6839–6850. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26554
Ureche C, Tapoi L, Volovat S, Voroneanu L, Kanbay M, Covic A (2019) Cardioprotective apelin effects and the cardiac-renal axis: review of existing science and potential therapeutic applications of synthetic and native regulated apelin. J Hum Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-019-0163-5
Besserer-Offroy E, Berube P, Cote J, Murza A, Longpre JM, Dumaine R, Lesur O, Auger-Messier M, Leduc R, Marsault E, Sarret P (2018) The hypotensive effect of activated apelin receptor is correlated with beta-arrestin recruitment. Pharmacol Res 131:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.02.032
Furuya M, Okuda M, Usui H, Takenouchi T, Kami D, Nozawa A, Shozu M, Umezawa A, Takahashi T, Aoki I (2012) Expression of angiotensin II receptor-like 1 in the placentas of pregnancy-induced hypertension. Int J Gynecol Pathol 31(3):227–235. https://doi.org/10.1097/PGP.0b013e31823b6e71
Najafipour H, Soltani Hekmat A, Nekooian AA, Esmaeili-Mahani S (2012) Apelin receptor expression in ischemic and non- ischemic kidneys and cardiovascular responses to apelin in chronic two-kidney-one-clip hypertension in rats. Regul Pept 178(1–3):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2012.06.006
Zhou Q, Chen L, Tang M, Guo Y, Li L (2018) Apelin/APJ system: a novel promising target for anti-aging intervention. Clin Chim Acta 487:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.10.011
Vinel C, Lukjanenko L, Batut A, Deleruyelle S, Pradere JP, Le Gonidec S, Dortignac A, Geoffre N, Pereira O, Karaz S, Lee U, Camus M, Chaoui K, Mouisel E, Bigot A, Mouly V, Vigneau M, Pagano AF, Chopard A, Pillard F, Guyonnet S, Cesari M, Burlet-Schiltz O, Pahor M, Feige JN, Vellas B, Valet P, Dray C (2018) The exerkine apelin reverses age-associated sarcopenia. Nat Med 24(9):1360–1371. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0131-6
Ji W, Shi H, Shen H, Kong J, Song J, Bian H, Lv X (2019) Mechanism of KLF4 protection against acute liver injury via inhibition of apelin signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longevity 2019:6140360. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6140360
Huang Z, Wu L, Chen L (2018) Apelin/APJ system: a novel potential therapy target for kidney disease. J Cell Physiol 233(5):3892–3900. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26144
He S, Li J, Wang J, Zhang Y (2019) Hypoxia exposure alleviates impaired muscular metabolism, glucose tolerance, and aerobic capacity in apelin-knockout mice. FEBS Open Bio 9(3):498–509. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12587
Andersen CU, Markvardsen LH, Hilberg O, Simonsen U (2009) Pulmonary apelin levels and effects in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Respir Med 103(11):1663–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2009.05.011
Seyedabadi M, Goodchild AK, Pilowsky PM (2002) Site-specific effects of apelin-13 in the rat medulla oblongata on arterial pressure and respiration. Auton Neurosci 101(1–2):32–38
Zhang H, Gong Y, Wang Z, Jiang L, Chen R, Fan X, Zhu H, Han L, Li X, Xiao J, Kong X (2014) Apelin inhibits the proliferation and migration of rat PASMCs via the activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal and the inhibition of autophagy under hypoxia. J Cell Mol Med 18(3):542–553. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12208
Hosoya M, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Fujii R, Habata Y, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Honda S, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Nishimura O, Fujino M (2000) Molecular and functional characteristics of APJ. Tissue distribution of mRNA and interaction with the endogenous ligand apelin. J Biol Chem 275(28):21061–21067. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M908417199
O'Carroll AM, Selby TL, Palkovits M, Lolait SJ (2000) Distribution of mRNA encoding B78/apj, the rat homologue of the human APJ receptor, and its endogenous ligand apelin in brain and peripheral tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492(1):72–80
Kawamata Y, Habata Y, Fukusumi S, Hosoya M, Fujii R, Hinuma S, Nishizawa N, Kitada C, Onda H, Nishimura O, Fujino M (2001) Molecular properties of apelin: tissue distribution and receptor binding. Biochim Biophys Acta 1538(2–3):162–171
Kleinz MJ, Davenport AP (2004) Immunocytochemical localization of the endogenous vasoactive peptide apelin to human vascular and endocardial endothelial cells. Regul Pept 118(3):119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2003.11.002
Goetze JP, Rehfeld JF, Carlsen J, Videbaek R, Andersen CB, Boesgaard S, Friis-Hansen L (2006) Apelin: a new plasma marker of cardiopulmonary disease. Regul Pept 133(1–3):134–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2005.09.032
Baek HS, Kim YD, Shin JH, Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB (2011) Serum leptin and adiponectin levels correlate with exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children with asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 107(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2011.03.013
Hofmann AD, Friedmacher F, Takahashi H, Hunziker M, Gosemann JH, Puri P (2014) Decreased apelin and apelin-receptor expression in the pulmonary vasculature of nitrofen-induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 30(2):197–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3450-1
Fan XF, Xue F, Zhang YQ, Xing XP, Liu H, Mao SZ, Kong XX, Gao YQ, Liu SF, Gong YS (2015) The apelin–APJ axis is an endogenous counterinjury mechanism in experimental acute lung injury. Chest 147(4):969–978. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.14-1426
Andersen CU, Hilberg O, Mellemkjaer S, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Simonsen U (2011) Apelin and pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ 1(3):334–346. https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-8932.87299
Samareh Fekri M, Etminan A, Rashidnedjad A, Mojibian A, Masoomi Y (2018) Serum apelin peptide level in hemodialysis patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Iran J Kidney Dis 12(4):209–214
Li Y, Ren W, Wang X, Yu X, Cui L, Li X, Zhang X, Shi B (2019) MicroRNA-150 relieves vascular remodeling and fibrosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Biomed Pharmacother 109:1740–1749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.058
Ikeda KT, Hale PT, Pauciulo MW, Dasgupta N, Pastura PA, Le Cras TD, Pandey MK, Nichols WC (2018) Hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in different mouse strains—relation to transcriptome. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2017-0435OC
Sheikh AY, Chun HJ, Glassford AJ, Kundu RK, Kutschka I, Ardigo D, Hendry SL, Wagner RA, Chen MM, Ali ZA, Yue P, Huynh DT, Connolly AJ, Pelletier MP, Tsao PS, Robbins RC, Quertermous T (2008) In vivo genetic profiling and cellular localization of apelin reveals a hypoxia-sensitive, endothelial-centered pathway activated in ischemic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294(1):H88–98. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00935.2007
Chandra SM, Razavi H, Kim J, Agrawal R, Kundu RK, de Jesus PV, Zamanian RT, Quertermous T, Chun HJ (2011) Disruption of the apelin-APJ system worsens hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(4):814–820. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.219980
Soon E, Southwood M, Sheares K, Pepke-Zaba J, Morrell NW (2014) Better off blue: BMPR-2 mutation, arteriovenous malformation, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 189(11):1435–1436. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201311-2019IM
Braam EA, Quanjel MJ, Van Haren-Willems JH, Van Oosterhout MF, Vink A, Heijdra YF, Kwakkel-van Erp JM (2016) Extensive pulmonary sarcoid reaction in a patient with BMPR-2 associated idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 33(2):182–185
Hautefort A, Mendes-Ferreira P, Sabourin J, Manaud G, Bertero T, Rucker-Martin C, Riou M, Adao R, Manoury B, Lambert M, Boet A, Lecerf F, Domergue V, Bras-Silva C, Gomez AM, Montani D, Girerd B, Humbert M, Antigny F, Perros F (2019) Bmpr2 mutant rats develop pulmonary and cardiac characteristics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 139(7):932–948. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033744
Alastalo TP, Li M, Perez Vde J, Pham D, Sawada H, Wang JK, Koskenvuo M, Wang L, Freeman BA, Chang HY, Rabinovitch M (2011) Disruption of PPARgamma/beta-catenin-mediated regulation of apelin impairs BMP-induced mouse and human pulmonary arterial EC survival. J Clin Investig 121(9):3735–3746. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI43382
D'Amico RW, Faley S, Shim HN, Prosser JR, Agrawal V, Bellan LM, West JD (2018) Pulmonary vascular platform models the effects of flow and pressure on endothelial dysfunction in BMPR2 associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092561
Ozkan M, Dweik RA, Laskowski D, Arroliga AC, Erzurum SC (2001) High levels of nitric oxide in individuals with pulmonary hypertension receiving epoprostenol therapy. Lung 179(4):233–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004080000064
Albarran-Juarez J, Iring A, Wang S, Joseph S, Grimm M, Strilic B, Wettschureck N, Althoff TF, Offermanns S (2018) Piezo1 and Gq/G11 promote endothelial inflammation depending on flow pattern and integrin activation. J Exp Med 215(10):2655–2672. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20180483
McLean DL, Kim J, Kang Y, Shi H, Atkins GB, Jain MK, Chun HJ (2012) Apelin/APJ signaling is a critical regulator of statin effects in vascular endothelial cells—brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(11):2640–2643. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300317
Wang X, Wu Z, He Y, Zhang H, Tian L, Zheng C, Shang T, Zhu Q, Li D, He Y (2018) Humanin prevents high glucose-induced monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells by targeting KLF2. Mol Immunol 101:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.07.008
Young A, Wu W, Sun W, Benjamin Larman H, Wang N, Li YS, Shyy JY, Chien S, Garcia-Cardena G (2009) Flow activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in vascular endothelium leads to Kruppel-like factor 2 expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(11):1902–1908. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.193540
Zippel N, Loot AE, Stingl H, Randriamboavonjy V, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B (2018) Endothelial AMP-activated kinase alpha1 phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and decreases endothelial NO formation. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092753
He L, Zhou Q, Huang Z, Xu J, Zhou H, Lv D, Lu L, Huang S, Tang M, Zhong J, Chen JX, Luo X, Li L, Chen L (2019) PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy promotes apelin-13-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by AMPKalpha and exacerbates atherosclerotic lesions. J Cell Physiol 234(6):8668–8682. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27527
Zhu G, Zhang W, Liu Y, Wang S (2018) miR371b5p inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis in monocrotalineinduced pulmonary arterial hypertension via PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep 18(6):5489–5501. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9614
Kim J, Kang Y, Kojima Y, Lighthouse JK, Hu X, Aldred MA, McLean DL, Park H, Comhair SA, Greif DM, Erzurum SC, Chun HJ (2013) An endothelial apelin-FGF link mediated by miR-424 and miR-503 is disrupted in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Med 19(1):74–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3040
Bertero T, Lu Y, Annis S, Hale A, Bhat B, Saggar R, Saggar R, Wallace WD, Ross DJ, Vargas SO, Graham BB, Kumar R, Black SM, Fratz S, Fineman JR, West JD, Haley KJ, Waxman AB, Chau BN, Cottrill KA, Chan SY (2014) Systems-level regulation of microRNA networks by miR-130/301 promotes pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Investig 124(8):3514–3528. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI74773
Yamamoto T (2018) Management of patients with high-risk pulmonary embolism: a narrative review. J Intensive Care 6:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-018-0286-8
Tang M, Huang Z, Luo X, Liu M, Wang L, Qi Z, Huang S, Zhong J, Chen JX, Li L, Wu D, Chen L (2019) Ferritinophagy activation and sideroflexin1-dependent mitochondria iron overload is involved in apelin-13-induced cardiomyocytes hypertrophy. Free Radic Biol Med 134:445–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.052
Celik Y, Yardan T, Baydin A, Demircan S (2016) The role of NT-proBNP and Apelin in the assessment of right ventricular dysfunction in acute pulmonary embolism. J Pak Med Assoc 66(3):306–311
Selimoglu Sen H, Kaplan I, Abakay O, Sezgi C, Yilmaz S, Taylan M, Abakay A, Tanrikulu AC (2016) Serum apelin 13 levels in patients with pulmonary embolism. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 22(6):543–547. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029615572467
Feng JH, Li WM, Wu XP, Tan XY, Gao YH, Han CL, Li SQ, Xie HN (2010) Hemodynamic effect of apelin in a canine model of acute pulmonary thromboembolism. Peptides 31(9):1772–1778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.06.004
Maguire JJ, Kleinz MJ, Pitkin SL, Davenport AP (2009) [Pyr1]apelin-13 identified as the predominant apelin isoform in the human heart: vasoactive mechanisms and inotropic action in disease. Hypertension 54(3):598–604. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.134619
Lee JH, Kim S, Park BK, Kim WS, Kim DS, Kim WD, Lee SD (2005) The effect of a combination of inhaled nitric oxide and an endothelinA-receptor antagonist on hemodynamic dysfunction in experimental acute pulmonary thromboembolism. Lung 183(2):139–149
Mughal A, Sun C, O'Rourke ST (2018) Apelin reduces nitric oxide-induced relaxation of cerebral arteries by inhibiting activation of large-conductance, calcium-activated K channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 71(4):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0000000000000563
Dalzell JR, Rocchiccioli JP, Weir RA, Jackson CE, Padmanabhan N, Gardner RS, Petrie MC, McMurray JJ (2015) The emerging potential of the apelin–APJ system in heart failure. J Card Fail 21(6):489–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2015.03.007
Cheng J, Luo X, Huang Z, Chen L (2018) Apelin/APJ system: a potential therapeutic target for endothelial dysfunction-related diseases. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27942
Kurowska P, Barbe A, Rozycka M, Chmielinska J, Dupont J, Rak A (2018) Apelin in reproductive physiology and pathology of different species: a critical review. Int J Endocrinol 2018:9170480. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9170480
Bertrand C, Pradere JP, Geoffre N, Deleruyelle S, Masri B, Personnaz J, Le Gonidec S, Batut A, Louche K, Moro C, Valet P, Castan-Laurell I (2018) Chronic apelin treatment improves hepatic lipid metabolism in obese and insulin-resistant mice by an indirect mechanism. Endocrine 60(1):112–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1536-1
Ge Y, Li Y, Chen Q, Zhu W, Zuo L, Guo Z, Gong J, Cao L, Gu L, Li J (2018) Adipokine apelin ameliorates chronic colitis in Il-10(−/−) mice by promoting intestinal lymphatic functions. Biochem Pharmacol 148:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.011
Vafaee F (2016) Using multi-objective optimization to identify dynamical network biomarkers as early-warning signals of complex diseases. Sci Rep 6:22023. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22023
Ju YS, Zangrilli MA, Finn MB, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM (2019) Obstructive sleep apnea treatment, slow wave activity, and amyloid-beta. Ann Neurol 85(2):291–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25408
Heinonen I, Vuolteenaho O, Koskenvuo J, Arjamaa O, Nikinmaa M (2017) Systemic hypoxia increases circulating concentration of apelin in humans. High Alt Med Biol 18(3):292–295. https://doi.org/10.1089/ham.2017.0017
Henley DE, Buchanan F, Gibson R, Douthwaite JA, Wood SA, Woltersdorf WW, Catterall JR, Lightman SL (2009) Plasma apelin levels in obstructive sleep apnea and the effect of continuous positive airway pressure therapy. J Endocrinol 203(1):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-09-0245
Zirlik S, Hauck T, Fuchs FS, Neurath MF, Konturek PC, Harsch IA (2011) Leptin, obestatin and apelin levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Med Sci Monit 17(3):CR159–CR164
Nizam N, Basoglu OK, Tasbakan MS, Lappin DF, Buduneli N (2016) Is there an association between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and periodontal inflammation? Clin Oral Investig 20(4):659–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1544-y
Ming H, Tian A, Liu B, Hu Y, Liu C, Chen R, Cheng L (2019) Inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-8 and sleep monitoring in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Exp Ther Med 17(3):1766–1770. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.7110
Jiang YQ, Xue JS, Xu J, Zhou ZX, Ji YL (2017) Efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure treatment in treating obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome associated with carotid arteriosclerosis. Exp Ther Med 14(6):6176–6182. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5308
Masoumi J, Abbasloui M, Parvan R, Mohammadnejad D, Pavon-Djavid G, Barzegari A, Abdolalizadeh J (2018) Apelin, a promising target for Alzheimer disease prevention and treatment. Neuropeptides 70:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2018.05.008
Augustin HG, Koh GY (2017) Organotypic vasculature: from descriptive heterogeneity to functional pathophysiology. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal2379
Antushevich H, Wojcik M (2018) Review: apelin in disease. Clin Chim Acta 483:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.05.012
Zhao H, Tian X, He L, Li Y, Pu W, Liu Q, Tang J, Wu J, Cheng X, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Tan Z, Bai F, Xu F, Smart N, Zhou B (2018) Apj(+) vessels drive tumor growth and represent a tractable therapeutic target. Cell Rep 25(5):1241–1254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.015(e1245)
Rayalam S, Della-Fera MA, Kasser T, Warren W, Baile CA (2011) Emerging role of apelin as a therapeutic target in cancer: a patent review. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 6(3):367–372. https://doi.org/10.2174/157489211796957856
Lv D, Li L, Lu Q, Li Y, Xie F, Li H, Cao J, Liu M, Wu D, He L, Chen L (2016) PAK1-cofilin phosphorylation mediates human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration induced by apelin-13. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 43(5):569–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12563
Berta J, Kenessey I, Dobos J, Tovari J, Klepetko W, Jan Ankersmit H, Hegedus B, Renyi-Vamos F, Varga J, Lorincz Z, Paku S, Ostoros G, Rozsas A, Timar J, Dome B (2010) Apelin expression in human non-small cell lung cancer: role in angiogenesis and prognosis. J Thorac Oncol 5(8):1120–1129. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e2c1ff
Ermin S, Cok G, Veral A, Kose T (2016) The role of apelin in the assessment of response to chemotherapyand prognosis in stage 4 nonsmall cell lung cancer. Turk J Med Sci 46(5):1353–1359. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1411-9
Yang S, Chen X, Pan Y, Yu J, Li X, Ma S (2016) Proteins associated with EGFR-TKIs resistance in patients with non-small cell lung cancer revealed by mass spectrometry. Mol Med Rep 14(5):4823–4829. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5823
Yang L, Su T, Lv D, Xie F, Liu W, Cao J, Sheikh IA, Qin X, Li L, Chen L (2014) ERK1/2 mediates lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and autophagy induced by apelin-13. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 46(2):100–111. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmt140
Jang I, Jeon BT, Jeong EA, Kim EJ, Kang D, Lee JS, Jeong BG, Kim JH, Choi BH, Lee JE, Kim JW, Choi JY, Roh GS (2012) Pak1/LIMK1/cofilin pathway contributes to tumor migration and invasion in human non-small cell lung carcinomas and cell lines. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 16(3):159–165. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.3.159
Mishra A, Kohli S, Dua S, Thinlas T, Mohammad G, Pasha MA (2015) Genetic differences and aberrant methylation in the apelin system predict the risk of high-altitude pulmonary edema. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(19):6134–6139. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1422759112
Miller CN, Dye JA, Schladweiler MC, Richards JH, Ledbetter AD, Stewart EJ, Kodavanti UP (2018) Acute inhalation of ozone induces DNA methylation of apelin in lungs of Long-Evans rats. Inhal Toxicol 30(4–5):178–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/08958378.2018.1483984
Machura E, Ziora K, Ziora D, Swietochowska E, Krakowczyk H, Halkiewicz F, Kasperska-Zajac A (2013) Serum apelin-12 level is elevated in schoolchildren with atopic asthma. Respir Med 107(2):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2012.10.026
Jin G, Chen Z, Zhang J, Song J, Shi J, Zhou B (2018) Association of brain natriuretic peptide gene polymorphisms with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with pulmonary hypertension and its mechanism. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180905
Huang Z, He L, Chen Z, Chen L (2018) Targeting drugs to APJ receptor: from signaling to pathophysiological effects. J Cell Physiol 234(1):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27047
Yokoyama Y, Sekiguchi A, Fujiwara C, Uchiyama A, Uehara A, Ogino S, Torii R, Ishikawa O, Motegi SI (2018) Inhibitory regulation of skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by apelin/APJ signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol 70(10):1661–1672. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40533
Iturrioz X, Alvear-Perez R, De Mota N, Franchet C, Guillier F, Leroux V, Dabire H, Le Jouan M, Chabane H, Gerbier R, Bonnet D, Berdeaux A, Maigret B, Galzi JL, Hibert M, Llorens-Cortes C (2010) Identification and pharmacological properties of E339–3D6, the first nonpeptidic apelin receptor agonist. FASEB J 24(5):1506–1517. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-140715
Margathe JF, Iturrioz X, Alvear-Perez R, Marsol C, Riche S, Chabane H, Tounsi N, Kuhry M, Heissler D, Hibert M, Llorens-Cortes C, Bonnet D (2014) Structure–activity relationship studies toward the discovery of selective apelin receptor agonists. J Med Chem 57(7):2908–2919. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm401789v
Khan P, Maloney PR, Hedrick M, Gosalia P, Milewski M, Li L, Roth GP, Sergienko E, Suyama E, Sugarman E, Nguyen K, Mehta A, Vasile S, Su Y, Shi S, Stonich D, Nguyen H, Zeng FY, Novo AM, Vicchiarelli M, Diwan J, Chung TDY, Pinkerton AB, Smith LH (2010) Functional agonists of the apelin (APJ) receptor. In: Probe reports from the NIH molecular libraries program. National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda (MD)
Zhou N, Fang J, Acheampong E, Mukhtar M, Pomerantz RJ (2003) Binding of ALX40-4C to APJ, a CNS-based receptor, inhibits its utilization as a co-receptor by HIV-1. Virology 312(1):196–203
Lee DK, Saldivia VR, Nguyen T, Cheng R, George SR, O'Dowd BF (2005) Modification of the terminal residue of apelin-13 antagonizes its hypotensive action. Endocrinology 146(1):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-0359
Zhou L, Sun H, Cheng R, Fan X, Lai S, Deng C (2019) ELABELA, as a potential diagnostic biomarker of pre-eclampsia, regulates abnormally shallow placentation via APJ. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00383.2018
Cheng L, Zhao Y, Qi D, Li W, Wang D (2018) Wnt/beta-catenin pathway promotes acute lung injury induced by LPS through driving the Th17 response in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(2):1890–1895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.058
Guo Y, Mishra A, Howland E, Zhao C, Shukla D, Weng T, Liu L (2015) Platelet-derived Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 is implicated in ICAM-1/VCAM-1-mediated neutrophilic acute lung inflammation. Blood 126(19):2220–2229. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-02-622233
Han XF, Zhang XX, Liu KM, Zhang Q (2018) Apelin-13 deficiency alters cortical bone geometry, organic bone matrix, and inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Gen Comp Endocrinol 267:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.05.024
Chen QX, Song SW, Chen QH, Zeng CL, Zheng X, Wang JL, Fang XM (2014) Silencing airway epithelial cell-derived hepcidin exacerbates sepsis induced acute lung injury. Crit Care 18(4):470. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-014-0470-8
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81603108) and Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2019JJ80063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Wang, A., Cao, J. et al. Apelin/APJ system: an emerging therapeutic target for respiratory diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 2919–2930 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03461-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03461-7