Summary
Sensitivy of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) to soils treated with preparations of Bacillus thuringiensis and of a juvenil hormone analogue
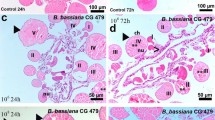
Various instar larvae ofSpodoptera littoralis were exposed to soil treated, with aBacillus thuringiensis-containing preparation (Bactospeine) and a juvenile hormone analogue (Ro 20–36 000).
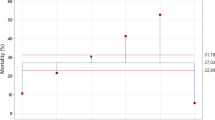
After treatment with Bactospeine, only high concentrations could affect emergence. Suppressed egg laying and sterility were the most marked effects. Also, the produced eggs were smaller in size.
The juvenile hormone analogue showed high activity, particularly against freshly moulted 6th. instar larvae. Greater effects were elicited after ecposing the larvae to treated soil than to treated leaves for 48 hours. It appears to be fairly stable in soil. Its morphogenetic activity could be detected 60 days after application.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literaturverzeichnis
Abdallah, M. D.;Zaazou, M. H.;El-Tantawi, M. (a): The morphogenetic activity of juvenile hormone and analogues inSpodoptera littoralis Boisd. Toxicology (im Druck).
Abdallah, M. D.;Zaazou, M. H.;El-Tantawi, M. (b): Sensitivity of the larval stage ofSpodoptera littoralis Boisd, to a juvenile hormone analogue. Toxicology (im Druck).
Benskin, J.;Vinson, S. B., 1973: Factors affecting juvenile hormone analogue activity in the tobacco-budworm. J. Econ. Entomol.66, 15–20.
Bowers, W. S., 1971: Insect hormones and their derivatives as insecticides. Bull. Wld. Hlth. Org.44, 381–389.
Bowman, M. C.;Wright, J. E.;Beroza, M., 1973: Determination of two juvenile hormone — active compounds and their stability in stable fly medium. J. Econ. Entomol.66, 301–304.
El-Tantawi, M.;Zaazou, M. H.;Abdallah, M. D.: Teratological effects ofBacillus thuringiensis inSpodoptera littoralis Boisd. (in Vorbereitung).
Harris, C. R., 1966: Influence of soil type on the activity of insecticides in soil. J. Econ. Entomol.59, 1221–1225.
Harris, C. R., 1972: Factors influencing the effectiveness of soil insecticides. Ann. Rev. Entomol.17, 177–198.
Hitchings, D. L., 1967:Bacillus thuringiensis: A reproductive inhibitor for southern armyworm. J. Econ. Entomol.60, 596–597.
Ignoffo, C. M.;Graham, H. M., 1967: Laboratory and field cage tests withBacillus thuringiensis against pink bollworm larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol.9, 390–394.
Metwally, M. M.;Sehnal, F.;Landa, V., 1972: Reduction of fecundity and control of the Khapra beetle by juvenile hormone mimics. J. Econ. Entomol.65, 1603–1605.
Novak, K.;Sehnal, F., 1973: Action of juvenile hormone analogues onEuproctis chrysorrhoea andYponomeuta malinella under field conditions. Acta ent. bohemoslov.70, 20–29.
Staal, G. B., 1971: Practical aspects of insect control by juvenile hormone. Bull. Wld. Hlth. Org.44, 391–394.
Williams, C. M., 1967: Third generation pesticides. Sci. Amer.217, 13–17.
Wright, J. E.;Bowman, M. C., 1973: Determination of the juvenile hormone — active compound Altosid and its stability in stable fly medium. J. Econ. Entomol.66, 707–709.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdallah, M.D., Zaazou, H.H. & El-Tantawi, M. Wirkungen einesBacillus thuringiensis-Präparats und eines Juvenilhormon-Analogons über den Erdboden aufSpodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Lep.,Noctuidae). Anz. Schadlingskde. Pflanzen-Umweltschutz 47, 170–172 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868933
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868933