Summary
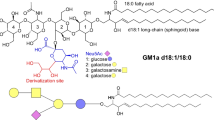
GM1- and GM2-gangliosides were isolated from brain and radio-labelled. The labelled moieties were localized by hydrolysis with lysosomal enzymes, followed by thin-layer chromatography of the products. High-resolution loading tests with labelled gangliosides were developed and found to differentiate infantile and juvenile forms of GM1- and GM2-gangliosidoses as well as the identification of B, O and AB types of GM2-gangliosidosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhunov VS, Krasnopolskaya XD (1987) Identification of GM2-gangliosidoses by means of a loading test in vitro.Voprosy Meditsinskoi Khimii 4: 115–119 (in Russian).
Ando S, Chang N, Yu RK (1978) High-performance thin-layer chromatography and densitometric determination of brain ganglioside compositions of several species.Anal Biochem 89: 437–450.
Aronovich EL, Akhunov VS, Krasnopolskaya XD (1990) Isolation and characterization of hexosaminidase A and activator protein from human kidney.Biochimia 55: 43–51.
Barton NW, Rosenberg A (1975) Metabolism of glucosyl3H-ceramide by human skin fibroblasts from normal and glucosylceramidotic subjects.J Biol Chem 250: 3966–3971.
Beaudet AL, Manschreck AA (1982) Metabolism of sphingomyelin by intact cultured fibroblasts: differentiation of Niemann-Pick disease types A and B.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 105: 14–19.
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding.Anal Biochem 72: 248–254.
Callies R, Schwarzmann G, Radsak K, Siegert R, Wiegandt H (1977) Characterization of the cellular binding of exogenous gangliosides.Eur J Biochem 80: 425–432.
Chen WW, Moser AB, Moser HW (1981) Role of lysosomal acid ceramidase in the metabolism of ceramide in human skin fibroblasts.Arch Biochem Biophys 20B: 444–455.
Chester MA, Hultberg B, Norden NE, Szabo L (1980) The nature of mannose-containing material which accumulates in cultured fibroblasts from patients with mannosidosis.Biochim Biophys Acta 627: 244–249.
Dawson G, Matalon R, Dorfman A (1972) Glycosphyngolipids in cultured human skin fibroblasts.J Biol Chem 247: 5951–5958.
Fortuin JJH, Kleijer WJ (1978) Pericellular glycosaminoglycans in cultured human cells. A possible source of error in prenatal diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses.Clin Chim Acta 82: 79–83.
Harzer K (1983) Assay of the GM2-ganglioside hexosaminidase activity of skin fibroblasts for GM2-gangliosidoses.Clin Chim Acta 135: 89–93.
Higashi H, Basu S (1982) Specific14C-labeling of sialic acid andN-acetylhexosamine residues of glycosphyngolipids after hydrozinolysis.Anal Biochem 120: 159–164.
Krasnopolskaya KD, Mirenburg TV, Aronovich EL et al (1993) Diagnosis and prevention of lysosomal storage diseases in Russia.J Inher Metab Dis 16: 994–1002.
Kudoh T, Wenger DA (1982) Diagnosis of metachromatic leukodystrophy, Krabbe disease, and Farber disease after uptake of fatty acid-labelled cerebroside sulfate into cultured skin fibroblasts.J Clin Invest 70: 89–97.
Porter MT, Fluharty AL, Harris SE, Kihara H (1970) The accumulation of cerebroside sulfates by fibroblasts in culture from patients with late infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy.Arch Biochem Biophys 138: 646–652.
Raghavan S, Krusell A, Lyerla TA, Bremer EG, Kolodny EH (1985) GM2-ganglioside metabolism in cultured human skin fibroblasts: unambiguous diagnosis of GM2-gangliosidosis.Biochim Biophys Acta 834: 238–248.
Sandhoff K, Christomanou H (1979) Biochemistry and genetics of gangliosidoses.Hum Genet 50: 107–143.
Schwarzmann G (1978) A simple and novel method for tritium labeling of gangliosidosis and other sphingolipids.Biochim Biophys Acta 529: 106–114.
Sonderfeld S, Brandler S, Sandhoff K, Galjaard H, Hoogeveen AT (1985) Genetic complementation in somatic cell hybrids of four variants of infantile GM2-gangliosidosis.Hum Genet 71: 196–200.
Zeigler M, Bach G (1986) Internalisation of exogenous gangliosides in cultured skin fibroblasts for the diagnosis of mucolipidosis IV.Clin Chim Acta 157: 183–190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhunov, V.S., Mirenburg, T.V. & Krasnopolskaya, X.D. High-resolution loading tests in the study of genetic heterogeneity in gangliosidosis fibroblasts. J Inherit Metab Dis 17, 104–111 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735405
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735405