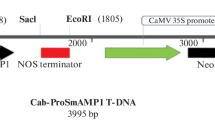
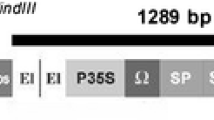
Abstract
Tachyplesin I is a 2.3 kDa antimicrobial peptide isolated from Southeast Asian horseshoe crabs. Bacterial suspensions containing 1×106 colony-forming units/ml of six isolates of pectolytic Erwinia spp., the causal pathogens of potato soft rot and blackleg, were killed in vitro by 1.4 to 11.1 μg/ml of tachyplesin I. In an attempt to enhance resistance to Erwinia spp., each of the potato cultivars Bintje, Karnico and Kondor were transformed with two gene constructs encoding different precursor tachyplesin I proteins under the control of a cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promotor. Northern and western blot analysis showed that the tachyplesin I gene was expressed in transgenic plants. Small tubers of 17 transgenic clones were screened twice for soft rot resistance to Erwinia carotovora ssp. atroseptica. Under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, transgenic clones showed slightly less rot than control tubers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP:
-
acidic carboxyl terminal polypeptide
- Eca :
-
Erwinia carotovora ssp. atroseptica
- Ecc :
-
E. carotovora ssp. carotovora
- Ech :
-
E. chrysanthemi
- IF:
-
intercellular fluid
- SP:
-
signal peptide
- TPNI (tpnI):
-
tachyplesin I
References
Allefs JJHM, van Dooijeweert W, de Jong ER, Prummel W, Hoogendoorn J: The role of the seed tuber in determining partial resistance to potato blackleg caused by Erwinia spp. Eur J Plant Path 101: 189–199 (1995).
Allefs JJHM, van Dooijeweert W, de Jong ER, Prummel W, Hoogendoorn J: Factors affecting potato soft rot resistance to pectolytic Erwinia species in a tuber slice assay. J Phytopath, in press.
Boman HG: Antibacterial peptides: Key components needed in immunity. Cell 65: 205–207 (1991).
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254 (1976).
Carmona MJ, Molina A, Fernández JA, López-Fando JJ, García-Olmedo F: Expression of the α-thionin gene from barley in tobacco confers enhanced resistance to bacterial pathogens. Plant J 3: 457–462 (1993).
Chrispeels MJ: Sorting of proteins in the secretory system. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42: 21–53 (1991).
Davis MC, Butler W, Vayda ME: Molecular responses to environmental stress and their relationship to soft rot. In: Vayda ME, Park WD (eds) The Molecular and Cellular Biology of the Potato, pp. 71–87. CAB International, Wallingford, UK (1990).
Deen C, Claassen E, Gerritse K, Zegers ND, Boersma WJA: A novel carbodiimide coupling method for synthetic peptides. Enhanced anti-peptide antibody responses. J Immunol Meth 129: 119–125 (1990).
de Wit PJGM, Spikman G: Evidence for the occurrence of race and cultivar-specific elicitors of necrosis in intercellular fluids of compatible interactions of Cladosporium fulvum and tomato. Physiol Plant Path 21: 1–11 (1982).
Düring K, Porsch P, Fladung M, Lörz H: Transgenic potato plants resistant to the phytopathogenic bacterium Erwinia carotovora. Plant J 3: 587–598 (1993).
Florack D, Allefs S, Bollen R, Bosch D, Visser B, Stiekema W: Expression of giant silkmoth cecropin B encoding genes in transgenic tobacco. Transgenic Res, 4: 132–141 (1995).
Florack DEA, Dirkse WG, Visser B, Heidekamp F, Stiekema WJ: Expression of biologically active hordothionins in tobacco. Effects of pre- and pro-sequences at the amino and carboxyl termini of the hordothionin precursor on mature protein expression and sorting. Plant Mol Biol 24: 83–96 (1994).
Fraley RT: Genetic engineering for crop improvement. In: Kung S (ed) Plant Biotechnology, pp. 395–407. Butterworths, Boston (1989)
García-Olmedo F, Rodriguez-Palenzuela P, Hernández-Lucas C, Ponz F, Maraña C, Carmona MJ, Lopez-Fando J, Fernandez JA, Carbonero P: The thionins: a protein family that includes purothionins, viscotoxins and crambins. Oxford Surv Plant Mol Cell Biol 6: 31–60 (1989).
Hoekema A, Huisman MJ, Molendijk L, van den Elzen PJM, Cornelissen BJC: The genetic engineering of two commercial potato cultivars for resistance to potato virus X. Bio/technology 7: 273–278 (1989).
Jaynes JM, Nagpala P, Destéfano-Beltrán L, Huang JH, Kim J, Denny T, Cetiner S: Expression of a Cecropin B lytic peptide analog in transgenic tobacco confers enhanced resistance to bacterial wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum. Plant Sci 89: 43–53 (1993).
Miyata T, Tokunaga F, Yoneya T, Yoshikawa K, Iwanaga S, Niwa M, Takao T, Shimonishi Y: Antimicrobial peptides, isolated from horseshoe crab hemocytes, tachyplesin II and polyphemusins I and II: chemical structures and biological activity. J Biochem 106: 663–668 (1989).
Nakamura T, Furunaka H, Miyata T, Tokunaga F, Muta T, Iwanaga S, Niwa M, Takao T, Shimonishi Y: Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). J Biol Chem 263: 16709–16713 (1988).
Pérombelon MCM: Potato blackleg: Epidemiology, hostpathogen interaction and control. Neth J Plant Path 98 (Suppl. 2): 135–146 (1992).
Shigenaga T, Muta T, Toh Y, Tokunaga F, Iwanaga S: Antimicrobial tachyplesin peptide precursor. J Biol Chem 265: 21350–21354 (1990).
Stiekema WJ, Heidekamp F, Louwerse D, Verhoeven HA, Dijkhuis P: Introduction of foreign genes into potato cvs. Bintje and Désirée using an Agrobacterium tumefaciens binary vector. Plant Cell Rep 7: 47–50 (1988).
Tsugita A: Phage lysozyme and other lytic enzymes. In: Boyer PD (ed) The Enzymes, vol. 5, pp. 344–411. Academic Press, New York (1971).
Wada K-N, Aota S-I, Tsuchiya R, Ishibashi R, Gojobori T, Ikemura T: Codon usages tabulated from the GenBank genetic sequence data. Nucl Acids Res 18: 2367–2411 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allefs, S.J.H.M., De Jong, E.R., Florack, D.E.A. et al. Erwinia soft rot resistance of potato cultivars expressing antimicrobial peptide tachyplesin I. Mol Breeding 2, 97–105 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441425
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441425