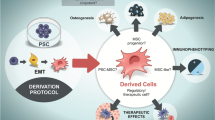
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from different sources, such as bone marrow, cord blood, and adipose tissue; however, there are variations in MSC capabilities based on their origin, donor age, and culturing method. Recently, human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have been proposed as an alternative renewal source for generating MSCs with large number. Herein, we describe our recently established All-trans retinoic acid (RA)-based approach for generating a scalable number of MSCs from hPSCs. Our protocol generates highly proliferating MSCs that have all MSC characteristics, including fibroblast-like morphology, expression of the key MSC markers, lack of the hematopoietic markers, and ability to differentiate into the three mesodermal lineages. This RA-based method provides a protocol for generating an unlimited number of hPSC-derived MSCs that could be useful for cell therapy, drug screening, and disease modeling applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown C, McKee C, Bakshi S, Walker K, Hakman E, Halassy S et al (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells: cell therapy and regeneration potential. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 13(9):1738–1755. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2914
Hass R, Kasper C, Bohm S, Jacobs R (2011) Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): a comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Signal 9:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-9-12
Wagner W, Bork S, Horn P, Krunic D, Walenda T, Diehlmann A et al (2009) Aging and replicative senescence have related effects on human stem and progenitor cells. PLoS One 4(6):e5846. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005846
Brown PT, Squire MW, Li WJ (2014) Characterization and evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human embryonic stem cells and bone marrow. Cell Tissue Res 358(1):149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1926-5
Trivedi P, Hematti P (2008) Derivation and immunological characterization of mesenchymal stromal cells from human embryonic stem cells. Exp Hematol 36(3):350–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2007.10.007
Arpornmaeklong P, Brown SE, Wang Z, Krebsbach PH (2009) Phenotypic characterization, osteoblastic differentiation, and bone regeneration capacity of human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 18(7):955–968. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2008.0310
Barberi T, Willis LM, Socci ND, Studer L (2005) Derivation of multipotent mesenchymal precursors from human embryonic stem cells. PLoS Med 2(6):e161. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020161
Karam M, Younis I, Elareer NR, Nasser S, Abdelalim EM (2020) Scalable generation of mesenchymal stem cells and adipocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. Cell 9(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030710
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8(4):315–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240600855905
Lv FJ, Tuan RS, Cheung KM, Leung VY (2014) Concise review: the surface markers and identity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 32(6):1408–1419. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1681
Ali G, Elsayed AK, Nandakumar M, Bashir M, Younis I, Abu Aqel Y et al (2020) Keratinocytes derived from patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells recapitulate the genetic signature of psoriasis disease. Stem Cells Dev 29(7):383–400. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2019.0150
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a grant from Qatar National Research Fund (QNRF) (Grant No. NPRP9-283-3-056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Karam, M., Abdelalim, E.M. (2020). Robust and Highly Efficient Protocol for Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Mesenchymal Stem Cells. In: Nagy, A., Turksen, K. (eds) Induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2454. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_318
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_318
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2118-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2119-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols