Abstract
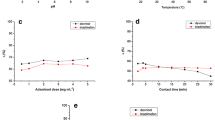
The present study deals with removal of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol (4C2NP) as a model contaminant from pharmaceutical and pesticide industries using titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an adsorbent. 4C2NP is recalcitrant and persistent toward biodegradation and its generation in aqueous environment during formulation, distribution and field application of pesticides is often unavoidable. Batch experiments were carried out to investigate the effect of contact time, nano-titanium dioxide dosage, initial pH, initial 4C2NP concentration and temperature on adsorption efficiency. The results showed that the adsorption capacity was increased with increasing 4C2NP concentration and temperature. Optimum conditions for 4C2NP adsorption were found to be initial pH ≈ 2, nano-titanium dioxide dosage ≈ 0.01 g/250 mL and equilibrium time ≈ 1 h. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles recorded a maximum capacity of 86.3 mg/g at optimal conditions. The linear correlation coefficients of Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isotherms were obtained. The results revealed that the Freundlich isotherm fitted the experimental data better than the other isotherm models.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acero JL, Benitez FJ, Leal AI, Real FJ (2005) Removal of phenolic compounds in water by ultrafiltration membrane treatments. J Environ Sci Health A 40(8):1585–1603
Agarry SE, Solomon BO (2008) Kinetics of batch microbial degradation of phenols by indigenous Pseudomonas fluorescence. Int J Environ Sci Tech 5(2):223–232
Anbia M, Ghaffari A (2009) Adsorption of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions using carbon nanoporous adsorbent coated with polymer. Appl Surf Sci 255(23):9487–9492
Arellano-Cardenas S, Gallardo-Velazquez T, Osorio-Revilla G, Lopez-Cortezl MS, Gomez-Pereal B et al (2005) Adsorption of phenol and dichlorophenols from aqueous solutions by porous clay heterostructure (PCH). J Mex Chem Soc 49(3):287–291
Bekkouche S, Bouhelassa M, Hadj Salah N, Meghlaoui FZ et al (2004) Study of adsorption of phenol on titanium oxide (TiO2). Desalination 166:355–362
Belarbi H, Al-Malack MH (2010) Adsorption and stabilization of phenol by modified local clay. Int J Environ Res 4(4):855–860
Belessi V, Romanos G, Boukos N, Lambropoulou D, Trapalis C (2009) Removal of Reactive Red 195 from aqueous solutions by adsorption on the surface of TiO2 nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 170(2):836–844
Benitez FJ, Beltran-Heredia J, Acero JL, Rubio FJ (2000) Rate constants for the reactions of ozone with chlorophenols in aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater B 79(3):271–285
Bourikas K, Stylidi M, Kondarides DI, Verykios X (2005) Adsorption of acid orange 7 on the surface of titanium dioxide. Langmuir 21(20):9222–9230
Calace N, Nardi E, Petronio BM, Pietroletti M (2002) Adsorption of phenols by peparmill sludge. Environ Poll 118(3):315–319
Chen S, Xu ZP, Zhang O, Lu GQ, Hao ZP, Liu S (2009) Studies on adsorption of phenol and 4-nitrophenol on MgAl-mixed oxide derived from MgAl-layered double hydroxide. Sep Purif Technol 67(2):194–200
Dabhade MA, Saidutta MB, Murthy DVR (2009) Adsorption of phenol on granular activated carbon from nutrient medium:equilibrium and kinetic study. Int J Environ Res 3(4):557–568
Derylo-Marczewska A, Miroslaw K, Marczewski AW, Sternik D (2010) Studies of adsorption equilibria and kinetics of o-, m-, p-nitro- and chlorophenols on microporous carbons from aqueous solutions. Adsorption 16:359–375
Dursun AY, Tepe O (2005) Internal mass transfer effect on biodegradation of phenol by Ca-alginate immobilized Ralstonia eutropha. J Hazard Mater 126:105–111
Gharbani P, Khosravi M, Tabatabaii SM, Zare K, Dastmalchi S, Mehrizad A (2010) Degradation of trace aqueous 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol occurring in pharmaceutical industrial wastewater by ozone. Int J Environ Sci Tech 7(2):377–384
Gonzalez-Serrano E, Cordero T, Rodriguez-Mirasol J, Cotoruelo L, Rodriguez JJ (2004) Removal of water pollutants with activated carbons prepared from H3PO4 activation of lignin from kraft black liquors. Water Res 38(13):3043–3050
Hameed BH, Ahmad AL, Latif KNA (2007) Adsorption of basic dye (methylene blue) onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Dyes Pigments 75(1):143–149
Haque E, Khan NA, Talapaneni SN, Vinu A, Jegal J, Jhung SH et al (2010) Adsorption of phenol on mesoporous carbon cmk-3: effect of textural properties. B Kor Chem Soc 31(6):1638–1642
Hashizume H (2004) Adsorption of some aromatic compounds by a synthetic mesoporous silicate. J Environ Sci Health A 39(10):2615–2625
Khan Z, Anjaneyulu Y (2005) Influence of soil components on adsorption-desorption of hazardous organics-development of low cost technology for reclamation of hazardous waste dumpsites. J Hazard Mater B 118:161–169
Kumar A, Kumar S, Kumar S, Gupta D (2007) Adsorption of phenol and 4-nitrophenol on granular activated carbon in basal salt medium: equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 147:155–166
Lei Z, Yuan Z, Hongmei L, Na L, Xueyan L, Xuejun G (2010) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of gallium(III) on nano-TiO2. Rare Metals 29(1):16–20
Mahvi AH (2008) Application of agricultural fibers in pollution removal from aqueous solution. Int J Environ Sci Tech 5(2):275–285
Nandi BK, Goswami A, Purkait MK (2009) Adsorption characteristics of brilliant green dye on kaolin. J Hazard Mater 161(1):387–395
Onal Y, Akmil-Basar C, Sarici-Ozdemir C (2007) Investigation kinetics mechanisms of adsorption malachite green onto activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 146(1):194–203
Robert D, Parra S, Pulgarin C, Krzton A, Weber JV (2000) Chemisorption of phenols and acids on TiO2 surface. Appl Surf Sci 167:51–58
Roostaei N, Tezel FH (2004) Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption. J Environ Manage 70(2):157–164
Samarghandi MR, Nouri J, Mesdaghinia AR, Mahvi AH, Nasseri S, Vaezi F (2007) Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int J Environ Sci Tech 4(1):19–25
Saritha P, Aparana C, Himabindu V, Anjaneyulu Y (2007) Advanced oxidation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol (4C–2-NP): a comparative study. J Hazard Mater 149(3):609–614
Sokol W, Korpal W (2004) Determination of the optimal operational parameters for a three-phase fluidized bed bioreactor with a light biomass support when used in treatment of phenolic wastewaters. Biochem Eng J 20:49–56
Subramanyam B, Das A (2009) Linearized and non-linearized isotherm models comparative study on adsorption of aqueous phenol solution in soil. Int J Environ Sci Tech 6(4):633–640
Terzyk AP (2003) Further insights into the role of carbon surface functionalities in the mechanism of phenol adsorption. J Colloid Interf Sci 268:301–329
Tseng RL, Wu KT, Wu FC, Juang RS (2010) Kinetic studies on the adsorption of phenol, 4-chlorophenol, and 2,4-dichlorophenol from water using activated carbons. J Environ Manage 91:2208–2214
Wang Z, Zhang LS, Jing ZQ (2010) Study the adsorption of phenol on attapulgite-zeolite nano-structure adsorbent from aqueous solution. Key Eng Mat 426:118–121
WHO (1963) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: international standards for drinking water. World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank from the School of Pharmacy, Tabriz-Iran, specially Dr. Hamidi and Miss Faridi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrizad, A., Zare, K., Aghaie, H. et al. Removal of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol occurring in drug and pesticide waste by adsorption onto nano-titanium dioxide. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 9, 355–360 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0038-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0038-6