Abstract
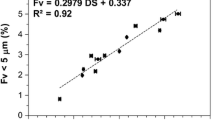
The particle size effects of high-amylose rice (Goami 2) flour on quality attributes of frying batters were characterized in terms of physicochemical, rheological, and oil-resisting properties. High-amylose rice flours were fractionated into four fractions (70, 198, 256, and 415 μm) of which morphology was also analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. Rice flour with smaller particle size exhibited a higher degree of starch gelatinization, giving rise to increased pasting parameters. When the rice flours were incorporated into frying batters, higher steady shear viscosity was observed in the batters with finer rice flour, which could be well characterized by the power law model. In addition, the dynamic viscoelastic properties of the batters were enhanced by the use of rice flour with smaller particle size, which also caused an increase in batter pickup. When subjected to deep fat frying, the batters with finer rice flour exhibited reduced moisture loss. Furthermore, the oil uptake was found to have a positive correlation with the particle size of rice flour (R 2 = 0.88), even showing the reduction of oil uptake by 15%. It could be synergistically attributed to the formation of outer starch granular layers, high batter viscosity/pickup, and reduced moisture loss by finer rice flour.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdeniz, N., Sahin, S., & Sumnu, G. (2005). Effects of different batter formulations on the quality of deep-fat-fried carrot slices. European Food Research and Technology, 221, 99–105.
AOAC. (2005). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. Maryland: AOAC international.
Bolade, M. K., Adeyemi, I. A., & Ogunsua, A. O. (2009). Influence of particle size fractions on the physicochemical properties of maize flour and textural characteristics of a maize-based nonfermented food gel. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 44, 646–655.
Choi, H. C. (2004). Current status of varietal improvement and use of specialty rice in Korea. Tsukuba: World Rice Research Conference.
Dogan, S. F., Sahin, S., & Sumnu, G. (2005). Effects of soy and rice flour addition on batter rheology and quality of deep-fat fried chicken nuggets. Journal of Food Engineering, 71, 127–132.
FAO. (2009). Rice market monitor. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Gaines, C. S., Donelson, J. R., & Finney, P. L. (1988). Effects of damaged starch, chlorine gas, flour particle size, and dough holding time and temperature on cookie dough handling properties and cookie size. Cereal Chemistry, 65, 384–389.
Ha, H. S., Kim, H. A., & Lee, K. H. (2009). Quality characteristics of Ssukgaen Dduk made with high-dietary fiber rice ‘Goami 2’ focused on yam. Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life, 19, 1032–1038.
Hemavathy, J., & Bhat, K. K. (1994). Effect of particle size on viscoamylographic behaviour of rice flour and vermicelli quality. Journal of Texture Studies, 5, 469–476.
Jung, Y. J., Seo, H. S., Myung, J. E., Shin, J. M., Lee, E., & Hwang, I. K. (2007). Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of rice cookies based on Goami 2 with sesames (white and black) and perilla seeds. Korea Society of Food and Cookery Science, 23, 785–792.
Kang, H. J., Hwang, I. K., Kim, K. S., & Choi, H. C. (2003). Comparative structure and physicochemical properties of Ilpumbyeo, a high-quality japonica rice, and its mutant, Suweon 464. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51, 6598–6603.
Kawas, M. L., & Moreira, R. G. (2001). Effect of degree of starch gelatinization on quality attributes of fried tortilla chips. Journal of Food Science, 66, 300–306.
Kim, J. S., Kim, S. B., & Kim, T. Y. (2006). Noodle making characteristics of Goami rice composite flours. The Korean Journal of Community Living Science, 17, 61–68.
Kim, J., Lim, J., Bae, I. Y., Park, H. G., Lee, H. G., & Lee, S. (2010). Particle size effect of lentinus edodes mushroom (Chamsong-I) powder on the physicochemical, rheological, and oil-resisting properties of frying batters. Journal of Texture Studies, 41, 381–395.
KREI. (2011). Rice supply and prospect. Suwon: Korean Rural Economic Institute.
Kum, J. S., & Lee, H. Y. (1999). The effect of the varieties and particle size on the properties of rice flour. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 31, 1542–1548.
Lee, S., & Inglett, G. E. (2007). Effect of an oat β-glucan-rich hydrocolloid (C-trim30) on the rheology and oil uptake of frying batters. Journal of Food Science, 72, E222–E226.
Lee, E. J., Seo, H. S., Lee, S. Y., Kim, S. H., & Hwang, I. K. (2006a). Quality characteristics of black sesame gruel with high-dietary fiber rice ‘Goami 2’. Korean Society of Food and Cookery Science, 22, 940–948.
Lee, K. W., Song, K. E., Lee, H. S., Kim, Y. K., Lee, S. W., Kim, D. J., et al. (2006b). The effects of Goami no. 2 rice, a natural fiber-rich rice, on body weight and lipid metabolism. Obesity, 14, 423–430.
Marshall, W. E. (1992). Effect of degree of milling of brown rice and particle size of milled rice on starch gelatinization. Cereal Chemistry, 69, 632–636.
Mellema, M. (2003). Mechanism and reduction of fat uptake in deep-fat fried foods. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 14, 364–373.
Moreira, R. G., Sun, X., & Chen, Y. (1997). Factors affecting oil uptake in tortilla chips in deep-fat frying. Journal of Food Engineering, 31, 485–498.
NASS. (2011). Rice stocks. Washington, DC: United States Department of Agriculture.
Nishita, K. D., & Bean, M. M. (1982). Grinding methods: their impact on rice flour properties. Cereal Chemistry, 59, 46–49.
Onwulata, C. I., & Konstance, R. P. (2006). Extruded corn meal and whey protein concentrate: effect of particle size. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 30, 475–487.
Salamone, J. C. (1996). Polymeric materials encyclopedia. New York: CRC Press.
Seo, S. J., Choi, Y. M., Lee, S. M., Kim, K. J., Son, J. R., & Lee, J. S. (2007). Determination of selected antioxidant compounds in specialty rice. Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition, 36, 499–502.
Shih, F., & Daigle, K. (1999). Oil uptake properties of fried batters from rice flour. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47, 1611–1615.
Shin, M., & Song, J. Y. (2007). Effects of soaking and particle sizes on the properties of rice flour and gluten-free rice bread. Food Science and Biotechnology, 16, 759–764.
Subba, D., & Katawal, S.B. (2011). Effect of particle size of rice flour on physical and sensory properties of Sel-roti. Journal of Food Science and Technology, (in press).
Thanatuksorn, P., Pradistsuwana, C., Jantawat, P., & Suzuki, T. (2005). Effect of surface roughness on post-frying oil absorption in wheat flour and water food model. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 85, 2574–2580.
Tie, J., Lee, E. S., Hong, S. T., & Ryu, G. H. (2007). Manufacturing of Goami flakes by using extrusion process. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 39, 146–151.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2010–0008483)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.M., Yoo, J., Inglett, G.E. et al. Particle Size Fractionation of High-Amylose Rice (Goami 2) Flour as an Oil Barrier in a Batter-Coated Fried System. Food Bioprocess Technol 6, 726–733 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0721-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0721-5