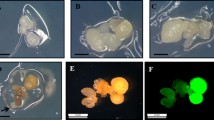
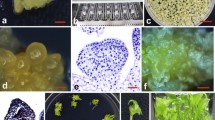
Abstract
An efficient and reproducible Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system via repetitive secondary somatic embryogenesis was developed for Rosa rugosa ‘Bao white’. Somatic embryogenesis was induced from in vitro-derived unexpanded leaflet explants on MS medium supplemented with 4.0 mg/L 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), 0.05 mg/L Kinetin and 30 g/L glucose. Secondary somatic embryos were successfully proliferated via cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis on MS medium containing 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D, 0.01 mg/L 6-benzyladenine and 45 g/L glucose under light intensity of 500–1,000 lux. The highest germination rate (86.33 %) of somatic embryos was observed on 1/2-strength MS medium containing 1.0 mg/L BA. Relying on the repetitive secondary somatic embryogenesis and A. tumefaciens strain EHA105 harboring the binary vector pBI121, a stable and effective Agrobacterium-mediated transformation pattern was developed. The presented transformation protocol, in which somatic embryo clumps at globular stage (0.02–0.04 g) were infected by Agrobacterium for 60 min and co-cultivated for 2 days, and then selected under a procedure of 3 steps, were confirmed to be optional by GUS histochemical assay and Southern blot analysis. The procedure described here will be very useful for the introgression of desired genes into R. rugosa ‘Bao white’ and the molecular analysis of gene function.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1976)
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
- BA:
-
6-Benzyladenine
- NAA:
-
a-Naphthalene acetic acid
- KT:
-
Kinetin
- ABA:
-
Gibberellin
- PGR:
-
Plant growth regulator
- nptII :
-
Neomycin phosphotransferase
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- Kan:
-
Kanamycin
- Cef:
-
Cefotaxime
- AS:
-
Acetosyringone
- X-Gluc:
-
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-glucuronide
References
An JH, Kim TI, Park HJ, Kim HM, Choi HJ, Lee TK (2011) Tormentic acid, a triterpenoid saponin, isolated from Rosa rugosa, inhibited LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2, and TNF-α expression through inactivation of the nuclear factor-κb pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 11:504–510
Bao Y, Liu GF, Shi XP, Xing W, Ning GG, Liu J, Bao MZ (2012) Primary and repetitive secondary somatic embryogenesis in Rosa hybrida ‘Samantha’. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109:411–418
Dai JL, Tan X, Zhan YG, Zhang YQ, Xiao S, Gao Y, Dong WX, Wang T, Wang XC, You XL (2011) Rapid and repetitive plant regeneration of Aralia elata Seem. via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:125–130
Dohm A, Ludwig C, Schilling D, Debener T (2001) Transformation of roses with genes for antifungal protein. Acta Hortic 547:27–31
Estabrooks T, Browne T, Dong ZM (2007) 2, 4, 5-Trichlorophenoxy-acetic acid promotes somatic embryogenesis in the rose cultivar‘Livin’ Easy’ (Rosa sp.). Plant Cell Rep 26:153–160
Feng LG, Chen C, Sheng LX, Liu P, Tao J, Su JL, Zhao LY (2010) Comparative analysis of headspace volatiles of Chinese Rosa rugosa. Molecules 15:8390–8399
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hoekema A (1993) New Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Transgenic Res 2:208–218
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: B-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Katsumoto Y, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Fukui Y et al (2007) Engineering of the rose flavonoid biosynthetic pathway successfully generated blue-hued flowers accumulating delphinidin. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1589–1600
Kaur N, Pratap PK, Sharma M, Ahuja PS (2006) Somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of Rosa bourboniana Desp. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:124–127
Khan H, Siddique I, Anis M (2006) Thidiazuron induced somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Capsicum annuum. Biol Plant 50:789–792
Kim CK, Chung JD, Park SH, Burrell AM, Kamo KK, Byrne DH (2004) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Rosa hybrida using the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 78:107–111
Kim SW, Oh JM, Liu JR (2009) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in zygotic embryo explant cultures of Rugosa rose. Plant Biotechnol Rep 3:199–203
Komatsuda T, Lee W, Oka S (1992) Maturation and germination of somatic embryos as affected by sucrose and plant growth regulators in soybeans Glycine gracilis Skvortz and Glycine max (L.) Merr. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 28:103–113
Kunitake H, Imamizo H, Mii M (1993) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature seed-derived calli of rugosa rose (Rosa rugosa Thunb.). Plant Sci 90:187–194
Lee YH, Jung MG, Kang HB, Choi KC, Haam S, Jun W, Kim YJ, Cho HY, Yooh HG (2008) Effect of anti-histone acetyltransferase activity from Rosa rugosa Thunb. (Rosaceae) extracts on androgen receptor-mediated transcriptional regulation. J Ethnopharmacol 118:412–417
Li XQ, Krasnyanski FS, Korban SS (2002a) Somatic embryogenesis, secondary somatic embryogenesis, and shoot organogenesis in Rosa. J Plant Physiol 159:313–319
Li XQ, Krasnyanski FS, Korban SS (2002b) Optimization of the uidA gene transfer into somatic embryo of rose via Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:453–459
Marchant R, Power JB, Lucas JA, Davey MR (1998) Biolistic transformation of rose (Rosa hybrida L.). Ann Bot 81:109–114
Mauri PV, Manzanera JA (2004) Effect of abscisic acid and stratification on somatic embryo maturation and germination of holm oak (Quercus ilex L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 40:495–498
Murali S, Sreedhar D, Lokeswari TS (1996) Regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from petal-derived calli of Rosa hybrida L. cv arizona (hybrid tea). Euphytica 91:271–275
Murashige T, Skoog F (1976) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ng TB, He JS, Niu SM, Zhao L, Pi ZF, Shao W, Liu F (2004) A gallic acid derivative and polysaccharides with antioxidative activity from rose (Rosa rugosa) flowers. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:537–545
Ning GG, Xiao X, Lv HY, Li X, Zuo Y, Bao MZ (2012) Shortening tobacco life cycle accelerates functional gene identification in genomic research. Plant Biol 14:934–943
Park JC, Kim SC, Choi MR, Song SH, Yoo EJ, Kim SH, Miyashro H, Hattori M (2005) Anti-HIV protease activity from rosa family plant extracts and rosamultin from Rosa rugosa. J Med Food 8:107–109
Peña L, Pérez RM, Cervera M, Juárez JA, Navarro L (2004) Early events in Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Citrus explants. Ann Bot 94:67–74
Pinto G, Silva S, Park YS, Neves L, Araujo C, Santos C (2008) Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis induction in Eucalyptus globulus Labill.: basal medium and anti-browning agents. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 95:69–78
Prange ANS, Serek M, Bartsch M, Winkelmann T (2010) Efficient and stable regeneration from protoplasts of Cyclamen coum Miller via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 101:171–182
Raemakers CJJM, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (1995) Secondary somatic embryogenesis and applications in plant breeding. Euphytica 81:93–107
Ribas AF, Dechamp E, Champion A, Bertrand B, Combes MC, Verdeil JL, Lapeyre F, Lashermes P, Etienne H (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Coffea arabica (L.) is greatly enhanced by using established embryogenic callus cultures. BMC Plant Bio 11:92. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-92
Sharma P, Pandey S, Bhattacharya A, Nagar PK, Ahuja PS (2004) ABA associated bio-chemical changes during somatic embryo development in Camellia sinensis (L.) O Kuntze. J Plant Physiol 161:1269–1276
Shi XP, Dai XG, Liu GF, Zhang JW, Ning GG, Bao MZ (2010) Cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis and efficient plant regeneration in camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 46:117–125
Vergne P, Maene M, Guillaume G, Aurelie C, Debener T, Mohammed B (2010) Somatic embryogenesis and transformation of the diploid Rosa chinensis cv Old Blush. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 100:73–81
Wang Z, Ye SF, Li JJ, Zheng B, Bao MZ, Ning GG (2011) Fusion primer and nested integrated PCR (FPNI-PCR): a new high-efficiency strategy for rapid chromosome walking or flanking sequence cloning. BMC Biotech 11:109
Xing W, Bao MZ, Qin HD, Ning GG (2010) Micropropagation of Rosa rugosa through axillary shoot proliferation. Acta Biol Cracov Bot 52:69–75
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171985) and the National Science and Technology Ministry of China (No. 2011AA100208). We thank all the colleagues in our lab for constructive discussion and technical support. We are also grateful to Dr. Alex C. McCormac for critical editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Werbrouck.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, W., Bao, Y., Luo, P. et al. An efficient system to produce transgenic plants via cyclic leave-originated secondary somatic embryogenesis in Rosa rugosa . Acta Physiol Plant 36, 2013–2023 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1578-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1578-9