Abstract
Introduction
We hypothesized that an elevated preoperative alkaline phosphatase (AP) predicted worse outcomes for patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for neuroendocrine tumor (NET) liver metastases.
Methods
We reviewed all patients who underwent TACE for metastatic NET between 2009 and 2013. Survival was evaluated using preprocedure variables.
Results
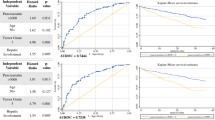
One hundred and nine patients underwent 210 TACE procedures. The average age was 57.7 years (range 20–78). Primary sites included pancreas (N = 20), other gastrointestinal (N = 52), lung (N = 9), and unknown (N = 28). The tumor was grade 1 in 68 (62 %), grade 2 in 21 (19 %), and grade 3 in 3 (3 %). Extrahepatic disease was present in 54 (50 %) and greater than 50 % hepatic tumor burden by imaging in 63 (58 %). Elevated bilirubin occurred in 8 (7 %), elevated AP in 22 (20 %), elevated ALT in 21 (19 %), and elevated AST in 41 (38 %). Univariate predictors included tumor grade (43 vs 27 vs 21 months, p = 0.015), hepatic tumor burden (59 vs 37 months, p = 0.009), and elevated AP (59 vs 23 months, p < 0.001). On multivariate analysis, only elevated AP (p = 0.001) predicted worse survival.
Conclusions
Elevated AP prior to TACE for metastatic NET portends a worse survival outcome, even more so than tumor grade or extent of hepatic disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim SJ, Kim JW, Han SW, Oh DY, Lee SH, Kim DW, Im SA, Kim TY, Seog Heo D, Bang YJ. Biological characteristics and treatment outcomes of metastatic or recurrent neuroendocrine tumors: tumor grade and metastatic site are important for treatment strategy. BMC Cancer 2010;10:448
Mayo SK, Herman JM, Cosgrove D, Bhagat N, Kamel I, Geschwind JFH, Pawlik TM. Emerging approaches in the management of patients with neuroendocrine liver metastasis: Role of liver-directed and systemic therapies. J Am Coll Surg 2013;216(1):123–134
Schmidt C, Bloomston M, Shah MH. Well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: a review covering basic principles to loco-regional and targeted therapies. Oncogene 2011;30:1497–1505
Burns WR, Edil BH. Neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors: Guidelines for management and update. Current Treatment Option in Oncology 2012;13:24–34
Arrese D, McNally ME, Chokshi R, Feria-Arias E, Schmidt C, Klemanski D, Gregory G, Khabiri H, Shah M, Bloomston M. Extrahepatic disease should not preclude transarterial chemoembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:1114–1120
Vogl TJ, Naguib NNN, Zangos S, Eichler K, Hedayati A, Nour-Eldi NEA. Liver metastases of neuroendocrine carcinomas: Interventional treatment via transarterial embolization, chemoembolization and thermal ablation. Euro J Rad 2009;72:517–528
Ho AS, Picus J, Darcy MD, Tan B, Gould JE, Pilgram TK, Brown DB. Long-term outcome after chemoembolization and embolization of hepatic metastatic lesions from neuroendocrine tumors. AJR 2007;188:1201–1207
Hoffmann RT, Paprottka P, Jakobs TF, Trumm CG, Reiser MG. Arterial therapies of non-colorectal cancer metastases to the liver (from chemoembolization to radioembolization). Abdom Imaging 2011;36:671–676
Guiu B, Deschamps F, Aho S, Munck F, Dromain C, Boige V, Malka D, Leboulleux S, Ducreux M, Schlumberger M, Baudin E, de Baere T. Liver/biliary injuries following chemoembolization of endocrine tumours and hepatocellular carcinoma: Lipiodol vs. drug-eluting beads. J Hepatology 2012;56:609–617
Bhagat N, Reyes DK, Lin M, Kamel I, Pawlik TM, Frangakis C, Geshwind JF. Phase II study of chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: High incidence of biliary injury. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2013;36(2):449–459
Whitney R, Valek V, Fages JF, Garcia A, Narayanan G, Tatum C, Hahl M, Martin RC 2nd. Transarterial chemoembolization and selective internal radiation for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: A comparison of efficacy and cost. The Oncologist 2011;16:594–601
Akahori T, Sho M, Tanaka T, Nishiofuku H, Kinoshita S, Nagai M, Kichikawa K, Nakajima Y. Significant efficacy of new transcatheter arterial chemoembolization technique for hepatic metastases of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Anticancer Research 2013;13:3355–3358
Glazer ES, Tseng JF, Al-Refaie W, Solorzano CC, Liu P, Willborn KA, Abdalla EK, Vauthey JN, Curley SA. Long-term survival after surgical management of neuroendocrine hepatic metastases. HPB (Oxford) 2010;12:427–433
Hur S, Chung JW, Kim HY, Oh DY, Lee SH, Bang YJ, Kim WH. Survival outcomes and prognostic factors of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatic neuroendocrine metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2013;24:947–956
Gupta S, Johnson MM, Murthy R, Ahrar K, Wallace MJ, Madoff DC, McRae SE, Hicks ME, Rao S, Vauthey JN, Ajani JA, Yao JC. Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: Variables affecting response rates and survival. Cancer 2005;104(8):1590–1602
Varker KA, Martin EW, Klemanski D, Palmer B, Shah MH, Bloomston M. Repeat transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for progressive hepatic carcinoid metastases provides results similar to first TACE. J Gastrointest Surg 2007;11(12):1680–5
Therasse P, ARbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verwij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92(3):205–16
Lewis MA, Jaramillo S, Roberts L, Fleming CJ, Rubin J, Grothey A. Hepatic artery embolization for neuroendocrine tumors: Postprocedural management and complications. The Oncologist 2012;17:725–731
Touzios JG, Kiely JM, Pitt SC, Rilling WS, Quebbeman EJ, Wilson SD, Pitt HA. Neuroendocrine hepatic metastases: Does aggressive management improve survival? Ann Surg 2005;241:776–785
Reichling JJ, Kaplan MM. Clinical use of serum enzymes in liver disease. Dig Dis Sci 1988;33(12):1601–14
Bloomston M, Al-Saif O, Klemanski D, Pinzone JJ, Martin EW, Palmer B, Guy G, Khabiri H, Ellison EC, Shah MH. Hepatic artery chemoembolization in 122 patients with metastatic carcinoid tumor: Lessons learned. J Gastrointest Surg 2007;11:264–71
Janson ER, Holmberg L, Stridsberg M, Eriksson B, Theodorsson E, Wilander E, Oberg K. Carcinoid tumors: Analysis of prognostic factors and survival in 301 patients from a referral center. Ann Oncol 1997;8(7):685–90.
Clancy TE, Sengupta TP, Paulus J, Ahmed F, Duh MS, Kulke MH. Alkaline phosphatase predicts survival in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Dig Dis Sci 2006;51(5):877–84.
Ahmed A, Turner G, King B, Jones L, Culliford D, McCance D, ARdill J, Johnston BT, Poston G, Rees M, Buxton-Thomas M, Caplin M, Ramage JK. Midgut neuroendocrine tumours with liver metastases: results of the UKINETS study. Endocr Relat Cancer 2009;16(3):885–94.
Hur S, Chung JW, Kim HC, Oh DY, Lee SH, Bang YJ, Kim WH. Survival outcomes and prognostic factors of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatic neuroendocrine metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2013;24(7):947–56.
Dong XD, Carr BI. Hepatic artery chemoembolization for the treatment of liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: a long-term follow-up in 123 patients. Med Oncol 2011;28:S286-S290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onesti, J.K., Shirley, L.A., Saunders, N.D. et al. Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase Prior to Transarterial Chemoembolization for Neuroendocrine Tumors Predicts Worse Outcomes. J Gastrointest Surg 20, 580–586 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2998-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2998-6