Abstract
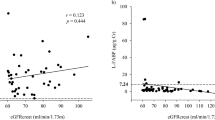
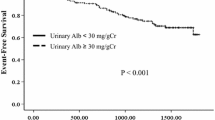
Background: We reported that urinary L-FABP reflected the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). This study is aimed to evaluate the clinical significance of urinary liver type fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) as a biomarker for monitoring CKD. Methods: Urinary L-FABP was measured using human L-FABP ELISA kit (CMIC.Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The relations between urinary L-FABP and clinical parameters were evaluated in non-diabetic CKD (n = 48) for a year. In order to evaluate the influence of serum L-FABP derived from liver upon urinary L-FABP, both serum and urinary L-FABP were simultaneously measured in patients with CKD (n = 73). Results: For monitoring CKD, the cut-off value in urinary L-FABP was determined as 17.4 μg/g.cr. by using a receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve. Renal function deteriorated significantly more in patients with ‘high’ urinary L-FABP (n = 36) than in those with ‘low’ L-FABP (n = 12). The decrease in creatinine clearance was accompanied by an increase in urinary L-FABP, but not in urinary protein. Serum L-FABP in patients with CKD was not correlated with urinary L-FABP. Conclusion: Urinary excretion of L-FABP increases with the deterioration of renal function. Serum L-FABP did not influence on urinary L-FABP. Urinary L-FABP may be a useful clinical biomarker for monitoring CKD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW: Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 108: 2154–2169, 2003
Kamijo A, Sugaya T, Hikawa A, Okada M, Okumura F, Yamanouchi M, Honda A, Okabe M, Fujino T, Hirata Y, Omata M, Kaneko R, Fujii H, Fukamizu A, Kimura K: urinary excretion of fatty acid-binding protein reflects stress overload on the proximal tubules. Am J Pathol 165: 1243–1255, 2004
Kamijo A, Kimura K, Sugaya T, Yamanouchi M, Hikawa A, Hirano N, Hirata Y, Goto A, Omata M: Urinary fatty acid binding protein as a new clinical marker for the progression of chronic renal disease. J Lab Clin Med 143: 23–30, 2004
Watanabe N, Kamei S, Ohkubo A, Yamanaka M, Ohsawa S, Makino K, Tokuda K: Urinary protein as measured with a pyrogallol red-molybdate complex, manually and in a Hitachi 726 automated analyzer. Clin Chem 32: 1551–1554, 1986
Horio M, Orita Y, Manabe S, Sakata M, Fukunaga M: Formula and nomogram for predicting creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Clin Exper Nephrol 1: 110–114, 1997
Kamisaka, Maezawa H, Inagaki T, Okano K: A low molecular weight binding protein for organic anions (Z protein) from human hepatic cytosol: purification and quantitation. Hepatology 1: 221–227, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamijo, A., Sugaya, T., Hikawa, A. et al. Urinary liver-type fatty acid binding protein as a useful biomarker in chronic kidney disease. Mol Cell Biochem 284, 175–182 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9047-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9047-9