Abstract
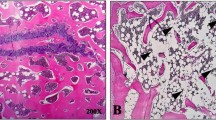
Osteoporosis is a most frequent systemic skeletal disease characterized as low bone mineral density and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, resulting in increased bone fragility and fracture risk. Although several drugs such as bisphosphonates, estrogen replacement treatment, and selective estrogen receptor modulators have been used to treat osteoporosis, all these are not the ideal drugs because of insufficient curative ability and adverse side effects. Recently, atorvastatin has ordinarily been prescribed as an anti-hyperlipidemia drug, not as an anti-osteoporosis drug. However, its clinical outcome and potential treatment mechanism are still unclear. In this study, the bilateral ovariectomy of rabbits was duplicated to develop osteoporosis animal model. The effect of atorvastatin on in vivo was determined, and the functional mechanism was studied in vitro after the curative effect was explored. Atorvastatin was observed to significantly increase the mechanical parameters such as maximum load, stiffness, and energy-absorbing capacity, and it improved the microarchitecture. The anti-osteoporosis activity of atorvastatin may be the result of the promotion of differentiation of osteoblasts by inducing synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor, bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), core-binding factor alpha 1 (CBFα1), and inhibition of osteoclast formation through the osteoprotegerin (OPG)-receptor activator for the nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) system. Our study observations give reliable experimental evidence for clinical application of atorvastatin to treat the disorder of osteoporosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furuzawa M, Chen H, Fujiwara S, Yamada K, Kubo KY (2014) Chewing ameliorates chronic mild stress-induced bone loss in senescence-accelerated mouse (SAMP8), a murine model of senile osteoporosis. Exp Gerontol 55:12–18
Hamrick I, Schrager S, Nye AM (2015) Treatment of osteoporosis: current state of the art. Wien Med Wochenschr 165:54–64
Lasota A, Danowska-Klonowska D (2004) Experimental osteoporosis: different methods of ovariectomy in female white rats. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst 49(suppl 1):129–131
Willson T, Nelson SD, Newbold J, Nelson RE, LaFleur J (2015) The clinical epidemiology of male osteoporosis: a review of the recent literature. Clin Epidemiol 7:65–76
Makras P, Delaroudis S, Anastasilakis AD (2015) Novel therapies for osteoporosis. Metabolism 64:1199–1214
Shirke SS, Jadhav SR, Jagtap AG (2008) Methanolic extract of Cuminum cyminum inhibits ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233:1403–1410
Salari Sharif P, Abdollahi M, Larijani B (2011) Current, new and future treatments of osteoporosis. Rheumatol Int 31:289–300
Wang PS, Solomon DH, Mogun H, Avorn J (2000) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of hip fractures in elderly patients. JAMA 283:3211–3216
Song C, Guo Z, Ma Q, Chen Z, Liu Z, Jia H, Dang G (2003) Simvastatin induces osteoblastic differentiation and inhibits adipocytic differentiation in mouse bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:458–462
Wong RW, Rabie AB (2005) Early healing pattern of statin-induced osteogenesis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43:46–50
Dai L, Xu M, Wu H, Xue L, Yuan D, Wang Y, Shen Z, Zhao H, Hu M (2016) The functional mechanism of simvastatin in experimental osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 34:23–32
Zhao FD, Pollintine P, Hole BD, Adams MA, Dolan P (2009) Vertebral fractures usually affect the cranial endplate because it is thinner and supported by less-dense trabecular bone. Bone (NY) 44:372–379
Hordon LD, Itoda M, Shore PA, Shore RC, Heald M, Brown M, Kanis JA, Rodan GA, Aaron JE (2006) Preservation of thoracic spine microarchitecture by alendronate: comparison of histology and microCT. Bone (NY) 38:444–449
Chen H, Wu M, Kubo KY (2012) Combined treatment with a traditional Chinese medicine, Hachimi-jio-gan (Ba-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan) and alendronate improves bone microstructure in ovariectomized rats. J Ethnopharmacol 142:80–85
Liu X, Lei W, Wu Z, Cui Y, Han B, Fu S, Jiang C (2012) Effects of glucocorticoid on BMD, micro-architecture and biomechanics of cancellous and cortical bone mass in OVX rabbits. Med Eng Phys 34:2–8
Schorlemmer S, Ignatius A, Claes L, Augat P (2005) Inhibition of cortical and cancellous bone formation in glucocorticoid-treated OVX sheep. Bone (NY) 37:491–496
Li L, Zeng Z, Cai G (2011) Comparison of neoeriocitrin and naringin on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1. Phytomedicine 18:985–989
Moshiri A, Shahrezaee M, Shekarchi B, Oryan A, Azma K (2015) Three-dimensional porous gelapin–simvastatin scaffolds promoted bone defect healing in rabbits. Calcif Tissue Int 96:552–564
Jules J, Ashley JW, Feng X (2010) Selective targeting of RANK signaling pathways as new therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14:923–934
Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A, Maffulli N (2014) Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res 9:18
Tsartsalis AN, Dokos C, Kaiafa GD, Tsartsalis DN, Kattamis A, Hatzitolios AI, Savopoulos CG (2012) Statins, bone formation and osteoporosis: hope or hype? Hormones (Athens) 11:126–139
Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, Chan J, Chen D, Rossini G, Boyce B, Zhao M, Gutierrez G (1999) Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science 286:1946–1949
Park YS, David AE, Park KM, Lin CY, Than KD, Lee K, Park JB, Jo I, Park KD, Yang VC (2013) Controlled release of simvastatin from in situ forming hydrogel triggers bone formation in MC3T3-E1 cells. AAPS J 15:367–376
Tan S, Zhang B, Zhu X, Ao P, Guo H, Yi W, Zhou GQ (2014) Deregulation of bone forming cells in bone diseases and anabolic effects of strontium-containing agents and biomaterials. Biomed Res Int 2014:814057
Drake MT, Clarke BL, Lewiecki EM (2015) The pathophysiology and treatment of osteoporosis. Clin Ther 37:1837–1850
Oryan A, Kamali A, Moshiri A (2015) Potential mechanisms and applications of statins on osteogenesis: current modalities, conflicts and future directions. J Control Release 215:12–24
Handal JA, John TK, Goldstein DT, Khurana JS, Saing M, Braitman LE, Samuel SP (2012) Effect of atorvastatin on the cortical bones of corticosteroid treated rabbits. J Orthop Res 30:872–876
Rajamannan NM (2015) Atorvastatin attenuates bone loss and aortic valve atheroma in LDLR mice. Cardiology 132:11–15
Lin S, Huang J, Fu Z, Liang Y, Wu H, Xu L, Sun Y, Lee WY, Wu T, Qin L, Cui L, Li G (2015) The effects of atorvastatin on the prevention of osteoporosis and dyslipidemia in the high-fat-fed ovariectomized rats. Calcif Tissue Int 96:541–551
Phimphilai M, Zhao Z, Boules H, Roca H, Franceschi RT (2006) BMP signaling is required for RUNX2-dependent induction of the osteoblast phenotype. J Bone Miner Res 21:637–646
Lee MH, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Park HD, Kang AR, Kyung HM, Sung JH, Wozney JM, Kim HJ (2003) Ryoo HM BMP-2-induced Runx2 expression is mediated by Dlx5, and TGF-beta 1 opposes the BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation by suppression of Dlx5 expression. J Biol Chem 278:34387–34394
Kim T, Ha H, Shim KS, Cho WK, Ma JY (2013) The anti-osteoporotic effect of Yijung-tang in an ovariectomized rat model mediated by inhibition of osteoclast differentiation. J Ethnopharmacol 146:83–89
Kim IS, Song YM, Cho TH, Kim JY, Weber FE, Hwang SJ (2009) Synergistic action of static stretching and BMP-2 stimulation in the osteoblast differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. J Biomech 42:2721–2727
Nahar-Gohad P, Gohad N, Tsai CC, Bordia R, Vyavahare N (2015) Rat aortic smooth muscle cells cultured on hydroxyapatite differentiate into osteoblast-like cells via BMP-2-SMAD-5 pathway. Calcif Tissue Int 96:359–369
Nishimura R, Hata K, Harris SE, Ikeda F, Yoneda T (2002) Core-binding factor alpha 1 (Cbfa1) induces osteoblastic differentiation of C2C12 cells without interactions with Smad1 and Smad5. Bone (NY) 31:303–312
Johan MF, Goodeve AC, Reilly JT (2004) Activating loop mutations in the PDGFR alpha and beta genes are rare in core binding factor acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 127:123–124
Lee MH, Kwon TG, Park HS, Wozney JM, Ryoo HM (2003) BMP-2-induced Osterix expression is mediated by Dlx5 but is independent of Runx2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:689–694
Jang H, Kim EJ, Park JK, Kim DE, Kim HJ, Sun WS, Hwang S, Oh KB, Koh JT, Jang WG, Lee JW (2014) SMILE inhibits BMP-2-induced expression of osteocalcin by suppressing the activity of the RUNX2 transcription factor in MC3T3E1 cells. Bone (NY) 61:10–18
Ito M (2013) Effect of anti-osteoporotic agents on cortical microstructure. Clin Calcium 23:1035–1039
Ito M (2006) Assessment of effect of anti-osteoporotic agents using high-resolution CT. Clin Calcium 16:2034–2042
Jadhav SB, Jain GK (2006) Statins and osteoporosis: new role for old drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 58:3–18
Zhang H, Xing WW, Li YS, Zhu Z, Wu JZ, Zhang QY, Zhang W, Qin LP (2008) Effects of a traditional Chinese herbal preparation on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Maturitas 61:334–339
Peng JH, Hu YY, Feng Q, Cheng Y, Xu LL, Chen SD, Tao Q, Li FH (2009) Effect of Jianpi Huoxue decoction-containing serum on tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion and gene expression of endotoxin receptors in RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide. Chin J Integr Med 15:198–203
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wu W (2008) Effects of the drug (BSZGC)-containing serum on proliferation of rat’s osteoclasts and TRACP activity in vitro. J Tradit Chin Med 28:211–216
Ito T, Takemasa M, Makino K, Otsuka M (2013) Preparation of calcium phosphate nanocapsules including simvastatin/deoxycholic acid assembly, and their therapeutic effect in osteoporosis model mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 65:494–502
Ito T, Saito M, Uchino T, Senna M, Iafisco M, Prat M, Rimondini L, Otsuka M (2012) Preparation of injectable auto-forming alginate gel containing simvastatin with amorphous calcium phosphate as a controlled release medium and their therapeutic effect in osteoporosis model rat. J Mater Sci Mater Med 23:1291–1297
Hamada H, Ohshima H, Otsuka M (2012) Dissolution medium responsive simvastatin release from biodegradable apatite cements and the therapeutic effect in osteoporosis rats. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater 10:22–28
Liu X, Zhang S, Lu X, Zheng S, Li F, Xiong Z (2012) Metabonomic study on the anti-osteoporosis effect of Rhizoma drynariae and its action mechanism using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Ethnopharmacol 139:311–317
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the participants who took part in this study. This study was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201101), and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (A2014206208), and the Natural Science Foundation of Bengbu City, China (Grants 10S090202, 2014-01-01-A-R-07-0006, 2016-05-06-A-R-07-0005). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author contributions
T.M. and H.Z. designed the study, and H.Z. and Y.X. performed the experiment. H.Z., Y.X., and Q.S. analyzed the data. Q.H. and T.M. contributed in reagents/materials/analysis tools; Z.B., K.M., and T.M. wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no actual or potential competing interests.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Xie, Y., baloch, Z. et al. The effect of atorvastatin, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor (HMG-CoA), on the prevention of osteoporosis in ovariectomized rabbits. J Bone Miner Metab 35, 245–254 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-016-0750-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-016-0750-2