Abstract
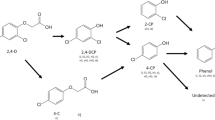
Molinate is a thiocarbamate herbicide used worldwide in rice crop protection. As with other pesticides, molinate is a recognized environmental pollutant, detected in soils, irrigation water, or rivers and bio-accumulated by some wildlife forms. For this reason, and in spite of its low toxicity to humans, environmental protection measures, which include reduction of use and/or remediation processes, are recommended. Due to its physic-chemical properties, molinate can easily disperse and react in the environment, originating diverse transformation products, some with increased toxicity. In spite of being a xenobiotic compound, molinate can also suffer microbial transformation by bacteria or fungi, sometimes serving as nutrient and energy source. In an attempt to isolate microorganisms to be used in the bioremediation of molinate-contaminated sites, a mixed culture, dominated by the actinobacterium Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T, was recovered from the runoff of a molinate-producing plant. Beyond a promising tool to decontaminate molinate-polluted sites, this culture also brought interesting insights into the biology of the degradation of this herbicide. In this review, an overview of the distribution and properties of molinate as environmental contaminant, the capability of microorganisms to transform this herbicide, and some reflections about possible bioremediation approaches are made.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar C, Ferrer I, Borrull F, Marcé RM, Barceló D (1999) Monitoring of pesticides in river water based on samples previously stored in polymeric cartridges followed by on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography diode array detection and confirmation by atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Act 386:237–248
Aktas O, Çençen F (2007) Bioregeneration of activated carbon: a review. Int Biodeter Biodegr 59:257–272
Albanis TA, Hela DG, Sakellarides TM, Konstantinou IK (1998) Monitoring of pesticide residues and their metabolites in surface and underground waters of Imathia (N. Greece) by means of solid-phase extraction disks and gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 823:59–71
Alister CA, Araya MA, Kogan M (2010) Adsorption and desorption variability of four herbicides used in paddy rice production. J Environ Sci Heal B 46:62–68
Barata C, Damasio J, López MA, Kuster M, López de Alda M, Barceló D, Riva MC, Raldúa D (2007) Combined use of biomarkers and in situ bioassays in Daphnia magna to monitor environmental hazards of pesticides in the field. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:370–379
Barreiros L, Fernandes A, Ferreira AC, Pereira H, Bastos MM, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2008) New insights into a bacterial metabolic and detoxifying association responsible for the mineralization of the thiocarbamate herbicide molinate. Microbiology 154:1038–1046
Barreiros L, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2011) Bacterial diversity and bioaugmentation in floodwater of a paddy field in the presence of the herbicide molinate. Biodegradation 22:445–461
Barreiros L, Nogales B, Manaia CM, Ferreira AC, Pieper DH, Reis MA, Nunes OC (2003) A novel pathway for mineralization of the thiocarbamate herbicide molinate by a defined bacterial mixed culture. Environ Microbiol 5:944–953
Barreiros L, Peres J, Azevedo NF, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2012) Environmental factors influencing molinate biodegradation by a two-member mixed culture in rice paddy field floodwater. Int Biodeter Biodegr 72:52–58
Batista S, Silva E, Galhardo S, Viana P, Maria Cerejeira MJ (2002) Evaluation of pesticide contamination of ground water in two agricultural areas of Portugal. Int J Environ An Ch 82:601–609
Boluda R, Quintanilla JF, Bonilla JA, Sáez E, Gamón M (2002) Application of the Microtox test and pollution indices to the study of water toxicity in the Albufera Natural Park (Valencia, Spain). Chemosphere 46:355–369
Bouchez T, Patureau D, Dabert P, Juretschko S, Doré J, Delgenès P, Moletta R, Wagner M (2000) Ecological study of a bioaugmentation failure. Environ Microbiol 2:179–190
Carrasco JM, Sabater C, Alonso JL, Gonzalez J, Botella S, Amoros I, Ibanez MJ, Boira H, Ferrer J (1992) Molinate decontamination processes in effluent water from rice fields. Sci Total Environ 123(124):219–232
Carvalho D, Mendes A, Magalhães FD, Nunes OC (2010) Treatment of waters containing the thiocarbamate herbicide molinate through an adsorption/bio-regeneration system using a low cost adsorbent. Water Air Soil Poll 207:289–298
Castro M, Manaia CM, Silva Ferreira AC, Nunes OC (2005) A case study of molinate application in a Portuguese rice field: herbicide dissipation and proposal of a clean-up methodology. Chemosphere 59:1059–1065
Cerejeira MJ, Viana P, Batista S, Pereira T, Silva E, Valerio MJ, Silva A, Ferreira M, Silva-Fernandes AM (2003) Pesticides in Portuguese surface and ground waters. Water Res 37:1055–1063
Cessna AJ, McConkey BG, Elliott JA (2013) Herbicide transport in surface runoff from conventional and zero-tillage fields. J Environ Qual 42:782–793
Charizopoulos E, Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E (1999) Occurrence of pesticides in rain of the Axios River Basin, Greece. Environ Sci Technol 33:2363–2368
Chen WR, Wu C, Elovitz MS, Linden KG, Mel Suffet IH (2008) Reactions of thiocarbamate, triazine and urea herbicides, RDX and benzenes on EPA Contaminant Candidate List with ozone and with hydroxyl radicals. Water Res 42:137–144
Chiron S, Alba FA, Barceló D (1993) Comparison of on-line solid-phase disk extraction to liquid–liquid extraction for monitoring selected pesticides in environmental waters. Environ Sci Technol 27:2352–2359
Christen EW, Chung S-O, Quayle W (2006) Simulating the fate of molinate in rice paddies using the RICEWQ model. Agr Water Manage 85:38–46
Claver A, Ormad P, Rodriguez L, Ovelleiro JL (2006) Study of the presence of pesticides in surface waters in the Ebro River Basin (Spain). Chemosphere 64:1437–1443
Cochran RC, Formoli TA, Pfeifer KF, Aldous CN (1997) Characterization of risks associated with the use of molinate. Regul Toxicol Pharm 25:146–157
Coelho C, Oliveira AS, Pereira MF, Nunes OC (2006) The influence of activated carbon surface properties on the adsorption of the herbicide molinate and the bio-regeneration of the adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 138:343–349
Coppotelli BM, Ibarrolaza A, Del Panno MT, Morelli IS (2008) Effects of the inoculant strain Sphingomonas paucimobilis 20006FA on soil bacterial community and biodegradation in phenanthrene-contaminated soil. Microb Ecol 55:173–183
Correia P, Boaventura RAR, Reis MAM, Nunes OC (2006) Effect of operating parameters on molinate biodegradation. Water Res 40:331–340
Council Directive 98/83/EC (1998) Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption as amended by regulation 1882/2003/EC
Coupe RH, Welch HL, Pell AB, Thurman EM (2005) Herbicide and degradate flux in the Yazoo River Basin. Int J Environ An Ch 85:1127–1140
Daffonchio D, Baggi G, Molinari GP, Ranalli G, Sorlini C (1996) Effects of the herbicide molinate on the metabolic activities of a degradative Streptomyces griseus strain. J Environ Sci Heal B 31:257–268
Daffonchio D, Zanardini E, Vatta P, Sorlini C (1999) Cometabolic degradation of thiocarbamate herbicides by Streptomyces sp. strain M2 and effects on the cell metabolism. Ann Microbiol Enzim 49:13–22
Decreto-Lei 261/2003, 21 Outubro 2003. Anexo. Objectivos de qualidade para determinadas substâncias perigosas incluídas nas famílias ou grupos de substâncias da lista II do anexo XIX ao Decreto-Lei nº 236/98, de 1 de Agosto. Diário da República, série I-A, nº 244.
Deuel LE, Turner FT, Brown KW, Price JD (1978) Persistence and factors affecting dissipation of molinate under flooded rice culture. J Environ Qual 7:373–377
Duarte M, Ferreira-da-Silva F, Lünsdorf H, Junca H, Gales L, Pieper DH, Nunes OC (2011) Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T molinate hydrolase, a novel cobalt-dependent amidohydrolase. J Bacteriol 193:5810–5816
Ellis MK, Richardson AG, Foster JR, Smith FM, Widdowson PS, Farnworth MJ, Moore RB, Pitts MR, Wickramaratne GA (1998) The reproductive toxicity of molinate and metabolites to the male rat: effects on testosterone and sperm morphology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 151:22–32
Feitz AJ, Joo SH, Guan J, Sun Q, Sedlak DL, Waite TD (2005) Oxidative transformation of contaminants using colloidal zero-valent iron. Colloid Surface A 265:88–94
Finocchiaro R, Meli SM, Cignetti A, Gennari M (2005) Adsorption of molinate, terbuthylazine, bensulfuron-methyl, and cinosulfuron on different Italian soils. Fresen Environ Bull 14:690–697
Galhano V, Peixoto F, Gomes-Laranjo J, Fernández-Valiente E (2009) Differential effects of bentazon and molinate on Anabaena cylindrica, an autochthonous cyanobacterium of Portuguese rice field agro-ecosystems. Water Air Soil Poll 197:211–222
Galhano V, Peixoto F, Gomes-Laranjo J, Fernández-Valiente E (2010) Comparative toxicity of bentazon and molinate on growth, photosynthetic pigments, photosynthesis, and respiration of the Portuguese rice field cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Environ Toxicol 25:147–156
Golovleva LA, Finkelshtein ZI, Popovich NA, Skriabin GK (1981) Ordram transformation by microorganisms. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol 3:348–358
Gomes NCM, Kosheleva IA, Abraham W-R, Smalla K (2005) Effects of the inoculant strain Pseudomonas putida KT2442 (pNF142) and of naphthalene contamination on the soil bacterial community. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:21–33
Gómez-Gutiérrez AI, Jover E, Bodineau L, Albaiges J, Bayona JM (2006) Organic contaminant loads into the Western Mediterranean Sea: estimate of Ebro River inputs. Chemosphere 65:224–236
Hernandez F, Beltran J, Lopez FJ, Gaspar JV (2000) Use of solid-phase microextraction for the quantitative determination of herbicides in soil and water samples. Anal Chem 72:2313–2322
Hsieh Y-N, Liu L-F, Wang Y-S (1998) Uptake, translocation and metabolism of the herbicide molinate in tobacco and rice. Pestic Sci 53:149–154
Imai Y, Kuwatsuka S (1982) Degradation of the herbicide molinate in soils. J Pest Sci 7:487–497
Imai Y, Kuwatsuka S (1986a) Characteristics of microflora degrading the herbicide molinate in soil. J Pest Sci 11:57–63
Imai Y, Kuwatsuka S (1986b) The mode of metabolism of the herbicide molinate by four strains of microorganisms isolated from soil. J Pest Sci 11:111–117
Imai Y, Kuwatsuka S (1986c) Metabolic pathways of the herbicide molinate in four strains of isolated soil microorganisms. J Pest Sci 11:245–251
Imai Y, Kuwatsuka S (1988) Residues of the herbicide molinate and its degradation products in pot soil and rice plants. J Pest Sci 13:247–252
Infantino A, Pereira T, Ferrari C, Cerejeira MJ, Di Guardo A (2008) Calibration and validation of a dynamic water model in agricultural scenarios. Chemosphere 70:1298–1308
Jewell WT, Hess RA, Miller MG (1998) Testicular toxicity of molinate in the rat: metabolic activation via sulfoxidation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 149:159–166
Jewell WT, Miller MG (1999) Comparison of human and rat metabolism of molinate in liver microsomes and slices. Drug Metabol Dispos 27:842–847
Jiménez B, Moltó JC, Font G, Soriano JM (1999) Evaluation by HPLC-UV of polar pesticides in rice fields. Bull Environ Contam Tox 63:813–820
Johnson WG, Lavy TL (1995) Organic chemicals in the environment. Persistence of carbofuran and molinate in flooded rice culture. J Environ Qual 24:487–493
Kang HS, Park CJ, Gye MC (2009) Effects of molinate on survival and development of Bombina orientalis (Boulenger) embryos. Bull Environ Contam Tox 82:305–309
Klysheva AL, Golovleva LA, Ilyaletdinov AN (1980) Transformation of ordram by microorganisms isolated from soils of Kazakhstan rice paddies. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol 4:29–34
Köck M, Farré M, Martínez E, Gajda-Schrantz K, Ginebreda A, Asunción Navarro A, López de Alda M, Barceló D (2010) Integrated ecotoxicological and chemical approach for the assessment of pesticide pollution in the Ebro River delta (Spain). J Hydrol 383:73–82
Kogan M, Araya M, Alister C (2012) Water and sediment dynamics of penoxsulam and molinate in paddy fields: field and lysimeter studies. Pest Manag Sci 68:399–403
Konstantinou IK, Zarkadis AK, Albanis TA (2001) Photodegradation of selected herbicides in various natural waters and soils under environmental conditions. J Environ Qual 30:121–130
Kuivila KM, Jennings BE (2007) Input, flux, and persistence of six select pesticides in San Francisco Bay. Int J Environ An Ch 87:897–911
Kumar A, Saison C, Grocke S, Doan H, Waller T, Kookana R (2007) Assessment of pesticide impacts on the biological health of the rice ecosystem. Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation, Barton
Kuster M, López de Alda MJ, Barata C, Raldúa D, Barceló D (2008) Analysis of 17 polar to semi-polar pesticides in the Ebro River delta during the main growing season of rice by automated on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 75:390–401
LeBlanc L, Kuivila K (2008) Occurrence, distribution and transport of pesticides into the Salton Sea Basin, California, 2001–2002. In: Hurlbert S (ed) The Salton Sea centennial symposium. Springer, Netherlands, pp 151–172
Lopes AR, Danko AS, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2013) Molinate biodegradation in soils: natural attenuation versus bioaugmentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2691–2700
Lopes AR, Faria C, Prieto-Fernández A, Trasar-Cepeda C, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2011) Comparative study of the microbial diversity of bulk paddy soil of two rice fields subjected to organic and conventional farming. Soil Biol Biochem 43:115–125
Mabury SA, Cox JS, Crosby DG (1996) Environmental fate of rice pesticides in California. Rev Environ Contam T 147:71–117
Manaia CM, Nogales B, Weiss N, Nunes OC (2004) Gulosibacter molinativorax gen. nov., sp. nov., a molinate degrading bacterium, and classification of “Brevibacterium helvolum” DSM 20419 as Pseudoclavibacter helvolus gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:783–789
Mogyoródy F (2006) Reaction pathways in the electrochemical degradation of thiocarbamate herbicides in NaCl solution. J Appl Electrochem 36:635–642
Molinari GP, Sorlini C, Daffonchio D, Baggi G, Ruffo L (1992) Activity and evolution of mixed microbial culture degrading molinate. Sci Total Environ 123(124):309–323
Mrozik A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2010) Bioaugmentation as a strategy for cleaning up of soils contaminated with aromatic compounds. Microbiol Res 165:363–375
Nagy I, Schoofs G, Compernolle F, Proost P, Vanderleyden J, de Mot R (1995) Degradation of the thiocarbamate herbicide EPTC (S-ethyl dipropylcarbamothioate) and biosafening by Rhodococcus sp. strain NI86/21 involve an inducible cytochrome P-450 system and aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol 177:676–687
Neumann M, Liess M, Schulz R (2003) A qualitative sampling method for monitoring water quality in temporary channels or point sources and its application to pesticide contamination. Chemosphere 51:509–513
Norberg-King TJ, Durhan EJ, Ankley GT, Robert E (1991) Application of toxicity identification evaluation procedures to the ambient waters of the Colusa Basin Drain, California. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:891–900
Olaniran AO, Pillay D, Pillay B (2006) Biostimulation and bioaugmentation enhances aerobic biodegradation of dichloroethenes. Chemosphere 63:600–608
Önneby K, Jonsson A, Stenström J (2010) A new concept for reduction of diffuse contamination by simultaneous application of pesticide and pesticide-degrading microorganisms. Biodegradation 21:21–29
Ormad MP, Lanao MN, Mosteo R, Ovelleiro JL (2010) Effect of application of ozone and ozone combined with hydrogen peroxide and titanium dioxide in the removal of pesticides. Ozone-Sci Eng 32:25–32
Park BJ, Kyung KS, Choi JH, Im GJ, Kim IS, Shim JH (2005) Environmental fate of the herbicide molinate in a rice-paddy-soil lysimeter. Bull Environ Contam Tox 75:937–944
Pereira WE, Hostettler FD (1993) Nonpoint source contamination of the Mississippi River and its tributaries by herbicides. Environ Sci Technol 27:1542–1552
Phyu YL, Warne MS, Lim RP (2004) Toxicity of atrazine and molinate to the cladoceran Daphnia carinata and the effect of river water and bottom sediment on their bioavailability. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:308–315
Quayle WC, Oliver DP, Zrna S (2006) Field dissipation and environmental hazard assessment of clomazone, molinate, and thiobencarb in Australian rice culture. J Agr Food Chem 54:7213–7220
Readman JW, Albanis TA, Barceló D, Galassi S, Tronczynski J, Gabrielides GP (1993) Herbicide contamination of Mediterranean estuarine waters: results from a MED POL pilot survey. Mar Poll Bull 26:613–619
Ross LJ, Sava RJ (1986) Fate of thiobencarb and molinate in rice fields. J Environ Qual 15:220–224
Saleh DK, Lorenz DL, Domagalski JL (2011) Comparison of two parametric methods to estimate pesticide mass loads in California's Central Valley. JAWRA 47:254–264
SANCO/3047/99-Final, 3 June 2003. Review report for the active substance molinate. European Commission. Health and consumer protection directorate-general
Sapari P, Ismail BS (2012) Pollution levels of thiobencarb, propanil, and pretilachlor in rice fields of the muda irrigation scheme, Kedah, Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 184:6347–6356
Seiber JN, McChesney MM, Woodrow JE (1989) Airborne residues resulting from use of methyl parathion, molinate and thiobencarb on rice in the Sacramento Valley, California. Environ Toxicol Chem 8:577–588
Silva E, Batista S, Viana P, Antunes P, Serôdio L, Cardoso AT, Cerejeira MJ (2006) Pesticides and nitrates in groundwater from oriziculture areas of the ‘Baixo Sado’ region (Portugal). Int J Environ An Ch 86:955–972
Silva M, Fernandes A, Manaia CM, Mendes A, Nunes OC (2004) Preliminary feasibility study for the use of an adsorption/bio-regeneration system for molinate removal from effluents. Water Res 38:2677–2684
Soderquist CJ, Bowers JB, Crosby DG (1977) Dissipation of molinate in a rice field. J Agr Food Chem 25:940–945
Sudo M, Kawachi T, Hida Y, Kunimatsu T (2004) Spatial distribution and seasonal changes of pesticides in Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnology 5:77–86
Sudo M, Kunimatsu T, Okubo T (2002) Concentration and loading of pesticide residues in Lake Biwa basin (Japan). Water Res 36:315–329
Tanabe A, Mitobe H, Kawata K, Sakai M (1996) Monitoring of herbicides in river water by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 754:159–168
Thomas VM, Holt CL (1980) The degradation of [14C]molinate in soil under flooded and nonflooded conditions. J Environ Sci Heal B 15:475–484
Thompson IP, van der Gast CJ, Ciric L, Singer AC (2005) Bioaugmentation for bioremediation: the challenge of strain selection. Environ Microbiol 7:909–915
Tjeerdema RS, Crosby DG (1988) Disposition, biotransformation, and detoxification of molinate (ordram) in whole blood of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Pestic Biochem Phys 31:24–35
Tomlin C (2000) The pesticide manual: a world compendium. The British Crop Protection Council, Farnham
Torra-Reventós M, Yajima M, Yamanaka S, Kodama T (2004) Degradation of the herbicides thiobencarb, butachlor and molinate by a newly isolated Aspergillus niger. J Pest Sci 29:214–216
Tsochatzis ED, Tzimou-Tsitouridou R, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U, Karpouzas DG, Papageorgiou M (2012) Development and validation of an HPLC-DAD method for the simultaneous determination of most common rice pesticides in paddy water systems. Int J Environ An Ch 92:548–560
Tsuda T, Kojima M, Harada H, Nakajima A, Aoki S (1998) Pesticides and their oxidation products in water and fish from rivers flowing into Lake Biwa. Bull Environ Contam Tox 60:151–158
Tsuda T, Nakamura T, Inoue A, Tanaka K (2009a) Pesticides in water and sediment from littoral area of Lake Biwa. Bull Environ Contam Tox 82:683–689
Tsuda T, Nakamura T, Inoue A, Tanaka K (2009b) Pesticides in water, fish and shellfish from littoral area of Lake Biwa. Bull Environ Contam Tox 82:716–721
Tsuda T, Igawa T, Tanaka K, Hirota D (2011) Changes of concentrations, shipment amounts and ecological risk of pesticides in river water flowing into Lake Biwa. Bull Environ Contam Tox 87:307–311
Uno S, Shiraishi H, Hatakeyama S, Otsuki A, Koyama J (2001) Accumulative characteristics of pesticide residues in organs of bivalves (Anodonta woodiana and Corbicula leana) under natural conditions. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:35–47
Uno S, Shiraishi H, Hatakeyama S, Otsuki A (1997) Uptake and depuration kinetics and BCFs of several pesticides in three species of shellfish (Corbicula leana, Corbicula japonica, and Cipangopludina chinensis): comparison between field and laboratory experiment. Aquat Toxicol 39:23–43
Vidal A, Dinya Z, Mogyorodi F Jr, Mogyorodi F (1999) Photocatalytic degradation of thiocarbamate herbicide active ingredients in water. Appl Catal B-Environ 21:259–267
Vogel TM (1996) Bioaugmentation as a soil bioremediation approach. Curr Opin Biotech 7:311–316
Vryzas Z, Vassiliou G, Alexoudis C, Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of pesticide residues in surface waters in northeastern Greece. Water Res 43:1–10
Wackett LP, Hershberger CD (2001) Biocatalysis and biodegradation: microbial transformation of organic compounds. ASM, Washington
Wang C, Chamberlainb E, Shia H, Adams CD, Ma Y (2011) Investigation of oxidative degradation of molinate in various oxidation treatment systems by using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Global J Anal Chem 2:107–113
Wang F, Dörfler U, Schmid M, Fischer D, Kinzel L, Scherb H, Munch JC, Jiang X, Schroll R (2010) Homogeneous inoculation vs. microbial hot spots of isolated strain and microbial community: what is the most promising approach in remediating 1,2,4-TCB contaminated soils? Soil Biol Biochem 42:331–336
Warman AJ, Robinson JW, Luciakova D, Lawrence AD, Marshall KR, Warren MJ, Cheesman MR, Rigby SEJ, Munro AW, McLean KJ (2012) Characterization of Cupriavidus metallidurans CYP116B1—a thiocarbamate herbicide oxygenating P450–phthalate dioxygenase reductase fusion protein. FEBS J 279:1675–1693
WHO 1988, Environmental health criteria 76: thiocarbamate pesticides- a general introduction. International programme on chemical safety (INCHEM). http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc76.htm. Accessed 27 September 2013
Wickramaratne GA, Foster JR, Ellis MK, Tomenson JA (1998) Molinate rodent reproductive toxicity and its relevance to man: a review. Regul Toxicol Pharm 27:112–118
Yan GA, Yan X, Wu W (1997) Effects of the herbicide molinate on mixotrophic growth, photosynthetic pigments, and protein content of Anabaena sphaerica under different light conditions. Ecotox Environ Safe 38:144–149
Zyakun AM, Nefedova MY, Baskunov BP, Finkelstein ZI (1983) New products of the microbial degradation of ordram. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol 1:126–130
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Adélio Mendes and Margarida Bastos (FEUP) for critical review and valuable suggestions. This work was financially supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia in the form of projects PTDC/AAG-TEC/3909/2012 and PEst-C/EQB/UI0511/2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nunes, O.C., Lopes, A.R. & Manaia, C.M. Microbial degradation of the herbicide molinate by defined cultures and in the environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 10275–10291 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5316-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5316-9