Abstract
Background
An aperture in the form of four squares arranged symmetrically along the cartesian coordinates with equal distances from the center investigated. Three models are suggested in the computation of the Point Spread Function PSF using the FFT technique. In the 1st model, circular annulus is placed in the center, while in the 2nd model a square annulus is shown, and in the 3rd model, two symmetric squares in the models 1, 2 are replaced by two symmetric rectangles while the center remains of square annulus. In all the models, central obstruction is made seeking to improve the PSF.
Results
An analytical formula for the PSF for the aperture described in the 1st model is obtained. In addition, the autocorrelation corresponding to these apertures are computed and compared with the known autocorrelation corresponding to the whole square aperture. An application on speckle imaging is given using these apertures combined with the diffuser. All images for the design of the apertures and the speckle images are made using the MATLAB code.
Conclusions
The resolution computed from the FWHM showed an improvement for the suggested square apertures as compared with the uniform square aperture where the total width is kept constant. In addition, the strength of the legs in the PSF for the suggested apertures is much higher than that corresponding the uniform aperture which makes it useful for imaging of extended objects.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Background
Speckle can be explained using the Hugen’s principle by considering the microscopic structure of the surface [1]. Since 1948 before the advent of laser, the aperture filtering suggested annular shape for the sake of resolution improvement realized by many authors like in [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11].
Aperture filtering methods proposed and investigated in 1983 where linear and quadratic apertures are studied in [12, 13]. Recently, a linear-quadratic arrangement is investigated in [14]. Different applications on speckle microscopic and medical images are investigated by the author using different filtering apertures e.g., in [15,16,17]. Novel techniques for the generation of customized speckle with a tailored speckle-size distributions are presented in [18,19,20].
Recently, design of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices with rectangular optical apertures was fabricated and used for the detection of transparent biological cells [21]. An interesting recent work provides that different approaches of mathematical modeling are considered in [21, 22]. For example, dynamic behavior of two predators-one prey model with generalized functional response and time-fractional derivative is outlined and discussed in [21].
In this paper, we propose new rectangular arrangement of apertures of two-fold symmetry with annular central disc, and we compute the PSF and the autocorrelation corresponding to these apertures. In addition, an application on speckle imaging modulated by the aperture is given. Theoretical analysis, results and discussion are followed by a conclusion.
2 Methods
A rectangular aperture composed of four equal squares placed at equal distances from the center. The total matrix of rectangular shape has dimensions 1024 × 1024 pixels. While, the dimensions of each square (x0, y0) = 128 × 128 pixels and located along the cartesian coordinates (x, y) at distances ± xd and ± yd as shown in the Fig. 1a. A central obstruction is governed by the difference between two circles where the width of the annulus = 32 pixels. A uniform illumination emitted from laser beam is incident upon this new aperture, hence the amplitude transmittance is written as follows:
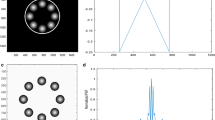
a An aperture composed of four squares arranged symmetrically along the cartesian coordinates and obstructed by a circular annulus placed in the center of diameter 128 pixels and annular width 16 pixels. Each square has dimensions 128 × 128 pixels compared with the whole matrix of dimensions 1024 × 1024 pixels. b An aperture composed of four squares arranged symmetrically along the cartesian coordinates and obstructed by a square annulus placed in the center of width 16 pixels. Each square has dimensions 128 × 128 pixels and shifted by 256 pixels along the coordinates. c An aperture composed of two squares arranged symmetrically along the y-axis, and two rectangles arranged along x-axis and obstructed by an annular rectangle placed in the center. Each square has dimensions 128 × 128 pixels and shifted by 256 pixels along the coordinates, and each rectangle has dimensions 128 × 512 pixels and shifted by ± 256 pixels from the x-axis. d An aperture composed of a square of dimensions 640 × 640 pixels
where
The Point Spread Function (PSF) corresponding to the novel aperture described by Eq. (1) is obtained by operating the Fourier transform as follows:
The 1st transformation is solved taking in consideration that convolution of two functions is equivalent to simple product of the F.T. of each function, hence we write:
\(F.T. \{rect\left(x,y\right)\otimes\) δ(\(x-{x}_{d},y)\}=F.T.\{rect\left(x,y\right)\}. F.T. \{\updelta ( x-{x}_{d},y)\}\)
It is known that the Fourier transform of rect function is written as:
where sinc function is defined as:
sinc(x’) = sin (πx’)/πx’, x’ = x0 u/λf, and a similar expression for sinc(y’).
Also, the Fourier transform of circ function as obtained as follows [11]:
where Z1 = 2πr01w1/λf and Z2 = 2πr02w2/λf represent the reduced coordinates in the Fourier planes corresponding to the external and internal circles of radii r01 and r02. \({w}_{\mathrm{1,2}}=\sqrt{{u}^{2}+{v}^{2 }}\,is\,the\,radial\,coordinate\,in\,the\,Fourier\,plane\) \(corresponding\,to\,each\,circle.\)
The Fourier transform of shifted dirac-delta function gives inclined plane wave as:
Similar expressions are obtained for the other shift of the dirac-delta function as follows:
Plugging Eqs. (3–8) in Eq. (2), we get:
Hence, the PSF is finally written as follows:
Equation (10) is rewritten as follows:
The intensity impulse response is computed from the modulus square of Eq. (11) as follows:
3 Results
The design of the new apertures is shown in the Fig. 1. It is fabricated using a MATLAB code. The aperture composed of four squares arranged symmetrically along the cartesian coordinates and obstructed by an annulus placed in the center is shown as in the Fig. 1a. Each square has dimensions 128 × 128 pixels compared with the whole matrix of dimensions 1024 × 1024 pixels. The total effective aperture in the whole matrix has dimensions of 640 × 640 pixels. Similar aperture is shown in the Fig. 1b while the circular annulus is replaced by square annulus. In addition, an aperture of two symmetric squares arranged along y-axis, and two symmetric rectangles placed along x-axis where the center remains of square annulus that is shown in the Fig. 1c. An effective square aperture of dimensions 640 × 640 pixels is shown in the Fig. 1d.
The PSF corresponding to the apertures under investigation are computed using the FFT technique. The plot of the PSF in the range from 460 pixels up to 560 pixels is shown in the Fig. 2a for the 1st model, while Fig. 2b represents the PSF for the 2nd model, and the Fig. 2c for the PSF for the 3rd model. A comparative result for the PSF corresponding to the effective square is shown in the Fig. 2d.
a The PSF for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1a, in the range from 460 to 560 pixels. The cut-off for the central lope = 55 pixels while the central peak at 54 pixels. FWHM = 1 pixels. b The PSF for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1b, in the range from 460 to 560 pixels. The cut-off for the central lope = 55 pixels while the central peak at 54 pixels. FWHM = 1 pixels. c The PSF for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1c, in the range from 460 to 560 pixels. The cut-off for the central lope = 55 pixels while the central peak at 54 pixels. FWHM = 1 pixels. The side lobes are strengthen compared with that shown in the figure (b). d The PSF for the whole aperture shown in the Fig. 1d, in the same range as in the figure (b). The cut-off for the central lope = 57 pixels while the central peak at 54 pixels. FWHM = 3 pixels
A magnified portion of the plot is shown in the range from 500 pixels up to 526 pixels as in the Fig. 3a–C Fig. 2a–c. The image of the diffraction for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1a is plotted as in the Fig. 4. It is named as the intensity Fourier spectrum or intensity impulse response equals the modulus square of the PSF corresponding to the aperture.
a The PSF for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1a, in the range from 500 to 526 pixels. The cut-off for the central lope = 15 pixels while the central peak at 14 pixels. FWHM = 1 pixels. b The PSF for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1b, in the range from 500 to 526 pixels. The cut-off for the central lope = 15 pixels while the central peak at 14 pixels. FWHM = 1 pixels. c The PSF for the aperture shown in the Fig. 1c, in the range from 500 to 526 pixels. The cut-off for the central lope = 15 pixels while the central peak at 14 pixels. FWHM = 1 pixels. The side lobes are strengthen compared with that shown in the figure (b). d The PSF for the whole square of dimensions 640 × 640 pixels in the same range as in the figure (c). The cut-off for the central lope = 17 pixels while the central peak at 14 pixels. FWHM = 3 pixels
The intensity impulse response corresponding to the aperture shown in the Fig. 1a
The speckle image in presence of the aperture shown in L.H.S., while in the R.H.S., speckle image in absence of the aperture is represented as in the Fig. 5a.
a In the L.H.S., speckle image in presence of the aperture shown in the Fig. 1a, while in the R.H.S., speckle image in absence of the aperture is shown. b In the L.H.S., speckle plot in presence of the aperture, while in the R.H.S., speckle plot in absence of the aperture is shown. The range is from 60 up to 120 pixels.
The corresponding line plots are shown as in the Fig. 5b. The range taken is from 60 up to 120 pixels for both line plots.
The autocorrelation of the apertures shown in the Fig. 1a–d are computed and plotted as shown in the Fig. 6a–d, where the total band width = 1280 pixels which is two times the aperture width of 640 pixels.
a The autocorrelation of the aperture shown in the Fig. 1a, where the total band width = 1280 pixels which is two times the aperture width 640 pixels. b The autocorrelation of the aperture shown in the Fig. 1b, where the total band width = 1280 pixels which is two times the aperture width 640 pixels. c The autocorrelation of the aperture shown in the Fig. 1c, where the total band width = 1280 pixels which is two times the aperture width 640 pixels. d The autocorrelation of the aperture shown in the Fig. 1d, where the total band width = 1280 pixels which is two times the aperture width 640 pixels
4 Discussion
It is shown, referring to the Figs. 2 and 3, that the full width at half-maximum (FWHM) is the same for the suggested models, shown in the Fig. 1, and equals to 1 pixels as compared with the FWHM for the effective aperture which equals 3 pixels. Hence, resolution improvement is attained using the suggested designs of apertures shown in the Fig. 1a–c. The difference between the 1st two models and the 3rd model is apparent in the strengthen of the legs shown in the Fig. 2c as compared with the legs shown in the Fig. 2a, b. In all cases, as shown in the Fig. 2a–c, the strength of the legs of the diffraction pattern (PSF) is considered useful for imaging of extended objects as compared with the weak strength obtained in Fig. 2d.
The magnified portions representing the PSF corresponding to the different models shown in the Fig. 3, is for the discrimination of the PSF structure.
The image of the diffraction from the aperture shown in the Fig. 4 is called the intensity impulse response or the modulus square of the PSF.
The speckle image formed in presence of the aperture using certain diffuser as a randomly distributed function is obtained by applying the Fourier transform (F.T.) upon the multiplication of the aperture and the diffuser illuminated by uniform amplitude emitted from spatially filtered laser beam. Hence, the formed speckle image is the convolution product of the PSF for the aperture and the F.T. corresponding to the diffuser. While the other speckle image shown in the R.H.S. is simply the F.T. corresponding to the same diffuser as in the Fig. 5a.
It is shown that the plots corresponding to the speckle images are different Fig. 5b. In addition, the contrast is decreased in presence of the aperture as expected for the modulating aperture.
The autocorrelation of the apertures has a new shape, as shown in the Fig. 6a–C, which depends on the geometry of the aperture as compared with the known autocorrelation of square aperture giving simple triangular distribution Fig. 6d. It is shown, referring to the Fig. 6a, b, that nearly equal shapes are obtained. In addition, the center has a peak much grater than the two nearly equal side peaks.
While in the Fig. 6c, the ratio of the side peaks to the central peak is much greater than the ratio obtained in the Fig. 6a, b. This is attributed to the unequal zones shown in the Fig. 1c where the arrangement has two conjugate rectangles along x-coordinate instead of two conjugate squares as in the Fig. 6a, b.
5 Conclusions
The resolution computed from the FWHM showed an improvement for the suggested square apertures as compared with the uniform square aperture where the total width is kept constant. In addition, the strength of the legs in the PSF for the suggested apertures is much higher than that corresponding the uniform aperture which makes it useful for imaging of extended objects. Further increase in the legs strength is attained in the 3rd model as shown in the Fig. 2c.
A comparison of the obtained speckle image using the different apertures with that obtained in absence of the aperture showed a remarkable difference since the speckle in case of apertures resulted from the convolution product of the ordinary speckle and the PSF. In addition, the autocorrelation corresponding to the different apertures showed a geometry related to its distribution.
We believe that the suggested apertures may be useful for imaging transparent cells in confocal microscopy since the resulted PSF is further improved as compared with the ordinary rectangular apertures.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PSF:
-
Point spread function
- FWHM:
-
Full width at half-maximum
- F.T.:
-
Fourier transform
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- ⊗ :
-
Symbol for convolution operation
References
Goldfscher LI (1965) Autocorrelation function and power spectral density of laser-produced speckle patterns. J Opt Soc Am 55:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSA.55.000247
Toroldo di Francia GJ (1955) Resolving power and information. Opt Soc Am 45:497
Sheppard CJR, Choudhury A (1977) Image formation in scanning microscope. Opt Acta 24:1051–1073
Sheppard CJR, Mattews HJ (1987) Imaging in high aperture optical systems. J Opt Soc Am A 4:1354–1360
Cox JJ, Sheppard CJR, Wilson T (1982) Super- resolution by confocal flourescent microscopy. Optik 60:391–396
Sheppard CJR, Larkin KG (1994) Optimal concentration of electromagentic radiation. J Mod Opt 41:1495–1505
Sheppard CJR, Hegedus ZS (1988) Axial behavior of pupil- plane filters. J Opt Soc Am A 5:643–647
Sheppard CJR, Choudhury A (2004) Annular pupils, radial polarization, and superresolution. Appl Opt 43:4322–4327
Sheppard CJR (2007) Filter performance parameters for high numerical aperture focusing. Opt Lett 32:1653–1655
Sheppard CJR, Martinez- Corral M (2008) Filter performance parameters for vectorial high aperture wave fields. Opt Lett 33:476–478
Sheppard CJR (2007) Fundamentals of superresolution. Micron 38:165–169
Hamed AM, Clair JJ (1983) Image and super-resolution in optical coherent microscopes. Optik 64:277–284
Hamed AM, Clair JJ (1983) Studies on optical properties of confocal scanning optical microscope using pupils with radially transmission distribution. Optik 65:209–218
Hamed AM (2017) Improvement of point spread function Optic (PSF) using linear- quadratic aperture. Optik 131:838–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.11.201
Hamed AM (2011) Discrimination between speckle images using diffusers modulated by some deformed apertures: simulations. J Opt Eng 50:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3530085
Hamed AM (2019) Design of a cascaded black-linear distribution (CBLD) in circular aperture and its application on confocal laser scanning microscope (CSLM). Am J Opt Photon 3
Hamed AM (2020) Image processing of Ramses II statue using speckle photography modulated by a new Hamming- Linear aperture. J Phys (PRAMANA) 94:126
R. V, V. & Singh RK, (2016) Determining helicity and topological structure of coherent vortex beam from laser speckle. Appl Phys Lett 109:111108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4962952
Funamizu H, Uozumi J (2007) Generation of fractal speckles by means of a spatial light modulator. Opt Express 15:7415–7422
Cabezas L, Amaya D, Bolognini N, Lencina A (2015) Speckle fields generated with binary diffusers and synthetic pupils implemented on a spatial light modulator. Appl Opt 54:5691–5696. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.54.005691
Zhou X, Poenar DP et al (2008) Design of MEMS devices with optical apertures for the detection of transparent biological cells. Biomed Microdevices 10:639–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-09175-6
Salih Djilali and Behzad Ghanbari (2021) Dynamic behavior of two predators- one prey model with generalized functional response and time- fractional derivative 2021:235. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-021-03395-9
Boudjema I, Djilali S (2018) Turing-Hopf bifurcation in Gauss-type model with cross diffusion and its application. Nonlinear Stud 25(3):665–687
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author AMH has presented all steps of manuscript preparation, including the idea, the method including the theoretical analysis, and the results with discussions. TAA-S has assisted in the results and idea of rectangular formation. Both the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamed, A.M., Al-Saeed, T.A. Investigation of rectangular apertures and their application on speckle imaging. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 11, 52 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-022-00237-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-022-00237-9