Abstract
“Eu,” is a traditional millet-based mild alcoholic beverage consumed by the Toto tribe of West Bengal. Eu is prepared through the fermentation of millet with locally groomed starter culture “Moaa.” The study highlighted the overview of the traditional process of Eu preparation along with its molecular and biochemical characterization. Semi-structured interviews were conducted for collecting the ethnobotanical data and the samples. We have also included qualitative assays like acute toxicity, antioxidant, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), molecular docking, and physiochemical characteristics such as pH and alcohol content. Moreover, metagenomics of the starter culture has been reported. This type of study on Eu has not been done previously. Therefore, it seems to be a pioneer report especially on the metagenomic analysis of Eu. Results revealed that Eu has a very low alcohol content (approximately 1-3%) and a high antioxidant capacity. GC-MS analysis identified thirteen different bioactive compounds. Metagenomics analysis revealed that the Eu has a high source of various beneficial gut microflora. Overall Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Enterococcus, Leuconostoc, and Pediococcus are dominant genera identified in the starter culture. The present study revealed that the consumption of Eu is safe and has the potential to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS). Hence, the commercialization of Eu can be an alternative source of income for the poor endangered Toto tribe.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Consumption of alcoholic beverages started way back in the pre-Vedic period [1]. India is an abode of several tribal communities and is widely distributed in different geographical regions. Cutting across the communities, alcoholic beverages are hugely popular among Indian tribal people. Natural fermentation is an ancient preservation technique that has been carried forward by the indigenous knowledge of the ancestors among tribes [2]. Socio-linguistic groups throughout India have traditionally used plants for fermentation and for brewing different types of beverages. Interestingly, almost every tribe has its indigenous alcoholic beverages and the preparation, as well as preservation techniques. There are several reports on the fermented beverages of different tribes like Judima, Haria, Jou, and Jaanr, but only a few pieces of literature are available on Eu [3].
Eu is the most popular recreational drink of Toto. Toto tribe is an endangered, most primitive Indo Bhutanese Mongoloid isolated group in West Bengal and they are “Forest dwellers.” This small group of primitive tribes living in a small enclave of Alipurduar District called “Totopara” in the vicinity of Madarihat (gateway to Jaldapara National park) (Fig. 1). As per the first census after Independence in 1951, Totos were almost extinct with only 321 members but now according to the latest census of 2011, the total population of Totos increased to 1387, among them 737 are men and 650 are women [4]. Eu preparation is an integral part of their culture and practices. It is consumed by both males and females equally in huge amounts during festivals, marriages and religious ceremonies, etc. [4]. People from the Toto tribe also often use Eu as the remedy for various chronic ailments. Besides, the poor economic condition of the tribe led them to use the brew as a health drink or as an energy source. A well-prepared Eu is sweet in taste with very mild alcohol content. Interestingly, every Toto family prepares this drink but only a few families sell it.
Map of Toto inhabited area. Totopara is situated in West Bengal, India [Source: earth.google.com]
Being a primitive resident of the sub-Himalayan Region, the Toto tribe has acquired knowledge of wild medicinal plants. The topographical features of the region remain the driving force for the selection of wild herbs used for Eu preparation. Eu is prepared from fermented seeds of finger millet (Eleusine coracana), grown in the semi-arid sub-Himalayan region. The traditionally prepared round and flattened rice ball or amylolytic starter culture is the main source for the mild alcohol production in the Eu. Generally, the starter cultures used in traditional drinks contain a heterogeneous mixture of probiotic microbes which may impact the digestibility of the people resulting in a stout physical body. Although some bacteria used in those starter cultures are culturable, several others are non-culturable too. Lamentably, this microbial population present in Eu starter culture has not been evaluated yet.
In the present study, we intended to characterize microbes present in Eu starter and also used Ilumina based 16S RNA for the evaluation of uncultured microbes. Moreover, we have also studied the methodology of the Eu preparation along with the herbs present in the starter culture. Characterization of Eu by way of the qualitative assay, antioxidant activity, and GC-MS analysis has also been done. Besides we have done in silico docking along with energy minimization to evaluate the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activity of Eu through various in silico techniques.
Materials and methods
Survey
“Totopara,” the home of the unique “Toto” tribes located 22 km away from Madarihat and situated in 26° 49′ 48.00″ N latitude and 89° 18′ 36.00″ E longitude in the Alipurduar District of West Bengal. The survey was started during 2018-2019. It is nearly impossible to know when the Toto tribe started preparing Eu. Eu is mainly a boiled and fermented millet product; however, modifications occur when a starter mixture is added. During the interactions with the Toto people, several questions have been asked including natural resources and ingredients, storage and preparation methods, and health-related problems. A total survey was further divided into two parts: (i). A starter culture or “Moaa” preparation (ii). Processing and fermentation methodology of millet for Eu preparation.
-
(1)
Basic ingredient used in starter culture/“Moaa”/rice tablet preparation
Moaa (the starter used in Eu preparation) serves as a source for microorganisms which is added for the initiation of fermentation. The diameter of the starter culture ranges from 2 to 14 cm. Moaa is made up of locally grown rice powder and variations come with the addition of formulated medicinal plants (Table 1). Preparation of this starter-culture is as follows:
Rice is soaked for 12-14 h, put in a large wooden motor. Four-five (4-5) chili and 3-4 g wild plants are blended using a heavy pastel. Water is added and rice cakes are made with variable diameters. Charcoal is added to the rice cakes to prevent fungal growth. The old starter culture is sprinkled over the new one. New rice cakes are covered by special ferns (containing sori) or the large size leaf of Hatipoilo. Then finally the “moaa” is sun-dried for 1-5 days. After drying these rice cakes can be used for several months.
-
(i)
Fermentation of millet
Seeds of finger millets are collected (5-10 g) and boiled in a large-sized (15-20 L) open container for at least 45 min. The excess water is removed by using a locally made filter called “Jitung” (a porous bamboo bucket). Boiled seeds are sun-dried for a day. After drying, starter culture or moaa is mixed with the boiled seeds and kept in a large mud container (15-20 L) called, “Monsoi” covering with a cotton cloth and kept it in dark for 1 week (5-8 days). After 1 week, the fermented seeds are soaked in freshwater for 1 h before use. Eu is now ready for consumption and this refreshing drink is served in a specially made bamboo glass called “polio” (Figs. 2, 3).
Sample collection and primary characterization
Freshly prepared Eu and the amylolytic starter culture (Moaa) were collected from Toto houses in Totopara near Madarihat, Alipuduar District. We have collected three replicates in three different seasons of the year. The alcohol content was measured by an alcohol meter (Borosil). The pH determination of the filtrate was measured by a pH meter (Lab India) at room temperature.
Ethical statement
For assessing the acute toxicity level of Eu, the rat animal model was used with proper guidelines. All the animals used in the experiment were reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethical Committee, Department of Zoology, NBU (Permit No. 840/ac/04/CPCSEA).
Animal maintenance
Male Wistar albino rats were used for the acute toxicity experiment. Animals were purchased from authorized vendors in Kolkata, India. Adult rats (n = 5) were kept in polypropylene cages (Tarson, India) with bedding material (padding husk). The rats were kept in the animal house of the Department of Zoology, the University of North Bengal, with proper food and water. The animals were kept for at least 7 days for acclimatization before the experiment.
In vivo acute toxicity test
Acute toxicity tests were done according to the OECD guideline No. 423 for rodents. The dosage was set as 2000 mg/kg/BW (according to OECD guideline 423). The treated rats were kept under observation for 7 days for any delayed signs of toxicological effects.
Solvent selection for qualitative assay
Fifty (50) milliliters fresh sample was filtrated through Whatman No. 1 filter paper. Filtered samples were concentrated at reduced pressure and temperature and lyophilized. Dry powder was stored at 4 °C for further use. Nine different solvents with different polarities were used as extracting solvents. They were hexene, benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, acetone, ethanol, methanol, and water (according to increasing polarity from hexane to water).
Qualitative screening of sample
Qualitative tests of the sample including total carbohydrate, reducing sugar, protein, flavonoid, tannin, ascorbate, cardiac glycoside, alkaloid, and saponin were done as per Labar et al. (2019) [12] with slight modifications.
In vitro antioxidant assay
A fresh sample (50 mL) was filtered using Whatman No. 1 filter paper, for avoiding the disturbance of bio-colloidal particles. The sample was concentrated at reduced pressure and temperature using a rotary evaporator then lyophilized. Dry powder was stored at 4 °C for further use.
Various in vitro antioxidant activity, namely, DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl), total antioxidant, nitric oxide, hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorous acid, superoxide radical scavenging activity, and ferric reducing power assay were performed to determine the free radical scavenging activity of the Eu sample [13, 14].
Quantification of total phenol and flavonoid content
The total phenol content was of the sample was measured by using Folincio Calteu at 725 nm where gallic acid used as standard [15]. Total flavonoid content was measured and absorbance was taken at 510 nm and Quercitin was used as standard [15].
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis
The active compounds of the sample were determined by the GC-MS analysis using the standard protocol of GCMS-QP2010. The details of the methodology have already been discussed in one of our previous papers [16].
In silico molecular docking
Compounds identified from GC-MS analysis were used for in silico molecular docking purposes. Nuclear factor-kappa beta (NF-κβ) plays a crucial role in coordinating the expression pattern of genes regulating cerebral ischemia. It has been proposed earlier that oxidative stress can decrease the expression of the NF-κβ complex [17]. Moreover, adenylate cyclase is important in regulating oxidative stress. This protein is also associated with neuroprotective functionalities following cell injury [18]. Previously, it has been reported that hemeoxygenase 1 can reduce the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, inflammatory stress, and oxidative stress. This protein is also associated with various emerging therapeutic strategies [19]. In this consequence, we have targeted three receptor proteins, namely, Human IkB kinase beta (4KIK), the crystal structure of human soluble adenylyl cyclase with the inhibitor bithionol (5D0R), and hemeoxygenase 1 in complex with inhibitor (6EHA) were used for molecular docking study. All the protein structures were downloaded from PDB database (https://www.rcsb.org/). PDB structures were converted to pdbqt after calculation of Gasteiger charge. Ligand molecules were downloaded from NCBI pubchem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) in sdf format. SMILES server (https://cactus.nci.nih.gov/translate/) converted sdf format to pdb. Finally, those ligand-pdb structures were converted to pdbqt format after torsion calculations. Finally, molecular docking was performed through the Auto-dock vina tool (http://vina.scripps.edu/). Energy minimization was done based on steepest descent and conjugant gradient methods with 100 cycles for each algorithm.
Metagenomic DNA extraction from the starter culture
The dry rice tablets (Moaa) were ground using a sterile motor pastel. Two (2 g) grams of powdered sample was dissolved and homogenized in 19 mL of 0.85% normal saline (NaOH) solution. The samples were filtered using Whatman No. 1 filter paper. The resulting filtrate was then centrifuged at around 8000 rcf for 15 min. The pallets were subjected to total community DNA extraction using a DNA extraction kit (QIAGEN, ZYMO RESEARCH, Thermo Fisher). The DNA was kept at −20 °C until further processing. Furthermore, 16S Metagenomic amplicon sequencing (V3-V4 region-based) was done and analyzed.
Metagenomic sequencing based on V3-V4 part of 16SrRNA
Illumina™ Nextseq platform used for the 16S rRNA. The primer sequences used were as follows: 5′AGAGTTTGATGMTGGCTCAG3′ for the forward strand and 5′ TTACCGCGGCMGCSGGCAC3′ for the reverse strand. Forty (40) nanograms of extracted DNA was used for amplification along with 10 pM (picoMolar) of each primer. The amplicons from each sample were purified with Ampure beads to remove unused primers and an additional 8 cycles of PCR was performed using Illumina barcoded adapters to prepare the sequencing libraries. Libraries were purified using Ampure beads and quantitated using Qubit dsDNA High Sensitivity assay kit. Sequencing was performed using Illumina Miseq with a 2 × 300PE v3 sequencing kit.
Bioinformatics analysis
Raw data QC was done using FASTQC and MULTIQC, followed by trimming of adapters and low-quality reads by TRIMGALORE. The trimmed reads are further taken for the processing which includes merging of paired-end reads, chimeria removal, and OUT abundance calculation and estimation correction, this is achieved by QIIME/MOTHUR/KRAKEN/BRACKEN workflows [20]. This workflow enables highly accurate investigations at genus level. The databases used are SILVA/GREENGENES/NCBI. Each read is classified based on percent (%) coverage and identity. For further validation of obtained result, we used MG-RAST web server (https://www.mg-rast.org/) [21].
Statistical analysis
For reproducibility, all analyses were performed three times and reported as the mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s test using KY Plot version 5.0 (32 bit) for windows. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results and discussion
Survey
The survey was conducted among the tribal people of Totopara in Alipurduar District of West Bengal to access the traditional knowledge of Eu preparation. After the successful interaction with more than 50 tribal people in Totopara, the Eu preparation technology has been summarized in two categories as the starter for Eu preparation and brew of Eu. The main ingredient of the beverage is low cost and easily grown finger millet and rice cake. The medicinal importance of Eu had been reported by the elders of the Toto community. A total of seven plants are used in Eu, which have a huge ethnomedicinal value in the locality. During this survey, we have found that the Toto community consumes Eu throughout the year. Another attraction of Eu preparation is that all the females of the community cooperatively made the brew.
Alcohol content and pH of the sample
The alcohol content of the brew was 0.5-3% (pH 3.2-4.1) and this mild alcohol content is not harmful to their health and is quietly refreshing and useful as an energy drink. As compared to other commercial alcoholic drinks (40-60%), low alcoholic content in Eu is useful in compensating for water loss during heavy work pressure in the summer season.
Acute toxicity test
Rats were fed with Eu extract at a dose of 2000 mg/kg/day/BW. It revealed no toxicological symptoms.
Qualitative test
Qualitative screening is very important for the functional characterization of the sample. Among the nine different extracting solvents, methanol and acetone persistently proved to be the most potent solvent. Solvent extraction plays a crucial role in the extraction of potential compounds. Total carbohydrate, reducing sugar, flavonoid, protein, and tannin were present in the higher polarity solvents that are in water, acetone, and ethanol. Methanol showed the best solvent for the extraction of chemicals (see Additional file 1).
Antioxidant assay
Cellular metabolism is the main reason for the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or reactive nitrogen species (RNS) [22]. Stress is also the reason for ROS production. Free radicals are originated from the unpaired electrons of reactive molecules. Major ROS includes hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorous acid whereas major RNS is peroxynitrite. This ROS and RNS play a crucial role in depression and anxiety [23]. Studies have reported that ROS generation causes endogenous disorder and also increases the probability of neurodegeneration and associated cognitive disorders.
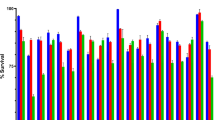
One of the important and most used assays is DPPH free radical scavenging assay. Eu showed the highest scavenging activity that is 59.95 ± 0.57% with respect to the standard ascorbic acid (Fig. 4A). DPPH can accept hydrogen or electron radicals and provide stability, work as a source of natural antioxidants [24]. A gradual decrease of the color was observed with the increasing concentration of the sample. DPPH scavenging assay showed the presence of a significant amount of antioxidants in the sample. Moreover, it was also revealed that the total antioxidant activity proportionally raised with Eu concentration. In the present study, total antioxidant activity was found to be 71.30 ± 1.73% (at 200 μg/mL) when compared to standard ascorbic acid (Fig. 4B). This result showed that the sample has a high neutralizing capacity of endogenous ROS formation.
Nitric oxide (NO) can easily couple with oxygen to form peroxynitrite and peroxynitrite. Nitric oxide is a mediator for cellular activation resulting in inflammatory cellular damage. However continuous coupling of NO with superoxide causes the formation of peroxynitrile that leads to a cognitive disorder. At the site of inflammation, hypochlorous acid is produced due to chlorine ion oxidation that causes the target cell lysis [25]. The sample has a significant capacity to scavenge this nitric oxide in its high concentration although it is lower than the standard curcumin (61.64 ± 0.65% at the 200 μg/mL) (Fig. 4C). It was found that Eu not only inhibits nitric oxide but also secures cellular lysis by preventing the formation of hypochlorous acid. Ferric reducing power assay is a method for the determination of antioxidant levels in biological samples. In this study, the highest concentration (200μg/mL) of Eu showed better reducing power activity than the standard BHT (Fig. 4D).
Oxygen is the most electronegative atom and is always ready to form superoxide. Mitochondria are the main site for cellular oxygen consumption [26]. Defective working of mitochondria due to the formation of superoxide leads to many neurodegenerative disorders, apoptosis, and tissue damage. Although the superoxide radical scavenging assay is lower in the sample than the standard quercetin (Fig. 5A). The sample has enough inhibition capacity to establish its positive role to protect our body from superoxide-mediated tissue damage.
Antioxidant activity of Eu. A Superoxide radical scavenging assay. B Hydrogenperoxide scavenging activity. C Hydroxyl radical scavenging assay. D Hypochlorous acid scavenging assay [Data expressed as mean ± SD. Units in μg/mL.*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001; NS, non-significant when compared with standard]
ROS production is enhanced by free ion that leads to reduction of hydrogen peroxide and formation of hydroxyl radical [27]. In the present study, Eu showed higher hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity than the standard sodium pyruvate (Fig. 5B) which proved the presence of some antioxidant compounds within the sample.
Hydroxyl radicals are formed by the excited atomic oxygen with water or the decomposition of hydrogen peroxides (H2O2). In the biological system, hydroxyl radicals are found to be formed in immune action through macrophages when exposed to pathogens but sometimes it leads to neurological autoimmune disorder [28]. Hydroxyl radicals are well known to break purine and pyrimidine bases also affects the deoxyribose backbones of DNA. Eu showed the ability to inhibit the formation of hydroxyl radical (41.83 ± 1.54% at 200 μg/mL) than the standard mannitol (Fig. 5C).
In the case of cellular inflammation, activated phagocytic cells (neutrophils) release hydrogen peroxide and generate potent reactive oxygen species (ROS) like hypochlorous acid (HOCl) by oxidation of Clˉ in the presence of myeloperoxidase enzyme (MOP) [29]. For hypochlorous acid scavenging assay, Eu showed significant radical scavenging activity when compared with respective standards (Fig. 5D).
Due to the presence of aromatic rings and redox potential in phenolic compounds, they can absorb and inhibiting free radicals. Flavonoids are also known as a scavenger of free radicals [30]. The total amount of phenolic content was 62 ± 7% gallic acid equivalent per 100 mg of the sample was observed. Total flavonoid content was 54 ± 6% quercitin equivalents per 100 mg sample. The presence of high phenolic and flavonoid content in the sample indicates the inhibition of free radicals and also antimutagenic properties. The presence of high antioxidants within the sample had been observed.
GC-MS analysis
Different bioactive compounds were identified in the GC-MS analysis of the Eu sample. A total of 13 compounds have been identified in the sample (Table 2) which corresponds to Fig. 6 and the screened phytoconstituents have been provided in Table 2. Of these compounds, ethyl .alpha.-d-glucopyranoside, hexadecanoic acid, and octadecanoic acid have an active role in the suppression of skin roughness against ultraviolet B radiation, antibacterial, and antioxidant activity respectively [32,33,34].
Molecular docking
The in silico docking study revealed that ethyl 9-hexadecenoate was showing a better binding affinity for IkB kinase (−6.9 kcal/mol), whereas 9-octadecenoic acid (Z)-, methyl ester, and n-hexadecanoic acid showed a better affinity for adenylyl cyclase (−7.4 kcal/mol) and hemeoxygenase 1 respectively (−6.0 kcal/mol) (Fig. 7). Thus, these mentioned compounds may have some beneficial roles on the signaling-related proteins modulating the signaling cascade (see Additional file 2).
Metagenomic profiling of Eu
The bacterial profiling was identified from Phylum to genus level in the amylolytic starter culture. The major bacterial phyla identified in the starter were Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Chlamydiae, Chloroflexi, Chlorophyta, Cyanobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, Euryarchaeota, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Nitrospirae, Planctomycetes, Proteobacteria, Streptophyta, Thaumarchaeota, Thermotogae, and Verrucomicrobia (Fig. 8). Some other unclassified sequences were present but they were not considered in this study. Interestingly, the major part of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) like Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Enterococcus, Leuconostoc, and Pediococcus were present in the starter culture (Fig. 9)A, B. These LAB strains can convert hexose sugar to lactic acid thus they inhibit the growth of other harmful bacteria by providing an acidic environment. Gluconobactor and Bifidobacteria present in the starter culture have been known to reside in the human gastrointestinal tract and proven to reduce gut inflammation and constipation [38]. The most abundant genus found in the starter culture was Weissella which exhibited antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity [39]. Faecalibacterium is a gram-positive bacteria and it boosts the immune system [40]. Dialister, a probiotic strain known to increase carbohydrate breakdown. Moaa, the starter culture is the source of this all functional microflora in Eu fermentation. The beneficial role of this probiotic and fermenting bacteria present in the starter culture has a direct effect on the health of these tribal people.
Conclusion
This study for the first time emphasizes the traditional practice of Eu preparation as well as GC-MS analysis and microbial association. The microbes present in the brew increase the breakdown of complex macromolecules into smaller substances thus facilitating bioavailability. The health-promoting effects of lactic acid bacteria, probiotic microflora, and herbs used in this brew likely make Eu a nutritional health drink rather than a recreational drink. The low pH, increased acidity, and alcohol content in Eu inhibit the growth of pathogenic organisms. Plants used in the starter culture and the microorganism have the synergistic scavenging activity of ROS and RNS. The metagenomic study has become one of the important tools for analyzing the unculturable microbial population present in a specific niche. The metagenomic study revealed that no harmful bacteria were present in the starter culture. As the tribe uses it as a stress releaser and intake of high amount without any harmful effect, the total nutrition properties have to be explored. The alcohol content is very low in the sample and could not cross the blood-brain barrier in high amounts and also compensate for water loss during heavy work pressure. This tribe belongs to the poor and primitive origin and they believe that Eu consumption helps them to do their hard work. Besides, the tribe also consumes Eu as a remedy for pain, headache, jaundice, and dysentery. They dedicate Eu to their spiritual God for their good health and protection of the natural resources. Eu is a harmless, source for plenty of beneficial bacteria. Thus, it may be used as an energy drink or as a food supplement. The probiotic nature of Eu should be explored further for its industrialization and recommendation as a health drink.
Availability of data and materials
Original data collected throughout interviews are recorded in a field notebook and kept in the workplace of authors.
Abbreviations
- DPPH:
-
2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- LAB:
-
Lactic acid bacteria
- RCF:
-
Relative centrifugal force
References
Thapa S, Tamang JP. Product characterization of kodo ko jaanr: fermented finger millet beverage of the Himalayas. Food Microbiol. 2004;21(5):617–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2004.01.004.
Das M, Kundu D, Singh J, Rastogi A, Banerjee R. Physiology and biochemistry of indigenous tribal liquor Haria: a state of art. Adv Biotechnol Microbiol. 2017;6(2):1–5.
Roy A. Traditional cereal-based alcoholic beverages of India: a rich source of unexplored microorganisms for potential health benefits. IJBPAS. 2020;9:791–802.
Dawn A. A peep into the lifestyle of the endangered Toto tribe of Jalpaiguri District of West Bengal. Int J Mod Res Rev. 2014;2(4):161–4.
Nirgude M, Babu BK, Shambhavi Y, Singh UM, Upadhyaya HD, Kumar A. Development and molecular characterization of genic molecular markers for grain protein and calcium content in finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.). Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(3):1189–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2825-7.
Zhu LJ, Liu QQ, Wilson JD, Gu MH, Shi YC. Digestibility and physicochemical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) flours and starches differing in amylose content. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;86(4):1751–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.07.017.
Bakht J, Noor N, Iqbal A, Shafi M. Antimicrobial activity of different solvent extracted samples from the leaves and fruits of Capsicum annuum. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020;33(1):27–32.
Sannigrahi S, Parida S, Patro VJ, Mishra US, Pathak A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of Pterospermum acerifolium. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2010;2(1):1–5.
Jain P, Sharma HP, Basri F, Baraik B, Kumari S, Pathak C. Pharmacological profiles of ethnomedicinal plant: Plumbagozeylanica l.-a review. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2014;24(1):157–63.
Patra S, Bhattacharya S, Bala A, Haldar PK. Antidiabetic effect of Drymaria cordata leaf against streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced diabetic albino rats. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2020;11(1):44–52. https://doi.org/10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_98_19.
Banerjee RD, Sen SP. Antibiotic activity of pteridophytes. Econ Bot. 1980;34(3):284–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858649.
Labar R, Sarkar I, Sen A, Bhattacharya M. Effect of solvent with varying polarities on phytochemical extraction from mature tea leaves and its evaluation using biochemical, antimicrobial and in-silico approaches. Int Res J Pharm. 2019;10(8):59–67. https://doi.org/10.7897/2230-8407.1008247.
Dutta S, Chakraborty AK, Dey P, Kar P, Guha P, Sen S, et al. Amelioration of CCl4 induced liver injury in Swiss albino mice by antioxidant-rich leaf extract of Croton bonplandianus Baill. PLoS One. 2018;13(4):1–30.
Kar P, Mishra DK, Roy A, Chakraborty AK, Sinha B, Sen A. Elucidation of phytomedicinal efficacies of Clerodendrum inerme (L.) Gaertn.(Wild Jasmine). South African J Bot. 2020:1–9.
Lala M, Modak D, Paul S, Sarkar I, Dutta A, Kumar A, et al. Potentbioactive methanolic extract of wild orange (Citrus macroptera Mont.) shows antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties in in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. Bull Nat Res Cent. 2020;44(1):1–5.
Das S, Vasudeva N, Sharma S. Chemical composition of ethanol extract of Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc. using GC-MS spectroscopy. Org Med Chem Lett. 2014;4(1):1–4.
Song YS, Lee YS, Chan PH. Oxidative stress transiently decreases the IKK complex (IKKα,β, and γ), an upstream component of NF-κB signaling, after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25(10):1301–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600123.
Ohtaki H, Satoh A, Nakamachi T, Yofu S, Dohi K, Mori H, et al. Regulation of oxidative stress by pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) mediated by PACAP receptor. J Mol Neuro Sci. 2010;42(3):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9350-0.
Son Y, Lee JH, Chung HT, Pae HO. Therapeutic roles of heme oxygenase-1 in metabolic diseases: curcumin and resveratrol analogues as possible inducers of heme oxygenase-1. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/639541.
Lu J, Salzberg SL. Ultrafast and accurate 16S rRNA microbial community analysis using Kraken 2. Microbiome. 2020;8(1):1–11.
Nakai R, Abe T, Takeyama H, Naganuma T. Metagenomic analysis of 0.2-μm-passable microorganisms in deep-sea hydrothermal fluid. Mar Biotechnol. 2011;13(5):900–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-010-9351-6.
Saha MR, Dey P, Begum S, De B, Chaudhuri TK, Sarker DD, et al. Effect of Acacia catechu (Lf) Willd. on oxidative stress with possible implications in alleviating selected cognitive disorders. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):1–19.
Bursal E, Köksal E, Gülçin İ, Bilsel G, Gören AC. Antioxidant activity and polyphenol content of cherry stem (Cerasu savium L.) determined by LC–MS/MS. F Res Int. 2013;51(1):66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.11.022.
Huang D, Ou B, Prior RL. The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity assays. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53(6):1841–56. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030723c.
Ulfig A, Leichert LI. The effects of neutrophil-generated hypochlorous acid and other hypohalous acids on host and pathogens. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;13:1–30.
Aruma OI. Methodological consideration for characterization for potential antioxidants actions of bioactive components in plant food. Mutat Res. 2003;532:19–20.
Reeder BJ, Hider RC, Wilson MT. Iron chelators can protect against oxidative stress through ferryl heme reduction. Free RadicBiol Med. 2008;44(3):264–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.08.006.
Packer L, Ong AS. Biological oxidants and antioxidants: AOCS Press; 1998.
Valentao P, Fernandes E, Carvalho F, Andrade PB, Seabra RM, de Lourdes Bastos M. Studies on the antioxidant activity of Lippia citriodora infusion: scavenging effect on superoxide radicals, hydroxyl radical and hypochlorous acid. Bio-Pharm Bull. 2002;25(10):1324–7.
Mustafa RA, Hamid AA, Mohamed S, Bakar FA. Total phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and radical scavenging activity of 21 selected tropical plants. J Food Sci. 2010;75(1):28–35.
Bansal A, Kumar P, Narasimhan B. Synthesis, antimicrobial evaluation and QSAR studies of 2-hydroxy propanoic acid derivatives. Drug Res. 2014;64(05):240–5.
Bogaki T, Mitani K, Oura Y, Ozeki K. Effects of ethyl-α-d-glucoside on human dermal fibroblasts. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017;81(9):1706–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2017.1353400.
Kar P, Dey P, Misra AK, Chaudhuri TK, Sen A. Phytometabolomic fingerprinting of selected actinorhizal fruits popularly consumed in North-East India. Symbiosis. 2016;70(1):159–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0415-x.
Hsouna AB, Trigui M, Mansour RB, Jarraya RM, Damak M, Jaoua S. Chemical composition, cytotoxicity effect and antimicrobial activity of Ceratonia siliqua essential oil with preservative effects against Listeria inoculated in minced beef meat. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011;148(1):66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.04.028.
Mujeeb F, Bajpai P, Pathak N. Phytochemical evaluation, antimicrobial activity, and determination of bioactive components from leaves of Aegle marmelos. BioMed Res In. 2014;2014:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/497606.
Salem MZ, Zayed MZ, Ali HM, Abd El-Kareem MS. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of extracts from Schinus molle wood branch growing in Egypt. J Wood Sci. 2016;62(6):548–61.
Tyagi T, Agarwal M. Phytochemical screening and GC-MS analysis of bioactive constituents in the ethanolic extract of Pistia stratiotes L. and Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) solms. J Pharmacog Phytochem. 2017;6(1):195–206.
Fijan S. Microorganisms with claimed probiotic properties: an overview of recent literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(5):4745–67.
Yu HS, Lee NK, Choi AJ, Choe JS, Bae CH, Paik HD. Anti-inflammatory potential of probiotic strain Weissella cibaria JW15 isolated from kimchi through regulation of nf-κb and mapks pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019;29(7):1022–32. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1903.03014.
Miquel S, Martin R, Rossi O, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Chatel JM, Sokol H, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013;16(3):255–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2013.06.003.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Biokart Pvt. Ltd., a Bangaluru (India) based company for DNA extraction and metagenomic sequencing. We are also thankful to the Toto community for sharing their traditional knowledge and providing samples.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CG conceived the idea. AS, CG, IS, PK, and SB designed the experiments. SB, PK, and IS carried out the experiments. IS designed and analyzed the in silico part. SB and PK perform the antioxidant experiment. CG identified the plants. All the authors contributed to drafting the manuscript and approved it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Animal Ethical Committee of the Department of Zoology, NBU reviewed and approved the experiments using animals (Permit No. 840/ac/04/CPCSEA, Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Supplementary Figure. Heat map representing thequalitative assay of different extracts of Eu sample
Additional file 2.
Supplementary Table. Docking Score
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharjee, S., Kar, P., Sarkar, I. et al. Biochemical and microbial profiling establish “Eu” (a traditional fermented beverage of Toto people) as a probiotic health drink. J. Ethn. Food 8, 16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42779-021-00093-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42779-021-00093-5