Abstract
Background
Natural products played an essential role as a complementary cytotoxic agent avoiding complications of other therapies. In phytoformulation research, herbal drugs of nano-size have attracted more attention for more bioavailability and less active dose. We aim in this work to introduce new non-mutagenic cytotoxic agent from Thevetia peruviana leaves extracts and potentiate the activity by loading upon microemulsion formulations as an advanced mode of drug delivery system.
Results
Thevetia peruviana toxicity test revealed its safety (LD50 = 3.083 g/kg). In vivo genotoxicity tests measuring chromosomal aberrations were done to prove non-mutagenicity of the plant for both somatic and germ cells. The plant showed antioxidant activity with 121.215, 128.925, and 120.098 mg/g extract, calculated as Trolox equivalent (TE/g) for DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays, respectively. Successive extracts of the plant were incorporated in microemulsion formulations (MEF) and characterized for their electrical conductivity, poly-dispersity index, and in vitro drug release action. Cytotoxic activity of successive extracts was investigated against breast MCF7 and liver HEPG2 carcinoma cell lines before and after loading upon MEs. Enhancement in activity was detected for both pet. ether and ethanol MEFs, as IC50 of pet. ether extract decreased from 25 to 6.5 μg/ml against MCF7 cell line, while ethanol formulation recorded IC50 = 3.58 μg/ml against HEPG2 cell line after showing no activity of the extract at the tested concentrations.
Regarding metabolites of polar fraction, total ethanol extract was estimated for total phenolic and flavonoid contents to record 47.7941 mg GAE/g calculated as gallic acid equivalent and 32.7667 mg CE/g measured as catechin equivalent, respectively. HPLC analysis for polar fraction recorded twelve compounds identified according to the available authentics with rutin the major flavonoid (7.33 mg/g) and rosmarinic acid (13.48 mg/g) the most abundant phenolic acid. Phytoconstituents of non-polar fraction were investigated after saponification of pet. ether extract using GC/MS analysis revealed the identification of 88.02% of the total unsaponifiable matter and 89.17 % of the total saponifiable matter.
Conclusion
Thevetia peruviana is a safe cytotoxic agent. Microemulsion formulations of active extracts potentiate the cytotoxic actions against HEPG2 and MCF7 cell lines with better bioavailability and less medicinal doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The number of deaths because of cancer is in continuity rise worldwide as World Health (WHO) Organization stated http://www.who.int/cancer/en/index.html. Natural products played an essential role in cytotoxic pharmaceutical drug discovery avoiding serious troubles that accompanied chemo and radio-therapies. Researches of natural products with help of advanced analytical techniques have been focused to introduce nutraceuticals as complementary cancer treatment (Cassileth & Deng, 2004). Therefore, natural cytotoxic drug with different technique of action is of crucial need for future anticancer agents.
Thevetia peruviana (Apocynaceae), commonly known as yellow oleander or lucky nut, is native to Central and South America along with Mexico and is also used in South-East Asia in folk medicine (Appa Rao et al., 1978; Samal et al., 1992). T. peruviana is considered as a household remedy for several ailments: scabies, ulcers, and hemorrhoids and to dissolve tumors; besides, the plant is well known for its cardio-active glycosides that are capable of exerting hearts positive inotropic effects (Langford & Boor, 1996; Oji & Okafor, 2000). T. peruviana leaves are well known traditionally as abortifacient (Samanta et al., 2016), while fruits possess potential antiproliferative action on colorectal and breast cancer cells and could induce apoptosis in human lung and prostate cancer cells (Ramos-Silva et al., 2017). In addition, T. peruviana exhibit inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and HIV-1 integrase (Tewtrakul et al., 2002).
Microemulsion (ME) is an advanced emulsion formulation that appear transparent to the naked eye, their tiny droplet size offer high thermodynamic stability protecting them from flocculation, aggregation, coalescence, and Ostwald ripening (Solans et al., 2005). Recently, incorporation of phytochemicals into nano-sized drug delivery formulations facilitate their transport through cell membranes, enhance the therapeutic efficacy, minimize adverse effects, and overcome instability to boost nutraceuticals bioavailability (Matloub et al., 2018a; Matloub et al., 2018b), knowing that MEs have increasing interest in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries (Rebolleda et al., 2015). Therefore, we aim in this work to introduce natural cytotoxic agent selective for malignancy versus to be non-mutagenic on normal cells and potentiate its activity and bioavailability by incorporation in microemulsion formulations along with profiling its metabolites using advanced techniques.
GC/MS is the analysis technique of our choice for volatilized lipoidal metabolites and fatty acids after derivatization, which has the advantage to separate and quantify each analyte in a complex mixture (Farag et al., 2017).
But for polar fraction, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an efficient and sensitive physicochemical technique used for metabolite separation, identification, and quantification (Elsawi et al., 2018).
Material
Plant material
The plant was collected from the Egyptian Orman Garden and was identified by the specialized botanist Trease Labib, Consultant of Plant Taxonomy at the Ministry of Agriculture and the former director of Orman Botanical Garden.
Material for phytochemical screening
Ferric chloride reagent for tannins I2/KI reagent for coumarins. Molisch’s reagent for carbohydrates and/or glycosides. Dragendorff’s reagent for alkaloids and nitrogenous bases, Lieberman-Burchard reagent for sterols and/or triterpenes. KOH for flavonoids (Shrestha et al., 2015).
Material for median lethal dose (LD50) determination
Animals: Albino mice, ranging 20–25 g, were taken from animal house colony of National Research Centre, Dokki, Egypt. Animals were remained under hygienic conditions with well-balanced diet and water and ethically approved.
Normal diet
It was made up of vitamin mixture (1%), mineral mixture (4%), corn oil (10%), sucrose (20%), cellulose (0.2%), casein 95% (10.5%), and starch (54.3%).
Material for in vitro cytotoxic study
Cell lines
Liver carcinoma (HEPG2) and breast carcinoma (MCF7) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Minnesota, USA). The tumor cell lines were maintained by serial sub-culturing at the National Cancer Institute, Cairo, Egypt.
Chemicals and kits
Dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), RPMI-1640 medium, trypan blue, fetal bovine serum, penicillin/streptomycin antibiotic, and Trypsin-EDTA (Sigma Aldrich Chemical Co., St. Louis, Mo, USA) and Tris buffer (Applichem, Germany).
Material for microemulsion (ME)
Tween 80 (Polysorbate 80) and polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Chem. Co., St. Louis, MO. Capmul MCM C8 was kindly donated by ABITEC Corporations, Cleveland, OH. All other components were of analytical grade.
Methods
Preparation of the plant extracts
Fifty grams of air-dried powdered leaves of the plant were exhaustively extracted by reflux using 70% ethanol to form the crude extract, while another 100 g of the dried powder was successively extracted by reflux using petroleum ether (60–80 °C), chloroform, and 80% ethanol. These extracts were evaporated to dryness using rotary evaporator under vacuum at 40 °C.
Determination of median lethal dose (LD50)
Total ethanol extract was tested on uninfected healthy mice to determine the median lethal dose. LD50 of the extract was determined using the method described by (Fayad et al., 2017).
Chromosome aberrations in somatic cells
Chromosome preparations from the bone marrow (somatic cells) carried out according to the method reported in (Aly et al., 2019). One hundred well-spread metaphases were analyzed per mouse. Metaphases with gaps, chromatid break, and fragments, under × 100 magnification with a light microscope (Olympus, Saitama, Japan), were recorded.
Chromosome abnormalities in germ cells
Chromosome preparations from spermatocytes (germ cells) were made according to the technique reported in (Aly et al., 2019). One hundred well-spread diakinase-metaphase I cells were analyzed per animal for chromosomal aberrations. Metaphases with X-Y univalents and autosomal univalents were recorded. Statistical analysis: the difference between treated groups and controls were tested with the t test.
Animals’ storage, handling, and feeding have been accepted by ethical guidelines of NRC Medical Ethical Committee (Egypt) that proved no suffering of animals during experiments (Approval no. 15/100).
Antioxidant activity
Determination of radical DPPH scavenging activity
Free radical scavenging capacity of total ethanol extract was assayed using the stable DPPH* according to (Hwang & Do, 2014). The final concentration was 200 μM for DPPH* with final reaction volume 3.0 mL. After 60 min of incubation in the dark, the absorbance was measured at 517 nm against pure methanol as a blank. Percent inhibition of the DPPH free radical was calculated according to the following equation: inhibition (%) = 100 × [(Acontrol − Asample)/Acontrol], where Acontrol is the absorbance of the control reaction (containing all reagents except the extract) and Asample is the absorbance recorded in the presence of extract. The standard curve was prepared using Trolox. Results were expressed as mg Trolox equivalent (TE)/g sample. Additional dilution was necessary in case the DPPH value measured exceeded the linear range of the standard.
ABTS radical scavenging assay
The ABTS scavenging capacity of the plant was recorded by a calibration curve of Trolox. Stock solutions of ABTS* reagent was prepared followed (Hwang & Do, 2014) by reacting equal amounts of 7 mM aqueous solution ABTS* with 2.45 mM potassium persulfate and kept in dark at 25 °C. One-milliliter ABTS* solution was diluted with 60 mL of ethanol to water (50:50, v/v) to measure absorbance of 1.0 ± 0.02 units at 734 nm using the spectrophotometer. Fifty microliters of total ethanol plant extract was reacted with 4.95 mL of the ABTS* solution for an hour in the dark. The absorbance was recorded at 734 nm by spectrophotometer. % inhibition of the ABTS* free radical was calculated following this equation: inhibition (%) = 100 × [(Acontrol − Asample)/Acontrol], where Acontrol is the absorbance of the control reaction and Asample is the absorbance with extract. The standard curve was prepared using Trolox. Result was expressed as mg Trolox equivalents (TE)/g sample. Additional dilution was required if the ABTS* result was over the linear range of standard.
Ferric reducing antioxidant power assay (FRAP)
The FRAP assay was done following (Hwang & Do, 2014). Stock solutions were performed of 300 mM acetate buffer [3.1 g sodium acetate (C2H3NaO2.3H2O) with 16 mL glacial acetic acid (C2H4O2), pH 3.6], 10 mM TPTZ solution in 40 mMHCl, and 20 mM ferric chloride (FeCl3.6H2O) solution. Working solution was ready by mixing 25 mL acetate buffer, 2.5 mL TPTZ solution, and 2.5 mL FeCl3.6H2O solution. Fifty microliters of extract was ready to react with 3.95 mL of the FRAP solution for half an hour in the dark. Record of colored [ferrous tripyridyltriazine complex] was taken at 593 nm. % inhibition was calculated following this equation: inhibition (%) = 100 × [(Acontrol − Asample)/Acontrol], where Acontrol is the absorbance of the control reaction and Asample is the absorbance with extract. The standard curve was prepared using Trolox. Result was expressed as mg Trolox equivalent (TE/g sample).
In vitro cytotoxic activity
Potential cytotoxicity of the plant extracts were tested as cells were inoculated in 96-well microtiter plates in concentration of 3 × 103 cell/well in a 150-μL fresh medium for a day to attach the plates. Different concentrations 0, 5, 12.5, 25, and 50 μg/mL of sample were added, and cytotoxic activity was recorded as reported in (Skehan et al., 1990).
Preparation of microemulsion
A microemulsion formulation was prepared where Capmul MCM C8 was chosen as the oil phase, Tween 80 as a surfactant, and PEG 400 as a co-surfactant. Surfactant and co-surfactant were mixed at specific weight ratio of 1:1, then vortexed for 1 min to obtain the surfactant/co-surfactant (Smix) mixture. Then, distilled water was added dropwise to the mixture with vortex mixing followed by sonication for 30 min (Bathsonicator, Branson 2510E-DHT, Richmond, VA, USA) until a homogeneous mixture is formed. The resulting clear, transparent ME systems were tightly sealed and stored at ambient temperature till further investigation.
Preparation of loaded MEs
One hundred milligrams of each of the tested bioactive fractions was added to 10 ml ME and shaken at room temperature for 72 h at 100 rpm. Different ME formulations were given codes and are presented in Table 1.
Characterization of optimized MEs
Globule size and polydispersity index determination
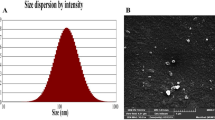
The globule size of the formulations and its distribution (characterized by polydispersity index, PDI) were measured at 25 °C using Nano-ZS (Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK). Samples were appropriately diluted with distilled water in ratio 1:100 before measurement.
Transmission electron microscopy
These studies were performed using incubating shaker (SR8 PLUS, Handson dissolution tester, USA). The release medium was 50 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) containing 20% ethanol, the temperature was set at 37 ± 0.5 °C, and the revolution speed was 100 rpm. Release experiments were conducted for 48 h as all tested preparations.
Electrical conductivity
The electrical conductivity of the selected MEs was measured using a conductivity meter (Jenway 4071, Staffordshire, UK) at 25 ± 2 °C. The electrode was dipped in the ME sample until equilibrium was reached. Before conductivity measurement, the conductivity cell was calibrated using standard KCl solution.
In vitro extract release studies
These studies were performed using the isothermal shaker (GFL 3032, Germany). The release medium was 50 mL of phosphate buffer (PH 7.4) containing 20% ethanol, the temperature was set at 37 ± 0.5 °C, and the revolution speed was 100 rpm. Aliquot samples were withdrawn at predetermined time intervals and replaced with fresh medium. Release experiments were conducted for 24 h.
Statistical analysis of ME formulations
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) and were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by the least significant difference procedure using SPSS® software. Statistical differences yielding p < 0.05 were considered significant.
Estimation of total phenolic content
The total phenolic content was determined according to the Folin-Ciocalteu procedure (Žilić et al., 2012).
Estimation of total flavonoidal content
The total flavonoid content was determined following (Žilić et al., 2012) by aluminum chloride (AlCl3) colorimetric assay.
HPLC analysis of phenolics
HPLC analysis was done following (Kim et al., 2006), using Agilent Technologies 1100 series liquid chromatograph with diode-array detector. Eclipse XDB-C18 (150 × 4.6 μm; 5 μm) column was used with a C18 guard column (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA). The mobile phase made up of acetonitrile (A) with 2% acetic acid in water (v/v) (B). The flow rate was 0.8 ml/min, and the total run time was 70 min. The gradient program was 100% B to 85% B in 30 min, 85% B to 50% B in 20 min, 50% B to 0% B in 5 min, and 0% B to 100% B in 5 min. The injection volume was 50 μl. Peaks were recorded at 280, 320, and 360 nm for the benzoic acid and cinnamic acid derivatives. Peaks were recorded for retention times and UV spectra in comparison with standards.
Investigation of lipoidal matter
Saponification of petroleum ether extract
The petroleum ether extract (1 g) was subjected to saponification according to the method reported by (Aboutab et al., 2010).
Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters
The free fatty acids obtained from saponification were methylated according to the method reported by (Aboutab et al., 2010).
GC/MS analysis study of both the unsaponifiable and saponifiable fractions was carried out to identify their contents using GC/MS analysis. The constituents were identified by comparison of their spectral fragmentation patterns with those of the available database libraries, Wiley (Wiley International, USA) and NIST (Nat. Inst. St. Technol., USA), and/or published data (Adams, 2009). Quantitative determination was carried out on the basis of peak area integration.
Conditions: Column capillary column of fused silica, 30 m length, 0.32 mm ID, and 0.25 μm thickness. Stationary phase: HP-5MS (5% methyl polysiloxane). Carrier gas: Helium at 1 ml/min, 13 psi, temperature programming 60 °C isothermal for 3 min, 60–300 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min, 280 °C isothermal for 10 min for unsaponifiable matter and 5 min for fatty acids methyl esters. Ionization voltage 70 eV GC/MS, gas chromatograph coupled with a mass spectrometer detector (EI).
Results
Phytochemical screening of Thevetia peruviana dried powered leaves
Phytochemical screening of Thevetia peruviana air-dried powdered leaves was done to identify phytoconstituent classes. It reveals that the plant is rich in flavonoids, tannins, carbohydrates and/or glycosides and terpenoidal and/or steroidal compounds, while anthraquinones, coumarins, and saponins are nearly absent.
Median lethal dose (LD50) of Thevetia peruviana leaves ethanolic extract
Median lethal dose of Thevetia peruviana leaves ethanol extract proved plant safety with high median lethal dose (LD50 = 3.083 g/kg).
Results of chromosomal aberrations in the bone marrow and spermatocyte cells (somatic and germ cells)
The results are referred in Tables 2 and 3 that showed number and percentage of chromosomal aberrations induced in animals treated with total ethanol extract of Thevetia peruviana leaves at doses 500, 1000, and 1500 mg/kg b.wt for 1 day along with the control group. The percentage of chromosomal aberrations induced in somatic and germ cells was statistically not significantly relative to non-treated control group, which indicates safety of the plant to genetic material. This result maybe contribute to flavonoidal contents in the plant extract as previous finding confirmed flavonoids inhibition mutagenicity that may induced by chemical mutagens (Negi, 2003). According to our knowledge, no previously reported data revealed the mutagenic activity of Thevetia peruviana leaves extracts.
Results of microemulsion formulation
Physicochemical characterization of microemulsions
Globule size analysis
The prepared microemulsions showed a mean droplet diameter of 223.33–265 nm (Table 4). All MEs showed homogeneous globule size distribution confirmed with small polydispersity index (PDI) value < 0.25. It is reported that PDI value < 0.25 indicates a narrow size distribution, while a PDI > 0.5 refers to a broad distribution (Patravale & A.A., 2004). Unlike coarse emulsions that are micronized with external energy, MEs are based on low interfacial tension achieved by adding a co-surfactant; the addition of the latter leads to spontaneous formation of a thermodynamically stable formulation. The droplet size in the dispersed phase is very small which makes the ME a transparent liquid (Tenjarla, 1999). This small average diameter was expected since, in microemulsions, the cosurfactant molecules penetrate the surfactant film, lowering the fluidity and surface viscosity of the interfacial film, decreasing the radius of curvature of the micro-droplets, and forming transparent systems (Tenjarla, 1999).
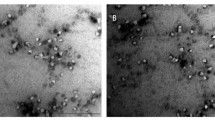
Morphological examination by transmission electron microscope (TEM)
The morphological examination of different ME formulations are illustrated by TEM photographs (Fig. 1). The images clearly indicated all exhibited discrete globules of spherical shape, with homogenous size distribution.
Electrical conductivity
Electrical conductivity behavior is an important property of ME. It has been proved to be the simplest, yet one of the most reliable and convenient methods to investigate the structure features of ME. In the present study, in order to assess the type of the prepared ME formulations, electrical conductivity measurements were performed and found to be in the range of 0.09–1.54 × 10−1μS/cm for ME. As the data revealed, the presented conductivity values are attributed to the high water content of the ME formulations. According to the obtained results, the type of the MEs is bicontinuous (Heuschkel et al., 2009).
In vitro drug release studies
Results of extract release from microemulsions are presented in Fig. 2 that showed great difference in the % released from ME-F1 (pet. ether), ME-F2 (chloroform), and ME-F3 (ethanol). The percentage released from the microemulsions containing fractions can be ranked in the following order ME-F1 > ME-F3 > ME-F2. The differences in the release behavior between the prepared formulae were greatly influenced by the nature of the loaded extracts.
.
Antioxidant activity
The antioxidant activity was done using three different assays DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP and calculated as Trolox equivalent (vitamin E analogue), using the standard calibration curve illustrated in Fig. 3.
In DPPH radical scavenging assay, antioxidant reacts with stable nitrogenous free radical DPPH and converts its violet color to yellow colored diphenyl-β-picryl hydrazine (Wannes et al., 2010). T. peruviana extract records 121.215 mg TE/g; degree of dis-coloration reflects the radical-scavenging potential of the plant extract.
ABTS assay determines the oxidation of 2,2′azinobis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-sulphonic acid) to give a green-colored nitrogen centered ABTS·+. Thevetia peruviana leaves extract quenches ABTS·+ cationic radical in reference to Trolox and resulting in 128.925 mg TE/g.
In addition, FRAP assay revealed that reading colored complex of ferrous tripyridyltriazine was employed to investigate the antioxidant potential of T. peruviana total ethanol extract to reveal 120.098 mg TE/g.
Cytotoxic activity
We investigate successive extracts of T. Peruviana leaves for cytotoxic activity and record the enhancement in activity after incorporation in emulsion formulation of micro-size particles. Two cell lines of our choice were liver and breast carcinoma cell lines; the results are illustrated in Table 5 and Figs. 4 and 5.
Although the ethanol extract of T. Peruviana leaves did not exhibit a considerable anti-proliferative effect on hepato-carcinoma cell line at the chosen tested concentrations, the ethanol (MEF) exhibited upgrading in activity to give higher action through formulations with IC50 = 3.58 μg/mL. Another upgrading was observed for pet. ether (MEF); the activity was potentiated from IC50 = 25 μg/mL to be IC50 = 6.5 μg/mL against breast carcinoma cell line. Chloroform extract showed activity, but unfortunately, the formulation was sparingly soluble which is considered unacceptable upon application on the cell lines.
It was concluded that the microemulsion formulation of T. peruviana leaves used in our study potentiates the cytotoxic activity of successive ethanol and pet. ether extracts against liver and breast carcinoma cell lines, respectively relative to the common antitumor agent Doxorubicin.
Total phenolic and total flavonoid contents
Concerning the upregulation of T. peruviana ethanolic extract in activity after incorporation in microemulsion formulation, beside the well-known anti-oxidative action of flavonoids and phenolics (Hashem et al., 2007), we target in this study to have a good insight on polar fraction phytoconstituents by estimating their contents using standard curves in Figs. 6 and 7. Total phenolic content of T. peruviana leaves ethanolic extract calculated as gallic acid equivalent was recorded to be 47.7941 mg GAE/g, while total flavonoid content as catechin equivalent was 32.7667 mg CE/g.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) profile of total ethanol extract of Thevetia Peruviana leaves
Promising antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of T. peruviana leaves which contribute to the high level of phenolics and flavonoids in the plant, beside that enhancement in cytotoxic activity of ethanol extract after microformulation against HEPG2 cell line, lead us to investigate the chemical constituents of the plant active fractions using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) upon three different wavelengths (280, 320, and 360 nm). Retention time along with peak area was used to determine and quantify flavonoid and phenolic contents according to available authentic as shown in Table 6. Twelve compounds were identified from Thevetia peruviana extract showing rosmarinic acid the major compound recording 13.5 mg/g, followed by caffeic acid accounting for 10 mg/g and chlorogenic acid amounted for 8.55 mg/g while rutin and apigenin-7-glucoside were the flavonoids detected in our study representing 7.335 and 3.361 mg/g, respectively.
Gas chromatography (GCMS) profile of pet. Ether extract of Thevetia peruviana leaves
Pet. ether (MEF) showed great improvement in cytotoxic activity against breast cancer cell line, concerning the decrement of IC50 (μg/ml) from 25 to 6.5 with all advantages of micro-particles size. On the other hand, no much work was done previously to investigate the chemical composition of lipoidal matter of this species. Consequently, we approach to give deep insight for its chemical composition by saponification of pet. ether extract to unsaponifiable fraction and saponifiable fraction. Consequently, saponifiable part was derivatized by methylation to be volatile and both fractions were subjected to GC/MS analysis (Tables 7 and 8).
Forty-nine compounds were identified (Table 7) by GC/MS of unsaponifiable matter, representing about 88.02% of its total content. The identified components comprise 47.57% unoxygenated compounds and 41.32% oxygenated compounds including several steroidal/triterpenoidal compounds (peaks 36, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 46, and 47) amounted for 16.3% from the total identified compounds. Butylated hydroxytoulene (peak 16, 21.03%) is the major compound in the unsaponifiable fraction, followed by phytol (peak 26, 9.84%), squalene (peak 36, 8.84%), and hentriacontane (peak 39, 8.23%).
Twenty-nine fatty acid methyl esters were identified, representing 89.17% of the total saponifiable matter (Table 8). It can be concluded that octadedecadienoic acid methyl ester, hexadecanoic acid methyl ester, and dodecanoic acid methyl ester acid represent the major components (peaks 11, 7, and 2) amounting for 37.82, 21.29, and 8.12%, respectively. Saturated fatty acids represent 45.15% of the total fatty acid content, whereas unsaturated fatty acids represent 44.02% of the total fatty acid content, respectively.
Discussion
Cancer is human genetic disease that is caused by mutation happened in growing controlling genes (proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes); it is considered as the principal cause of death nowadays. Mutation is defined as a shift in the sequence of DNA that takes place during replication, either due to mistakes or as the result of environmental stresses such as UV light and smokes, etc. (Liu et al., 2016).
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are effective in different cancer types, but their activity is often limited by toxicity to other body tissues. Therefore, other ways of treatment that avoid the serious problems associated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy are of crucial need. Many findings have proven that cytotoxic natural products have played an important role in the innovation of pharmaceuticals for malignancy disease as complementary medicine with lesser side effects.
In our study, safety of T. peruviana leaves extract was confirmed from its high median lethal dose (LD50 = 3.083 g/kg). Moreover, in vivo genotoxicity tests measuring chromosomal aberrations were done to prove non-mutagenicity of the plant for both somatic and germ cells (Tables 2 and 3). These results declare that the plant cytotoxic action is selective to cancer cells with no evidence for harming the normal tissue, an issue with crucial need in discovering new cytotoxic agents.
In this finding, Thevetia peruviana leaves extracts showed an activity against liver and breast carcinoma cell lines in comparison with doxorubicin (Table 5). Successive extracts of the plant were incorporated in microemulsion formulations (MEF) and characterized for their global size, electrical conductivity, and polydispersity index to reveal thermodynamically stable bicontinuous formulations with homogeneous globule size distribution (Table 4, Fig. 1). In vitro drug release pattern (Fig. 2) revealed that ethanol MEF, which showed potentiation in cytotoxicity against liver carcinoma cell line, exhibits satisfactory sustained drug release behavior, indicating their ability to act as a reservoir for the loaded extract versus rapid release of pet. ether MEF. Cytotoxic activity was potentiated upon application on microemulsion formulations for pet. ether and ethanol extracts, as IC50 of pet. ether MEF decreased to 6.5 (μg/ml) against MCF7 cell line, while ethanol MEF recorded IC50 = 3.58 μg/ml against HEPG2 cell line after showing no activity of the extract at the tested concentrations. Tween 80 used herein as a surfactant has been reported to accelerate hydrocortisone and lidocaine permeation (Kogan & Garti, 2006) in addition to have minimal toxicity (Lawrence & Rees, 2000). PEG 400 is chosen as co-surfactant for being safe, biocompatible, a known permeation enhancer, and largely used in topical preparations (Chessa et al., 2011). As a conclusion, MEFs have proved to increase bioavailability and minimize the effective dose.
Plant kingdom has diverse of phenolic compounds as complex organic substance. Phenolic metabolites have the ability to scavenge free radicals and chelate metals especially iron which affect both initiation and propagation of oxidation process. The stability of these metabolites is due to resonance in the aromatic ring, this ring along with the carboxyl and hydroxy or methoxy substitution may confer to the anti-oxidative power (Đorđević et al., 2010; Dai & Mumper, 2010; Gülcin, 2012). Antioxidant activity calculated for T. peruviana leaves extract as an equivalent to Trolox “a vitamin E analogue” using three different assays revealed its activity to scavenge free radicals and act as a natural antioxidant agent (see the “Antioxidant activity” section in the “Results” section). Flavonoids and phenolic acids have been reported to exhibit a plenty of biological activities such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant (Shon et al., 2004). In addition, many findings have confirmed that plant flavonoids inhibit the mutagenicity induced by chemical mutagens (Negi, 2003). The recordable level of phenolic (47.8 mg GAE/g) and flavonoid (32.7667 mg CE/g) contents of Thevetia peruviana leaves extract may contribute to antioxidant and cytotoxic performance of the plant. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was the sensitive accurate technique that used to identify and quantify the polar constituents in T. peruviana successive ethanolic extract. Rutin (7.3 mg/g) the major flavonoid detected in our study has been reported to improve harmful effects induced by radiation (Radwan & Kenawy, 2008). One finding reported rutin potential activity against colorectal and lung carcinogenesis (Ben Sghaier et al., 2016). The significant cytotoxic activity of the polar fraction could possibly be attributed to its antioxidative stress, a known risk factor of DNA damage and cancer.
Rosmarinic acid (13.5 mg/g), the most abundant phenolic acid herein, is one of natural phenolics found in many Lamiaceae herbs; previous work was done to prove protective effect of rosmarinic acid against aflatoxin B1- and ochratoxin A-induced cytotoxicity in liver carcinoma cell line. In addition, its ability to reduce production of reactive oxygen species and apoptosis along with anti-proliferative effect were investigated and revealed good activity (Renzulli et al., 2004). In addition, rosmarinic acid was reported as a potential chemotherapeutic agent that prevents cardiotoxicity in ADR-treated patients (Kim et al., 2005).
Dihydroxycinnamic or caffeic acid (10 mg/g) is one of secondary metabolites that show crucial role as antioxidant, with increasing collagen production that leads to prevent premature aging and thus used in dermal diseases with antimicrobial activity (Caroline Magnani, 2014). Caffeic acid is known as a natural health supplement and needs for metabolic diseases that shown to have biological effect in cancer treatment (Khan et al., 2016). Chlorogenic acid (8.55 mg/g) a polyphenol present in our diet is proved to have antiproliferative cytotoxic action against breast carcinoma cell line (Kampa et al., 2004).
Regarding the cytotoxic potential of lipoidal matter and its enhancement by incorporation in microemulsion formula, GC/MS phyto-constituents of these lipoids detailed in this platform may contribute to this promising result. Butylated hydroxytoluene (peak 16, 21%) the major lipoidal compound in our GC/MS profile reported for cytotoxicity on leukemia and squamous carcinoma cell lines with butylated hydroxyl anisole to reveal high cytotoxic action and induce apoptosis which may indicate reactive intermediates resulting from interaction between both compounds phenoxyl radicals (SH & Fujisawa, 2003). Phytol (peak 26, 9.8%) is an alcoholic diterpene produced from chlorophyll used mainly as an aromatic ingredient or food additive. Its cytotoxic activity was tested in vitro against tumor cell lines to reveal concentration-dependent cytotoxicity in all cell lines tested, with most activity against the breast adeno-carcinoma cell line (Pejin et al., 2014). Other previous study demonstrated that phytol induces apoptosis in human gastric adenocarcinoma (Song & Cho, 2015).
Seven steroidal compounds were detected in our study representing 7.5%. Phytosterols have been reported for their inhibition of tumor growth and development (Tapiero, 2003). Mechanisms of phytosterols cytotoxic actions have been studied; one is activation of sphingomyelin cycle and cause cell apoptosis, other study proved phytosterols might decrease the metastasis process and initiate apoptosis, besides phytosterols might alter cell membrane composition and interact with the membrane enzymes (Awad et al., 2003). Although there is a widespread belief that plants do not have cholesterol in their metabolites, while (Akihisa, 1991) published that plants contain cholesterol either free or esterified but its quantity is generally small when expressed as percent of total lipid and less than other phytosterols.
Squalene (peak 36, 8.8%) is an antioxidant isoprenoidal compound that revealed potential cytoprotective action against chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Squalene protects light-density bone marrow cells against cisplatin and carboplatin-induced toxicity without protecting tumor cells (Das et al., 2008), a research that adds value to the rule of phyto-constituents as complementary medicine with anticancer drugs.
Natural free fatty acids may be recognized as effective anticancer agents (Siegel et al., 1987). The major fatty acid, octadecenoic acid extract with oleic and linoleic acids revealed cytotoxic and antitumor activities on human gastric and hepatocellular carcinoma along with leukemia tumor cells relative to reference drug 5-fluorouracil, resulting in cell apoptosis/necrosis beside damaging the tumor cell membrane functionally and structurally (Yu et al., 2008).
As a conclusion, the phyto-constituents detected in our metabolic profile of both polar and non-polar fractions may contribute to the cytotoxic action.
Conclusion
Thevetia peruviana is safe cytotoxic antioxidant active plant which has no mutagenic effect against normal either somatic or germ cells. Loading the extracts on microemulsion formulations potentiate the pharmacological activity against liver carcinoma HEPG2 and breast carcinoma MCF7 cell lines with all the advances of nanonization that upgrades solubility, stability, and bioavailability along with reduction in medicinal doses. Analysis by HPLC showed the presence of various phenolic acids and flavonoids, while GC-MS analysis revealed the presence of other metabolites that are probably involved in the antioxidant and cytotoxic actions observed in this study. This work presumed potential candidate for future development of safe nano-cytotoxic agent, and this finding is courageous for further evaluation of the inhibitory effect of the plant on various forms of cancer cell lines. Finally, it is recommended to do further investigation along with clinical studies on Thevetia peruviana micro-formulations in a step to formulate a non-toxic selective anticancer nutraceutical agent.
Availability of data and materials
Data are available from authors on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- GC/MS:
-
Gas chromatography/mass spectrum
- DPPH:
-
Diphenyl picryl hydrazyl
- ABTS:
-
(2,2′-Azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)
- FRAP:
-
Ferric ion reducing antioxidant power
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- MEF:
-
Microemulsion formulation
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- Pet. ether:
-
Petroleum ether
- RRt:
-
Relative retention time
- M.wt:
-
Molecular weight
References
Aboutab E, Hashem F, Sleem A, Maamoun A (2010) Phytochemical and bioactivity investigations of Macfadyena unguis-cati L.(Bignoniaceae). Plant Products Research Journal 14(1):19–27
Adams R (2009) Identification of essential oil compounds by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy, 4th edn. Allured Publishing Corporation, USA
Akihisa T, Kokke W. C. M. C., Tamura, T. In Physiology and Biochemistry of Sterols;. In: Patterson GW, Nes, W. D., , editor. American Oil Chemists’ Society: Champaign, IL; 1991.
Aly FA, Farghaly AA, Salman AS, Hassan EM, Hassan EE,Omara EA, Salama AB (2019) Protective Effect of Rosmarinus officinalis Essential Oil Against Genotoxic and Histopathological Alterations Induced by Paracetamol. Int J Pharmacol 15(6):686-95.
Appa Rao M, Venkata E, Visweswaram D (1978) Effect of certain structural changes in cardiac glycosides of Thevetia peruviana on their toxicity. J Mol Cell Cardiol 10(Suppl. 1):86
Awad AB, Roy R, Fink CS (2003) β-Sitosterol, a plant sterol, induces apoptosis and activates key caspases in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 10(2):497–500
Ben Sghaier M, Pagano A, Mousslim M, Ammari Y, Kovacic H, Luis J (2016) Rutin inhibits proliferation, attenuates superoxide production and decreases adhesion and migration of human cancerous cells. Biomed Pharmacother 84:1972–1978
Caroline Magnani BGC, Vera Lucia Borges Isaac, Marcos Antonio Correa and Herida Regina Nunes Salgado in vitro safety evaluation of Caffeic acid. Athens Journal of Health September (2014) 1(3):181
Cassileth BR, Deng G (2004) Complementary and alternative therapies for cancer. Oncologist 9(1):80–89
Chessa M, Caddeo C, Valenti D, Manconi M, Sinico C, Fadda AM (2011) Effect of penetration enhancer containing vesicles on the percutaneous delivery of quercetin through new born pig skin. Pharmaceutics. 3(3):497–509
Dai J, Mumper RJ (2010) Plant phenolics: extraction, analysis and their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Molecules. 15(10):7313–7352
Das B, Antoon R, Tsuchida R, Lotfi S, Morozova O, Farhat W et al (2008) Squalene selectively protects mouse bone marrow progenitors against cisplatin and carboplatin-induced cytotoxicity in vivo without protecting tumor growth. Neoplasia. 10(10):1105–1104
Đorđević TM, Šiler-Marinković SS, Dimitrijević-Branković SI (2010) Effect of fermentation on antioxidant properties of some cereals and pseudo cereals. Food Chem 119(3):957–963
Elsawi SA, Aly HF, Elbatanony MM, Maamoun AA, Mowawad DM (2018) Phytochemical evaluation of Lagerstroemia indica (L.) Pers. leaves as anti-Alzheimer's. J Mater Environ Sci 9(9):2575–2586
Farag MA, Maamoun AA, Ehrlich A, Fahmy S, Wesjohann LA (2017) Assessment of sensory metabolites distribution in 3 cactus Opuntia ficus-indica fruit cultivars using UV fingerprinting and GC/MS profiling techniques. LWT. 80:145–154
Fayad W, El-Hallouty S, El-Manawaty MA, Mounier MM, Soliman AA, Mahmoud K et al (2017) A systematic multicellular spheroids screening approach lead to the identification of antineoplastic activity in three different plant extracts from the Egyptian flora. J Appl Pharm Sci 7(6):13–22
Gülcin I (2012) Antioxidant activity of food constituents: an overview. Arch Toxicol 86(3):345–391
Hashem F, Aboutabl E, Moharam M, Maamoon A (2007) Macfadyena unguis-cati (L.) A. gentry, a source of free radical scavenger coumestrol. Can J Pure Appl Sci 1:9–13
Heuschkel S, Wohlrab J, Neubert RH (2009) Dermal and transdermal targeting of dihydroavenanthramide D using enhancer molecules and novel microemulsions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 72:552–560
Hwang ES, Do TN (2014) Effects of extraction and processing methods on antioxidant compound contents and radical scavenging activities of laver (Porphyra tenera). Prev Nutr Food Sci 19:40–48
Kampa M, Alexaki V-I, Notas G, Nifli A-P, Nistikaki A, Hatzoglou A et al (2004) Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of selective phenolic acids on T47D human breast cancer cells: potential mechanisms of action. Breast Cancer Res 6(2):R63
Khan MSS, Iqbal MA, Abdul Majid AMS (2016) Effect of crystallization of caffeic acid enhanced stability and dual biological efficacy. Cogent Biology 2(1):1243460
Kim D-S, Kim H-R, Woo E-R, Hong S-T, Chae H-J, Chae S-W (2005) Inhibitory effects of rosmarinic acid on adriamycin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells by inhibiting reactive oxygen species and the activations of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Biochem Pharmacol 70(7):1066–1078
Kim K-H, Tsao R, Yang R, Cui SW (2006) Phenolic acid profiles and antioxidant activities of wheat bran extracts and the effect of hydrolysis conditions. Food Chem 95(3):466–473
Kogan A, Garti N (2006) Microemulsions as transdermal drug delivery vehicles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 123:369–385
Langford SD, Boor PJ (1996) Oleander toxicity: an examination of human and animal toxic exposures. Toxicology. 109(1):1–13
Lawrence MJ, Rees GD (2000) Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 45:89–121
Liu B, Xue Q, Tang Y, Cao J, Guengerich FP, Zhang H (2016) Mechanisms of mutagenesis: DNA replication in the presence of DNA damage. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research 768:53–67
Matloub AA, AbouSamra MM, Salama AH, Rizk MZ, Aly HF, Fouad GI (2018b) Cubic liquid crystalline nanoparticles containing a polysaccharide from Ulva fasciata with potent antihyperlipidaemic activity. Saudi Pharm J 26(2):224–231
Matloub AA, Salama AH, Aglan HA, AbouSamra MM, ElSouda SSM, Ahmed HH (2018a) Exploiting bilosomes for delivering bioactive polysaccharide isolated from Enteromorpha intestinalis for hacking hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 44(4):523–534
Negi PS, Jayaprakasha GK, Jena BS (2003) Antioxidant and antimutagenic activities of pomegranate peel extracts. Food Chem 80:393–397
Oji O, Okafor QE (2000) Toxicological studies on stem bark, leaf and seed kernel of yellow oleander (Thevetia peruviana). Phytother Res 14(2):133–135
Patravale VB, A.A. (2004) Date, and R.M. Kulkarni. Nanosuspensions: a promising drug delivery strategy. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:827–840
Pejin B, Kojic V, Bogdanovic G (2014) An insight into the cytotoxic activity of phytol at in vitro conditions. Nat Prod Res 28(22):2053–2056
Radwan RRSE, Kenawy SA (2008) Hepatoprotective efficiency of combined administration of natural antioxidants (rutin and vitamin E) and cysteine in hyperthermic irradiated rats. Egypt J Hosp Med 32:441–454
Ramos-Silva A, Tavares-Carreón F, Figueroa M, De la Torre-Zavala S, Gastelum-Arellanez A, Rodríguez-García A et al (2017) Anticancer potential of Thevetia peruviana fruit methanolic extract. BMC Complement Altern Med 17(1):241
Rebolleda S, Sanz MT, Benito JM, Beltran S, Escudero I, Gonzalez San-Jose ML (2015) Formulation and characterisation of wheat bran oil-in-water nanoemulsions. Food Chem 167:16–23
Renzulli C, Galvano F, Pierdomenico L, Speroni E, Guerra M (2004) Effects of rosmarinic acid against aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin-A-induced cell damage in a human hepatoma cell line (Hep G2). J Appl Toxicol 24(4):289–296
Samal KK, Sahu HK, Gopalakrishnakone P (1992) Clinico-pathological study of Thevetia peruviana (yellow oleander) poisoning. J Wild Med 3(4):382–386
Samanta J, Bhattacharya S, Rana AC (2016) Antifertility activity of Thevetia peruviana (Pers.) K. Schum leaf in female Sprague-Dawley rat. Indian J Pharmacol 48(6):669
SH SM, Fujisawa S (2003) Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction by butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT). Anticancer Res 23(6c):4693–4701
Shon MYCS, Kahng GG, Nam SH, Sung NJ (2004) Antimutagenic, antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of ethyl acetate extracts from white, yellow and red onions. Food Chem Toxicol 42:659–666
Shrestha P, Adhikari S, Lamichhane B, Shrestha BG (2015) Phytochemical screening of the medicinal plants of Nepal. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 1(6):11–17
Siegel I, Liu TL, Yaghoubzadeh E, Keskey TS, Gleicher N (1987) Cytotoxic effects of free fatty acids on ascites tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 78(2):271–277
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D et al (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82(13):1107–1112
Solans C, Izquierdo P, Nolla J, Azemar N, Garcia-Celma M (2005) Nano-emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 10(3-4):102–110
Song Y, Cho SK (2015) Phytol induces apoptosis and ROS-mediated protective autophagy in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells. Biochem Anal Biochem 4(4):1
Tapiero H (2003) TDTK. Phytosterols in the prevention of human pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother 57(8):321–325
Tenjarla S (1999) Microemulsions: an overview and pharmaceutical applications. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 16:461–521
Tewtrakul S, Nakamura N, Hattori M, Fujiwara T, Supavita T (2002) Flavanone and flavonol glycosides from the leaves of Thevetia peruviana and their HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and HIV-1 integrase inhibitory activities. Chem Pharm Bull 50(5):630–635
Wannes WA, Mhamdi B, Sriti J, Jemia MB, Ouchikh O, Hamdaoui G et al (2010) Antioxidant activities of the essential oils and methanol extracts from myrtle (Myrtus communis var. italica L.) leaf, stem and flower. Food Chem Toxicol 48(5):1362–1370
Yu F, Lu S, Yu F, Shi J, McGuire PM, Wang R (2008) Cytotoxic activity of an octadecenoic acid extract from euphorbia kansui (Euphorbiaceae) on human tumour cell strains. J Pharm Pharmacol 60(2):253–259
Žilić S, Serpen A, Akıllıoğlu G, Janković M, Gökmen V (2012) Distributions of phenolic compounds, yellow pigments and oxidative enzymes in wheat grains and their relation to antioxidant capacity of bran and debranned flour. J Cereal Sci 56(3):652–658
Acknowledgements
The authors would thank National Research Centre (NRC, Egypt) for funding this work (10010112).
Funding
National Research Centre (NRC, Egypt) funded this work under project (no.10010112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
El Sawi S.A. suggests the point, Maamoun A.A. performed all the phytochemical part with writing and editing the manuscript, Salama A.H. performed the pharmaceutical preparations, and Farghaly A.A. performed the pharmacological tests.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Medical Ethical Committee in NRC (Egypt) has approved this work on animals ethically according to its ethical guidelines with approval No. (15/100).
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sawi, S.A., Maamoun, A.A., Salama, A.H. et al. Chemical profiling of Thevetia peruviana leaves cytotoxic active extracts enhanced by microemulsion formulation. Bull Natl Res Cent 44, 93 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-020-00339-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-020-00339-3