Abstract
Background
Electrophoretic SDS-PAGE and SCoT-PCR techniques were used to study the fingerprints and genetic diversity of six Egyptian soybean (Glycine max L.) genotypes (Giza111, Giza21, Giza82, Giza35, Giza22, and Giza83).
Results
SDS-PAGE revealed a total of 23 bands with a polymorphism 30.43%. The maximum number of bands (22) was recorded in Giza111 and Giza82, while the minimum number of bands (18) was recorded in Giza35. The highest similarity index for SDS- PAGE (0.909) was observed between Giza111 and Giza82, while the lowest similarity index (0.714) was recorded between Giza35 and Giza83. SCoT technique was performed by using 11 primers to generate reproducible polymorphic products. The total number of bands was 106, from them 52 polymorphic and 54 monomorphic bands with a polymorphism 49.11%. The dendrogram of both SDS-PAGE and SCoT markers revealed two main clusters; the first cluster includes the cultivars Giza111and Giza21, while the second cluster includes the cultivars Giza82, Giza35, Giza22, and Giza83. The second group was further subdivided into two subgroups; the first subgroup includes cultivars (Giza82 and Giza35) while the second subgroup includes cultivars Giza22 and Giza83.
Conclusion
The markers used in this study created a number of polymorphic bands among the different cultivars that can be utilized as molecular markers for their differentiation. The obtained data indicated that SCoT and SDS-PAGE techniques could be used efficiently for identification and differentiation of the selected genotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Soybean (Glycine max L.) has an economic importance between leguminous plants. It is considered as a source of seed proteins and oil (Hrustić et al., 2006). The reduction of using insecticides and insecticide residues risk can increase profits the bearable levels of soybean insect resistance (Rowan et al., 1991). Soybean has one or more chemicals that consider the genetically controlled resistance factors. Molecular and biochemical characters of the resistance to insect or susceptible cultivars of soybean, as well as amount of genetic diversity among them, takes into account for many purposes for the breeding of soybean (Fahmy and Salama, 2002).
Soybean contains high levels of proteins, and eight essential amino acids such as lysine, arginine, and leucine (Messina, 1995). It also has high levels of fatty acids and appreciable levels of vitamins and minerals. Soybeans contain a huge amount of omega-6 fatty acid, linolenic acid, and isoflavones (daidzeinand genistein) (Chauhan et al., 2008). Soybean contains about 30% of soluble and insoluble carbohydrates (Rotundo and Westgate, 2009). Soybean proteins have the highest nutritional value for human food, being particularly high in lysine. For baking bread for diabetics, soybean flour is used. The soybean meals are indispensable sources of protein in fish, poultry, and livestock nutrition which obtained after defatted soybean flour and the extraction of oil (Popović et al., 2009). The reduction of developing breast cancer, ovarian, cervical, colon, and lung risk can be obtained by low amount of soybean isoflavones. Also, soybean contains asparaginase, which is considered as a therapeutically important protein used with other medicines in the acute lymphatic leukemia and melanosarcoma treatment.
For many years, the morphological traits, molecular and biochemical analysis have been performed to detect and assess in the phylogenetic relationships among soybean cultivars (Badr and Halawa, 2012; Barakat et al., 2013). Morphological characters may be not significantly distinguished and commonly demand plants growing to maturity before the identification. Also, the morphological traits are considered unsteady due to the environmental effects (Ghalmi et al., 2010).
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) is extensively used to detect the phylogenetic relationships between plants. Many researchers recommended using SDS-PAGE as a rapid method to identify and characterize soybean (Maged and Shawkat, 2012).
Molecular markers play an important role in assessing the phylogenetic relationships between and within different species and cultivars. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-based markers were commonly used in studies of genetic diversity, comparative biology, morphological characters, environmental conditions, conservation, and phylogenic phenomena between plant species and cultivars (Haq et al., 2014). Many molecular markers have been used for cultivar identification and phylogenetic analysis (Bornet and Branchard, 2004; Semagn et al., 2006).
After the advent of PCR, the improvement of different molecular markers such as amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), inter simple sequence repeats (ISSRs), simple sequence repeats (SSR), and several new concepts were used. Different markers were used for the determination of the relationships between plant species by many researchers in tomato cultivars (Nawaz et al., 2015), Poaceae plants (Haq et al., 2016), and Citrullus colocynthis (Verma et al., 2017).
Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism was considered as a novel molecular marker. This marker targets on short start codon ATG within plant genes and has been adduced by Collard and Mackill (2009). It was characterized by higher polymorphism and better marker resolvability than other DNA marker techniques like random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPD) and ISSR, therefore earning its popularity for its superiority (Gorji et al., 2011). SCoT markers have salutary properties such as easy to use, cheaper, faster, and including non-radioactive materials than other molecular markers (Mulpuri et al., 2013). SCoTs are more directly used in constructing marker-assisted breeding programs than RAPDs, ISSRs, and SSRs (Mulpuri et al., 2013). SCoT marker is concerned with the conserved start codon in plant genes or flanking short region of the ATG translation initiation (Collard and Mackill, 2009).
SCoT markers have been efficiently used for DNA fingerprinting of Tritordeum bergrothii L. Poaceae (Cabo et al., 2014). Different studies showed that start codon targeted marker has a large ability than other random primers for polymorphism identification and determination of genetic variations through species (Zeng et al., 2014; Tiwari et al., 2016). SCoT markers have been used in many crop plant species such as rice (Collard and Mackill, 2009), cowpea (Igwe et al., 2017), and Plantago (Rahimi et al., 2018).
The goal of this research is to evaluate the SCoT and protein banding pattern (SDS-PAGE) markers effectiveness to determine the phylogenetic relationships among six Egyptian soybean (Glycine max L.) cultivars.
Materials and methods
Plant material and growth conditions
Seeds of six Egyptian soybean (Glycine max L.) cultivars (Giza111, Giza21, Giza82, Giza35, Giza22, and Giza83) were kindly supplied from the Agricultural Research Center (ARC), Giza, Egypt.
DNA extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted and purified from young leaves of the cultivars by using Gene Jet Plant Genomic DNA Purification Mini Kit (Thermo-Scientific, K0791, made in Germany). The final concentration of DNA was adjusted to 50 ng/μl. All the DNA samples were stored at − 20 °C.
Primer design
Primers were designed from consensus sequences derived from the studies by Joshi et al., (1997) and Sawant et al., (1999). All primers were 18-mer and with GC content between 50 and 72% (Table 1). They were dissolved in sterilized water to a final concentration of 100 pM and kept at − 20 °C.
SCoT PCR reaction and amplification conditions
Fifteen primers were used for the amplification of the genomic DNA to assess the phylogenetic relationships. The primers which gave prominent and reproducible bands were selected for the final amplification and data analysis. The primers which gave lesser number of loci were not included in final data analysis. The prominent band was counted as (1) for a presence of the band, whereas for the absence of the band counted as (0) for the phylogram reconstruction. The faint bands were excluded from the final data analysis. Polymorphic information content (PIC) values were calculated for each SCoT primers according to the formula: PIC = 1 − p2 − q2 (Ghislain et al., 1999), where p is a frequency of the present band and q is a frequency of the absent band. All samples were subjected to be differentiated using finally eleven SCoT primers (Table 1). PCR was optimized for testing the SCoT method. The final optimized protocol is reported here. All PCR reactions were performed within a total volume of 50 μl in 96-well plates using a PTC-100 Thermocycler (MJ Research Model PTC100). PCR reaction mixtures contained PCR buffer (Promega; 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.4), 50 mM KCl), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.24 mM of each deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates, 5 U of Taq polymerase (Promega), and 0.8 μm of primer. Each reaction contained 25 ng of template DNA. A standard PCR protocol was used: an initial denaturation step at 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 1 min, 50 °C for 1 min, and 72 °C for 2 min; the final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. All PCR amplification products were separated on 1.2% agarose gels in tris-HCl acetic acid Edita (TAE) buffer stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under UV light. The gel was photographed by gel documentation (Bio-Rad) and analyzed by Total Lab program to find out the molecular weight of each band and that to compare the presence and absence of the band among cultivars, and this data was imported in multi-variant statistical package (MVSP) to find the similarity matrix and dendrogram (UPGMA, suing Jaccard’s coefficient) which reflect the relationships among the studied cultivars.
SDS-PAGE
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) was performed according to the method of Laemmli (1970) as modified by Studier (1973). Seed storage proteins (water soluble proteins) were extracted from seeds of soybean cultivars. Protein fractionations were performed exclusively on vertical slab gel (19.8 cm × 26.8 cm × 0.2 cm) using the electrophoresis apparatus manufactured by Cleaver, UK.
The images were captured by Digital camera (Sony, made in Japan) and transferred directly to the computer, and then the protein bands were analyzed by Total Lab program to find out the molecular mass of each band then compare the presence and absence of the band among studied cultivars, and these data were imported in multi-variant statistical package (MVSP) to find the similarity matrix and dendrogram (UPGMA, using Jaccardʼs coefficient) which reflect the relationships among the studied cultivars.
Results
Phylogenetic relationships of soybean cultivars as revealed by SCoT marker
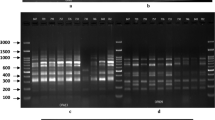
The amplification results of the SCoT primers used in this investigation are presented in Table 1. The 11 primers produced good reproducible and scorable patterns and the amplification profiles were screened for the presence of polymorphisms among the studied soybean cultivars (Fig. 1). The SCoT fingerprints revealed characteristic banding patterns for each cultivar.
SCoT products on 1.2% agarose gel using different primers: SCoT 2, SCoT 4, SCoT 5, SCoT 8, SCoT 13, SCoT 22, SCoT 24, SCoT 26, SCoT 27, SCoT 34, and SCoT 36. Lane M: 1 kb ladder DNA marker. Lanes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 represent cultivars: Giza 111, Giza21, Giza82, Giza 35 Giza 22, and Giza 83, respectively
Soybean cultivars Giza82 and Giza22 revealed positive and negative unique bands, respectively, with SCoT-5 (Table 3), and these bands could be used to distinguish the studied cultivars. A total of 106 bands were generated, among which 52 bands were polymorphic. The percentage of polymorphic bands ranged between 28.57% with SCoT-22 and 66.66% with SCoT-4 and 5 and total average percentage of polymorphism (49.11%) as reported in this study (Table 2).
The average polymorphism information content (PIC) of the SCoT markers was 0.44. The amplification profile (Fig. 1) revealed by the three SCoT primers SCoT-5, SCoT-2, and SCoT-4 yielded highly informative patterns based on calculated PIC (Table 2). These primers, with higher PIC values, have more potential for further study, allowing investigating more cultivars or sampling sites using a reduced number of primers. PIC ranged from 0.2 in SCoT-22 to 0.74 in SCoT-5 with an average of 0.44.
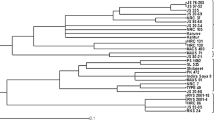
The highest similarity value 0.83 was recorded between the two cultivars Giza82 and Giza35, followed by 0.806 among Giza82 and Giza83; these values indicate that each two cultivars with high similarity were closely related. While the lowest value recorded was 0.646 among cultivars Giza82 and Giza21; this indicates that these two cultivars were distant cultivars genetically (Table 4). The dendrogram gave two main clusters; the first cluster includes the cultivars Giza111and Giza21, while the second cluster includes the cultivars Giza82, Giza35, Giza22, and Giza83. The second group was divided into two sub-cluster; the first sub-cluster includes cultivars (Giza82 and Giza35) while the second sub-cluster includes the cultivars Giza22 and Giza83 (Fig. 2).
Seed storage proteins analysis of soybean cultivars as revealed by using SDS-PAGE
The SDS-PAGE for seed storage proteins (soluble proteins) was used to investigate the biochemical differences among the tested soybean cultivars (Table 5 and Fig. 3). The bands pattern indicates the differences among the tested cultivars in molecular weight and optical intensity of the bands. The results of SDS-PAGE revealed a total of 23 bands with molecular weight (Mw) ranging from 20 to 270 kilodaltons (kDa). The maximum number of bands (22) was recorded in cultivars Giza111 and Giza82, while the minimum number of bands (18) was recorded in cultivar Giza35. Only one negative unique band was detected in the cultivar Giza 35 (33 kDa). The band at Mw 150 kDa was observed only in the cultivars Giza111 and Giza82. While, the band with Mw 120 kDa was absent in cultivars Giza22and Giza35.
The results reported from seed storage proteins profiles were used to determine the relationships between studied cultivars. The similarity indices among these cultivars were estimated for each pair-wise group (Table 6 and Fig. 4). The similarity relationships based on protein analysis ranged from 0.905, 0.909, to 0.714 (Table 6). The highest similarity index (0.909) was recorded between Giza 111 and Giza 82, while the lowest similarity index (0.714) was recorded between Giza35 and Giza83. The dendrogram gave two main genetic clusters; the first cluster includes the cultivars Giza22 and Giza35, while the second cluster includes the cultivars Giza83, Giza 21, Giza 82, and Giza 111. The second cluster was further divided into two sub-clusters; the first sub-cluster includes cultivars (Giza83 and Giza21) while the second sub-cluster includes cultivars Giza82 and Giza111 (Fig. 4).
Genetic similarity analysis based on the collective data of SCoT marker and SDS-PAGE
The highest similarity value 0.827 was recorded between the two cultivars Giza82 and Giza35, followed by 0.813 among Giza22 and Giza83; this indicates that these two cultivars were closely related. While, the lowest value (0.681) was reported among the two cultivars Giza82 and Giza21; this indicates that these two cultivars were genetically distant (Table 7). The dendrogram gave two main genetic clusters; the first clusters comprise the cultivars Giza111 and Giza21, while the second cluster includes the cultivars Giza82, Giza35, Giza22, and Giza83. The second cluster was divided into two sub-clusters; the first sub-cluster includes cultivars (Giza82 and Giza35), while the second sub-cluster includes cultivars Giza22 and Giza83 (Fig. 5). The unweighted pair-group arithmetic (UPGMA) results of collective data are similar to the UPGMA of SCoT marker; this indicates that SCoT marker is a powerful marker for discrimination and identification of deferent cultivars.
Discussion
Phylogenetic relationships of soybean cultivars as revealed by SCoT marker
Molecular markers are used for characterization of the phylogenetic relationships at genomic DNA level (Madhumati, 2014). The design of SCoT markers are very easy depending on a conserved sequence such as ATG that surrounding the start codon of translation (Xiong et al., 2011). Evaluation of SCoT markers has already been established in Elymus sibiricus and Vigna unguiculata (Zhang et al., 2015; Igwe et al., 2017), respectively. In the present study, there is no linkage between GC content of primer and the clarification of the banding profile was reported which is in harmony with Marilla and Scoles (1996). The percentage of polymorphic bands ranged between 28.57% with SCoT-22 and 66.66% with SCoT-4 and 5 as shown in Fig. 1 and Tables 2 and 3. Satya et al., (2013) obtained similar results in studying genetic diversity between 155 genotypes of Boehmeria nivea L. They used 24 SCoT markers, which produced 136 amplicons with 87.5% polymorphism. High polymorphism (49.11%) as reported in this study (Table 2) is in compliance with earlier investigations in soybean (Boerma and Mian, 1998) which reported (98.54% polymorphism) with RAPD markers. Fahmy and Salama (2002) observed 94% of genetic polymorphism with RAPD markers and then Barakat (2004) reported 90.84% of polymorphism in soybean cultivars by using RAPD markers. Also, our study is in harmony to other investigations such as in grape [the polymorphism was 93% (Guo et al., 2012)] and 97.10% in Atriplex halimus (El Framawy et al., 2016). Polymorphic information content (PIC) ranged from 0.2 in SCoT-22 to 0.74 in SCoT-5 with an average of 0.44 which is in agreement with PIC value obtained in another studies such as 0.72 by SSR marker (Ghose et al., 2013), while its value by RAPD was 0.38 Henuka et al., (2015). So, PIC parameters are used to investigate their usefulness in detecting the fingerprinting (Agarwal et al., 2018).
The highest similarity value 0.83 was recorded between the two cultivars Giza82 and Giza35, while the lowest value recorded was 0.646 among cultivars Giza82 and Giza21 (Table 4 and Fig. 2). Xiong et al., (2011) determined the phylogenetic relationships of cultivated peanut genotypes using SCoT marker, and they documented that not all genotypes related to the same variety were classified in the same group. Aboulila and Mansour (2017) studied the phylogenetic relationships among ten Hordeium vulgare genotypes using SCoT marker, and they reported that SCoT marker is an efficient technique for obtaining new fingerprint of Hordeium vulgare. Furthermore, Mohamed et al., (2017) used SCoT marker for the discrimination and identification of 14 wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars obtained from different location from North Africa and they classified these cultivars into many groups according to the resulting dendrogram.
Seed storage proteins analysis of soybean cultivars as revealed using SDS-PAGE
These protein profiles were used as a biochemical fingerprint for the tested six Egyptian soybean cultivars (Table 5 and Fig. 3). The low polymorphism of protein could be referred to the conservative nature of the seed proteins (Bonfitto et al., 1999). Low level of protein polymorphism was found in early ripening peach of Sinai (Mansour et al., 1998) and in mung bean cultivars (Hassan, 2001). Seed proteins of soybean have two types of proteins, trypsin inhibitor and lipoxygenase, that are responsible for the production of antibiosis in susceptible insects (Johnston et al., 1993). Trypsin inhibitor protein has Mw 20 kDa (Krishnan, 2001). In this investigation, the protein band at Mw 20 kDa may be a trypsin inhibitor, while the band at Mw 89 kDa (Fig. 1) may be lipoxygenase (Stejskal and Griga, 1995).
The highest similarity index (0.909) was found between Giza 111 and Giza 82, while the lowest similarity index (0.714) was found between Giza35 and Giza83 (Table 6 and Fig. 4). Our results were compared with Sofalian et al. (2015) results; they studied genetic variation among 17 soybean genotypes using seed storage proteins as biochemical marker, and they found that genotypes divided into four groups, proteins with low Mw (LMW-GS) and high Mw (HMW-GS) divided them into three groups.
Genetic similarity analysis based on the collective data of SCoT marker and SDS-PAGE
Our results of genetic similarity analysis based on the collective data of SCoT marker and SDS-PAGE as observed in (Fig. 5 and Table 7) were in agreement with the result of Barakat (2004), who used RAPD and SDS-PAGE techniques to study the phylogenetic relationships of six Egyptian soybean cultivars.
Conclusion
It was found from genetic similarity based on the collective data of SCoT marker and SDS-PAGE that the highest similarity was recorded between Giza82 and Giza35, while the lowest similarity was recorded between Giza82 and Giza21. The genetic similarity results from collective data of both SCoT and SDS-PAGE techniques indicate that the SCoT markers are more viable for discrimination and identification of cultivars than SDS-PAGE.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Adenine
- AFLP:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
- bp:
-
Base pair
- C:
-
Cytosine
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- G:
-
Guanine
- gm:
-
Gram
- HMW:
-
High molecular weight
- ISSRs:
-
Inter simple sequence repeats
- kDa:
-
Kilodalton
- LMW:
-
Low molecular weight
- M:
-
Monomorphic band
- min:
-
Minute
- P:
-
Polymorphic band
- PIC:
-
Polymorphic information content
- pM:
-
Picomole
- RAPDs:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNAs
- SCoT-PCR:
-
Start Codon Targeted polymerase chain reaction
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SNPs:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
- T:
-
Thymine
- TAE:
-
Tris-HCl acetic acid Edita
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair-group arithmetic
References
Aboulila AA, Mansour M (2017) Efficiency of triple-SCoT primer in characterization of genetic diversity and genotype-specific markers against SSR fingerprint in some Egyptian barley genotypes. Am J Mol Biol 7(03):123–137
Agarwal A, Gupta V, Haq S, PJb K, SLc K, Kachhwaha S (2018) Assessment of genetic diversity in 29 rose germplasms using SCoT marker. J King Saud Univ – Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.04.022
Badr A, Halawa M (2012) Genetics and molecular effects of gamma radiation on some varieties of cowpea A MSC Thesis for Faculty of Science, Tanta University
Barakat H (2004) Genetic fingerprinting and relationships of six soybeans [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] cultivars based on protein and DNA Polymorphis. J Agri Biol 6:877–883
Barakat HM, Amina AE, Nahla ASE, Sara AA (2013) Genetic studies on Egyptian landraces using molecular markers A MSC Thesis, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University
Boerma HR, Mian MAR (1998) Application of DNA markers for selection of intractable soybean traits. Kor Soybean Digest 15:106–121
Bonfitto R, Galleschi L, Macchia M, Saviozzi F, Navari-Izzo F (1999) Identification of melon cultivars by gel and capillary electrophoresis. Seed Sci Tech 27:779–783
Bornet B, Branchard M (2004) Use of ISSR fingerprints to detect microsatellites and genetic diversity in several related brassica taxa and arabidopsis thaliana. Hereditas 140:245–248
Cabo S, Ferreira L, Carvalho A, Martins-Lopes P, Martín A (2014) Potential of start codon targeted (SCoT) markers for DNA fingerprinting of newly synthesized tritordeumsand their respective parents. J Appl Genet 55:307–312
Chauhan GS, Kumar V, Pratap D, Rani A (2008) Genotypic variability for soymilk and tofu making quality of released Indian soybean cultivars. Fifth international soybean processing and utilization conference January 2008, Bhopal
Collard BCY, Mackill DJ (2009) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: a simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:86–93
El Framawy A, Elbakatoushi R, Deif H (2016) Genetic variation among fragmented populations of Atriplex halimus L. using start codon targeted (SCoT) and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 region markers. Am J Mol Biol 06(02):101–115
Fahmy KH, Salama SI (2002) Biochemical and genetic fingerprints for some soybean [Glycin max (L.) Merr.] cultivars resistant to Etiellazinekenlla (Triet.) Egypt. J Genet 31:309–329
Ghalmi N, Malice M, Jacquemin JM, Ounane SM, Mekliche L, Baudoin JP (2010) Morphological and molecular diversity within Algerian cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) Walp. Landraces. Genet Res Crop Evol 57:371–386
Ghislain M, Zhang DP, Fajardo D, Huamán Z, Hijmans RJ (1999) Marker assisted sampling of the cultivated andean potato solanum phureja collection using RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 46:547–555
Ghose K, McCallum J, Fillmore S, Kirby C, Sanderson K, Joly S, Bruneau A, Fofana B (2013) Structuration of the genetic and metabolite diversity among Prince Edward Island cultivated wild rose ecotypes. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 160:251–263
Gorji AM, Poczai P, Polgar Z, Taller J (2011) Efficiency of arbitrarily amplified dominant markers (SCoT, ISSR and RAPD) for diagnostic fingerprinting in tetraploid potato. Am J Potato Res 88:226–237
Guo DL, Zhang JY, Liu CH (2012) Genetic diversity in some grape varieties revealed by SCoT analyses. Mol Biol Rep 39:5307–5313
Haq S, Jain R, Sharma M, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2014) Identification and characterization of microsatellites in expressed sequence tags and their cross transferability in different plants. Int J Genom 2014:12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/86394812
Haq S, Kumar P, Singh RK, Verma KS, Bhatt R, Sharma M, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2016) Assessment of functional EST-SSR markers (sugarcane) in cross-species transferability, genetic diversity among poaceae plants, and bulk segregation analysis. Genetics Res Int 2016: 7052323. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7052323
Hassan HZ (2001) Biochemical and molecular genetics characterization of nine mung bean (Vigna radiate L.) cultivars. Bull Fac Assiut Univ 30:137–151
Henuka R, Raju D, Janakiram N (2015) Characterization and analysis of genetic diversity among different species of rose (Rosa species) using morphological and molecular markers. Indian J Agric Sci 85(2):240–245
Hrustić M, Miladinović J, Vidić M, Đukić V (2006) ZbornikradovaInstitutazaratarstvo i povrtarstvo, vol. 42, br, p 2
Igwe DO, Afiukwa CA, Ubi BE, Ogb KI, Ojuederie OB, Ude GN (2017) Assessment of genetic diversity in Vigna unguiculata L. (Walp) accessions using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphic markers. BMC Genet 18(1):98
Johnston KA, Gatehouse JA, Anstee JH (1993) Effect of soybean protease inhibitors on the growth and development of larval Helicoverpa armigera. J Insect Physiol 39:657–664
Joshi C, Zhou H, Huang X, Chiang VL (1997) Context sequences of translation initiation codon in plants. Plant Mol Biol 35:993–1001
Krishnan HB (2001) Characterization of soybean. Plant Sci 160:979–986
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Madhumati B (2014) Potential and application of molecular markers techniques for plant genome analysis. Int J Pure App Biosci 2(1):169–188
Maged AEA, Shawkat MA (2012) Interspecific diversity of Egyptian and foreign new lines of chickpea based on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and isozyme markers. AJB 6:135–139
Mansour NM, Fathi MA, Hassan HZ (1998) Selection and evaluation on the horticulture and biochemical genetic bases of early peach of Sinai. In Proc. of 26th Annual Meeting of Genetics. Alex. 29-30 Sept, pp 347–360
Marilla EF, Scoles GJ (1996) The use of RAPD markers in Hordeum phylogeny. Genome 39:646–654
Messina M (1995) Modern applications for the ancient bean: soybeans and the prevention and treatment of chronic disease. J Nutr 125:567S–569S
Mohamed AH, Ibrahim M, Teleb SS, Tantawy ME (2017) SEM and SCoT markers unveil new taxonomic and genetic insights about some northern African Triticum aestivum L. cultivars. Vegetos- An Int J Plant Res 30:1
Mulpuri S, Muddanuru T, Francis G (2013) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism in toxic and non-toxic accessions of jatropha curcas L. and development of a codominant SCAR marker. Plant Sci 207:117–127
Nawaz S, Chaudry Z, Bibi A, Jan SA, Bibi K (2015) Agro-morphological and molecular characterization of local tomato cultivars grown in pakhal region of Pakistan using RAPD markers. Middle-East J Sci 23(5):856–860
Popović V, Vlahović B, Malešević M, Đukić V, Jakšić S (2009) Proizvodnjasemena NS sortisoje. IV Savetovanje o biotehnologiji, zbornikradova, Čačak
Rahimi M, Nazari L, Kordrostami M, Safari P (2018) SCoT marker diversity among Iranian Plantago ecotypes and their possible association with agronomic traits. Sci Hortic 233:302–309
Rotundo JL, Westgate M (2009) Meta-analysis of environmental effects on soybean seed composition. Field Crop Res 110(2):147–156
Rowan GB, Boerma HR, All JN, Todd J (1991) Soybean cultivar resistance to defoliating insects. Crop Sci 31:678–682
Satya P, Karan M, Jana S, Mitra S, Sharma A, Karmakara PG, Rayb DP (2013) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism reveals genetic diversity in wild and domesticated populations of ramie (Boehmeria nivea L. Gaudich.), a premium textile fiber producing species. Meta Gene 3:62–70
Sawant SV, Singh PK, Gupta SK, Madnala R, Tuli R (1999) Conserved nucleotide sequences in highly expressed genes in plants. J Genet 78:123–131
Semagn K, Bjornstad A, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) An overview of molecular marker methods for plant. Afr J Biotechnol 25:2540–2569
Sofalian O, Bandarian P, Asghari A, Sedghi M, Firooozi B (2015) Identification of seed storage protein polymorphism in some soybean (Glycine max Merril) genotypes using SDS-PAGE technique. YYÜ TAR BİL DERG (YYU J AGR SCI) 25(2):127–133
Stejskal J, Griga M (1995) Comparative analysis of some isozymes and proteins in somatic and zygotic embryos of soybean [Glycine max (L.)Merr.]. J Plant Physiol 146:497–502
Studier FW (1973) Analysis of bacteriophage T1 early RNAs and proteins of slab gels. J Mol Biol 79:237–248
Tiwari G, Singh R, Singh N, Choudhury DR, Paliwal R, Kumar A, Gupta V (2016) Study of arbitrarily amplified (RAPD and ISSR) and gene targeted (SCoT and CBDP) markers for genetic diversity and population structure in Kalmegh [Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees]. Ind Crop Prod 86:1–11
Verma KS, ul Haq S, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2017) RAPD and ISSR marker assessment of genetic diversity in Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: a unique source of germplasm highly adapted to drought and high-temperature stress. 3 Biotech 7(5):288
Xiong F, Zhong R, Han Z, Jiang J, He L, Zhuang W, Tang R (2011) Start codon targeted polymorphism for evaluation of functional genetic variation and relationships in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes. Mol Biol Rep 38:3487–3494
Zeng B, Zhang Y, Huang L, Jiang X, Luo D, Yin G (2014) Genetic diversity of orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.) germplasms with resistance to rust diseases revealed by start codon targeted (SCoT) markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 54:96–102
Zhang J, Xie W, Wang Y, Zhao X (2015) Potential of start codon targeted (SCoT) markers to estimate genetic diversity and relationships among chinese Elymus sibiricus accessions. MoleculesVol. 30 Issue 1 20:5987–6001
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all the researchers whom we cited in this review for their significant and valuable research.
Funding
There are currently no funding sources in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WAR and SAO preformed the laboratory analysis. WAR and SAO wrote the paper, performed the data, and coordinated the data collection. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. So this work was carried out in collaboration between the two authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Rayan, W.A., Osman, S.A. Phylogenetic relationships of some Egyptian soybean cultivars (Glycine max L.) using SCoT marker and protein pattern. Bull Natl Res Cent 43, 161 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0197-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0197-4