Abstract
Purpose
To quantify and categorize fluoroscopically-guided procedures with radiation doses exceeding 5000 mGy reference point air kerma (Ka,r). Ka,r > 5000 mGy has been defined as a “significant radiation dose” by the Society of Interventional Radiology. Identification and analysis of interventions with high radiation doses has the potential to reduce radiation-induced injuries.
Materials and methods
Radiation dose data from a dose monitoring system for 19 interventional suites and 89,549 consecutive patient encounters from January 1, 2013 to August 1, 2019 at a single academic institution were reviewed. All patient encounters with Ka,r > 5000 mGy were included. All other encounters were excluded (n = 89,289). Patient demographics, medical specialty, intervention type, fluoroscopy time (minutes), dose area product (mGy·cm2), and Ka,r (mGy) were evaluated.
Results
There were 260 (0.3%) fluoroscopically-guided procedures with Ka,r > 5000 mGy. Of the 260 procedures which exceeded 5000 mGy, neurosurgery performed 81 (30.5%) procedures, followed by interventional radiology (n = 75; 28.2%), neurointerventional radiology (n = 55; 20.7%), and vascular surgery (n = 49; 18.4%). The procedures associated with the highest Ka,r were venous stent reconstruction performed by interventional radiology, arteriovenous malformation embolization performed by neurointerventional radiology, spinal hardware fixation by neurosurgery, and arterial interventions performed by vascular surgery. Neurointerventional radiology had the highest mean Ka,r (7,799 mGy), followed by neurosurgery (7452 mGy), vascular surgery (6849 mGy), and interventional radiology (6109 mGy). The mean Ka,r for interventional radiology performed procedures exceeding 5000 mGy was significantly lower than that for neurointerventional radiology, neurosurgery, and vascular surgery.
Conclusions
Fluoroscopically-guided procedures with radiation dose exceeding 5000 mGy reference point air kerma are uncommon. The results of this study demonstrate that a large proportion of cases exceeding 5000 mGy were performed by non-radiologists, who likely do not receive the same training in radiation physics, radiation biology, and dose reduction techniques as radiologists.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Minimally invasive, image-guided interventional procedures have expanded the scope of medical practice across numerous domains of medicine, owing to the demonstrated benefit to patients (Heilmaier et al. 2015). As the utilization of these procedures increases, the health risks associated with ionizing radiation to the patients and physicians must be given further consideration (Koenig et al. 2001; Jaschke et al. 2017). The radiation dose between fluoroscopically-guided procedures may vary significantly, and in an effort to reduce patient radiation exposure, radiation dose displays have been required on fluoroscopy equipment (International Electrotechnical Commission 2010; Food and Drug Administration, HHS 2005).
Radiation dose is traditionally measured using fluoroscopy time (FT), dose-area-product (DAP), also known as kerma-area-product (PKA), and reference point air kerma (Ka,r). Stochastic effects of radiation, including carcinogenesis and hereditary effects, are estimated using DAP. The deterministic health effects, which vary with the dose of radiation and include skin injury, hair loss, and cataracts, are assessed using peak skin dose (PSD) or Ka,r (Bundy et al. 2018; Duncan et al. 2013). In 2009, the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) set forth recommendations regarding radiation dose management related to interventional radiologic procedures (Stecker et al. 2009). These guidelines defined a significant radiation dose threshold as any of the following: PSD > 3000 mGy, Ka,r > 5000 mGy, DAP > 500 Gy·cm2, or FT > 60 min (Stecker et al. 2009). These thresholds were established to identify patients who require clinical follow-up for potential deterministic radiation-induced injury.
The varying complexity of pathologies treated using fluoroscopically-guided endovascular procedures leads to a significant number of prolonged procedures, which results in increased radiation exposure to patients and operators (Hassan and Amelot 2017; Kirkwood et al. 2015; Miller et al. 2003). Identifying those procedures associated with significantly high radiation doses will allow for more tactical dose management strategies that may reduce the likelihood of radiation injury to patients and limit the cumulative radiation exposure to physicians.
The purpose of this study was to quantify and categorize fluoroscopically-guided interventions with Ka,r exceeding 5000 mGy.
Materials and methods
Study design
This study was conducted with Institutional Review Board approval and complied with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. Radiation dose data were recorded and extracted using dose management software (DoseWatch; GE Healthcare, Buc, France) which was installed in all angiography suites. The DoseWatch software captured dosimetric data from 19 interventional suites including 4 hybrid operating rooms. Radiation dose data for 89,549 consecutive patient encounters from January 1, 2013 to August 1, 2019 at a single academic institution were reviewed.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
All patient encounters with Ka,r > 5000 mGy were included (n = 260). All other encounters were excluded (n = 89,289). Each intervention was treated as a single patient encounter. Patients who underwent more than one intervention in separate sessions were included as discrete encounters.
Collected and defined parameters
Patient demographics, medical specialty, intervention type, FT, DAP, and Ka,r were evaluated. Medical specialties included interventional radiology, neurointerventional radiology, neurosurgery, or vascular surgery. FT was defined as the total time that fluoroscopy was used during the intervention and was recorded in 0.1-min increments. DAP was defined as the product of the dose in air in a given plane by the area of the entire x-ray beam emitted from the x-ray tube. Ka,r was defined as the air kerma accumulated in space relative to the fluoroscopic gantry. All dosimetry parameters were automatically recorded by each fluoroscopic unit per industry standards (International Electrotechnical Commission 2010; Jones and Pasciak 2011; NCRP Report 168 | NCRP | Bethesda, MD n.d.).
Patient demographics
Patient demographics are shown in Table 1. Demographic and dosimetric data were collected for 260 discrete encounters. The study included 159 (61.2%) male subjects, 80 (30.8%) female subjects, and 21 (8.1%) subjects of unknown sex. Mean age was 61 ± 17 years (range: 18–94 years). There was no significant difference in demographics between medical disciplines.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis and graphic representations were derived using R software version 3.2.2 (R Core Team; Vienna, Austria). The mean FT, DAP, and Ka,r were obtained by summing the values for each individual procedure within each medical discipline and dividing by the total value from all procedures within the discipline. DAP and Ka,r were normalized prior to parametric testing. Independence between two categorical variables was assessed by Fischer’s exact test or one-way ANOVA. Two-sample t-tests were conducted to compare population means of two independent groups. During pairwise testing, p values were adjusted using the Benjamin and Hochberg correction. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all tests.
Results
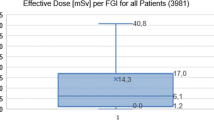
During the study period, 260 (0.3%) discrete fluoroscopically-guided procedures had a Ka,r which exceeded 5000 mGy. Table 2 displays the distribution of procedures by medical discipline and the mean FT, DAP, and Ka,r. Of the 260 procedures which exceeded 5000 mGy, neurosurgery performed 81 (30.5%), followed by interventional radiology (n = 75; 28.2%), neurointerventional radiology (n = 55; 20.7%), and vascular surgery (n = 49; 18.4%). Neurointerventional radiology had the highest mean Ka,r (7,799 mGy) followed by neurosurgery (7452 mGy), vascular surgery (6849 mGy), and interventional radiology (6109 mGy). Neurosurgery had the highest mean fluoroscopy time among the medical disciplines (99 min), followed by neurointerventional radiology (90 min), vascular surgery (73 min), and interventional radiology (51 min).
Figure 1 displays the radiation dose data distribution by intervention type and medical discipline. The interventions associated with the highest Ka,r were venous stent reconstruction performed by interventional radiology, arteriovenous malformation (AVM) embolization performed by neurointerventional radiology, spinal hardware fixation by neurosurgery, and arteriography performed by vascular surgery. The interventions associated with the highest fluoroscopy times were venous stent reconstruction performed by interventional radiology, AVM embolization performed by neurointerventional radiology, cerebral arteriography and embolization performed by neurosurgery, and spinal hardware fixation by neurosurgery. The interventions associated with the highest DAP were venous stent reconstruction performed by interventional radiology, arteriography performed by vascular surgery, and pelvic arteriography with embolization performed by vascular surgery.
Mean FT, DAP, and Ka,r distribution by intervention type and medical discipline (FT = fluoroscopy time, DAP = dose area product, Ka,r. = reference point air kerma, AVM = arteriovenous malformation, TIPS = transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, EVAR = endovascular aneurysm repair, TEVAR = thoracic endovascular aortic repair)
Figure 2 and Table 3 display the mean radiation dose data and standard deviation by medical discipline and the P values from radiation dose data comparisons between medical disciplines, respectively. The mean Ka,r for interventional radiology performed procedures exceeding 5000 mGy was significantly lower than that for neurointerventional radiology (p < 0.001), neurosurgery (p < 0.001), or vascular surgery (p = 0.02) performed procedures. The mean FT for interventional radiology performed procedures exceeding 5000 mGy was significantly lower than that for neurointerventional radiology (p < 0.001), neurosurgery (p < 0.001), or vascular surgery (p = 0.014) performed procedures. The mean DAPs for neurointerventional radiology and neurosurgery performed procedures exceeding 5000 mGy were both significantly lower than that for vascular surgery performed procedures (p = 0.015 and p = 0.039, respectively).
Discussion
A wide variety of endovascular procedures across many medical disciplines have documented Ka,r exceeding 5000 mGy, representing a proportion of procedures which reach a significant radiation dose. These findings comprehensively summarize the specific fluoroscopically-guided procedures which most commonly exceed the threshold radiation dose and are supported by previous studies: Fluoroscopically-guided fenestration, endovascular aneurysm repair, pedicle screw placement, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion, vertebral augmentation, and AVM embolization have all been previously associated with the highest level of radiation doses (Kirkwood et al. 2015; Srinivasan et al. 2014; Riabroi et al. 2018). Of note, the mean Ka,r and FT among all procedures performed by interventional radiology were significantly lower than those performed by neurointerventional radiology, neurosurgery, and vascular surgery. This study demonstrated a significant difference in radiation dose metrics between medical disciplines performing fluoroscopically-guided procedures. While the implications of these findings are not fully elucidated, it may imply that formal standards for radiation dose reduction, such as those put forth by the American College of Cardiology and SIR, have led to improved radiation safety practices (Stecker et al. 2009; Hirshfeld et al. 2018).
The RAD-IR study performed by Miller et al analyzed dosimetry data from a variety of interventional radiology and neurointerventional radiology procedures and proposed radiation reference levels for fluoroscopically-guided procedures (Miller et al. 2003; Miller et al. 2009). Their work was aimed at creating mean radiation dose thresholds that when exceeded, could prompt investigation into institution fluoroscopy equipment, procedure protocols, and operator technique to identify areas for improved radiation safety (Miller et al. 2009). Universal radiation dose reference values for all fluoroscopically-guided procedures would provide a means for individual institutions to oversee radiation safety and ensure that interventionalists across medical disciplines are practicing within the expected dose limits for the corresponding procedures.
While medical specialties performing fluoroscopy-guided procedures generally attempt to adhere to the radiation reduction principle of ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable), universal policies regarding patient follow-up when a significant radiation dose is reached are needed to optimize patient care (Hertault et al. 2015; Bartal et al. 2014). The post-procedural recommendations made by SIR when a significant radiation dose threshold is exceeded include: documentation in the patient’s medical record, clinical follow-up to assess for deterministic radiation-induced injury, providing written radiation follow-up instructions on the patient’s discharge instruction sheet, and procedural review by a qualified medical physicist (Stecker et al. 2009). The results of this study demonstrate that all physicians performing fluoroscopically-guided procedures may expect to exceed significant radiation dose thresholds occasionally. As such, structured, institution-wide post-procedural policies should be adopted to ensure adequate patient follow-up. Perry et al., for example, demonstrated the feasibility of a dose monitoring process utilizing software monitoring and documentation to alert physicians when procedures exceed Ka,r of 5000 mGy so clinical follow-up could be arranged to assess for skin injury (Perry et al. 2019). Particularly, all physician groups who perform the procedures that have shown to exceed significant dose thresholds should have an instituted failsafe method for the detection of high doses cases and post-procedural evaluation of the patients with a feedback loop to radiation safety officer/medical physicist after clinical evaluation and patient education.
Similarly, this study provides insight regarding the distribution of specific fluoroscopically-guided procedures which most commonly exceed significant radiation doses. It is critical to consider the adverse health risks associated with occupational radiation exposure and the cumulative impact of small radiation doses obtained during the course of a physician’s career. The cumulative radiation risks include premature cataract formation, early carotid atherosclerosis, and possibly left-sided brain malignancies (Roguin et al. 2013; Ciraj-Bjelac et al. 2010). With this in mind, more aggressive radiation safety practices may be used when performing the procedures listed in Fig. 1 to reduce physician and patient radiation dose. Specific steps which may be taken by interventionalists to reduce patient and operator dose include the use of radiation-absorbing pads, which have been demonstrated to reduce physician radiation dose by approximately 70% during procedures using femoral artery access (Miller et al. 2017; Fetterly et al. 2011). Further, utilization of real-time image noise-reduction technology have demonstrated significant reductions in radiation doses across interventional radiology, cardiology, and neurointerventional radiology-performed interventions (Söderman et al. 2013). Additionally, precisely adjusting collimator boundaries to the region of interest and limiting magnification modes may decrease the contribution of fluoroscopy to the overall radiation dose (NCRP Report 168 | NCRP | Bethesda, MD n.d.). Finally, utilizing the “last image-hold” feature and intermittent, pulsed fluoroscopy on lower frame rates are additional techniques which can minimize both patient and operator radiation doses. One further factor that should be considered regarding increased radiation safety practices is the complexity of the procedure to be performed. While some procedures may exceed significant dose thresholds owing to patient or case specific limitations, other procedures are inherently more complex and will have increased radiation dose exposure regardless of the case specifics (Bundy et al. 2018).
This study has limitations including the single-center, retrospective design of the analysis. Peak skin dose was not directly assessed in this current study; however, SIR recommends that Ka,r be used as the preferred best clinical approximation of skin dose (Stecker et al. 2009). Image magnification, which affects dose, was not recorded in dose management software and therefore not included in this study. Additionally, the procedures were categorized by MedWatch, the U. S Food and Drug Administration safety reporting program, which does not provide a detailed description of each individual procedure (FDA 2019). Finally, the current study only represents the experiences of physicians from a single-center, therefore potentially limiting the generalizability to other regions.
This study demonstrates that fluoroscopically-guided procedures with high radiation dose exceeding 5000 mGy reference point kerma are uncommon. The majority of cases exceeding 5000 mGy were performed by non-radiologists, who may not receive the same training in radiation physics, radiation biology, and dose reduction techniques as radiologists. This may provide an opportunity for radiology societies to reach out to other medical specialties which perform fluoroscopically-guided procedures to educate and collaborate on radiation safety and establish a multidisciplinary institutional database to ensure consistent follow-up for all high dose cases.
Conclusions
Fluoroscopically-guided procedures with radiation dose exceeding 5000 mGy reference point air kerma are uncommon. The results of demonstrate that a large proportion of cases exceeding 5000 mGy were performed by non-radiologists, who likely do not receive the same training in radiation physics, radiation biology, and dose reduction techniques as radiologists.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- FT:
-
Fluoroscopy time
- DAP:
-
Dose-area-product
- PKA :
-
Kerma-area-product
- Ka,r :
-
Reference point air kerma
- SIR:
-
Society of interventional radiology
- AVM:
-
Arteriovenous malformation
- ALARA:
-
As low as reasonably achievable
References
Bartal G, Vano E, Paulo G, Miller DL (2014) Management of patient and staff radiation dose in interventional radiology: current concepts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37(2):289–298
Bundy JJ, Chick JFB, Hage AN, Gemmete JJ, Srinivasa RN, Johnson EJ et al (2018) Contemporary interventional radiology Dosimetry: analysis of 4,784 discrete procedures at a single institution. J Am Coll Radiol 15(9):121–121
Ciraj-Bjelac O, Rehani MM, Sim KH, Liew HB, Vano E, Kleiman NJ (2010) Risk for radiation-induced cataract for staff in interventional cardiology: is there reason for concern? Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 76(6):826–834
Duncan JR, Street M, Strother M, Picus D (2013) Optimizing radiation use during fluoroscopic procedures: a quality and safety improvement project. J Am Coll Radiol 10(11):847–853
FDA. MedWatch: The FDA Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting Program. 2019. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/safety/medwatch-fda-safety-information-and-adverse-event-reporting-program
Fetterly KA, Magnuson DJ, Tannahill GM, Hindal MD, Mathew V (2011) Effective use of radiation shields to minimize operator dose during invasive cardiology procedures. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 4(10):1133–1139
Food and Drug Administration, HHS (2005) Electronic products; performance standard for diagnostic x-ray systems and their major components. Final rule. Fed Regist 70(111):33997–34042
Hassan AE, Amelot S (2017) Radiation exposure during Neurointerventional procedures in modern biplane angiographic systems: a single-site experience. Interv Neurol 6(3–4):105–116
Heilmaier C, Niklaus Z, Berthold C, Kara L, Weishaupt D (2015) Improving patient safety: implementing dose monitoring software in fluoroscopically guided interventions. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26(11):1699–1709
Hertault A, Maurel B, Midulla M, Bordier C, Desponds L, Saeed Kilani M et al (2015) Editor’s choice - minimizing radiation exposure during endovascular procedures: basic knowledge, literature review, and reporting standards. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 50(1):21–36
Hirshfeld JW, Ferrari VA, Bengel FM, Bergersen L, Chambers CE, Einstein AJ et al (2018) 2018 ACC/HRS/NASCI/SCAI/SCCT expert consensus document on optimal use of ionizing radiation in cardiovascular imaging: best practices for safety and effectiveness: a report of the American College of Cardiology Task Force on expert consensus decision pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(24):e283–e351
International Electrotechnical Commission (2010) Medical electrical equipment. Part 2-43. Particular requirements for the safety of X-ray equipment for interventional procedures, 2nd edn. International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva Report 60601
Jaschke W, Schmuth M, Trianni A, Bartal G (2017) Radiation-induced skin injuries to patients: what the interventional radiologist needs to know. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40(8):1131–1140
Jones AK, Pasciak AS (2011) Calculating the peak skin dose resulting from fluoroscopically guided interventions. Part I: Methods. J Appl Clin Med Phys 12(4):3670
Kirkwood ML, Guild JB, Arbique GM, Anderson JA, Valentine RJ, Timaran C (2015) Surgeon radiation dose during complex endovascular procedures. J Vasc Surg 62(2):457–463
Koenig TR, Wolff D, Mettler FA, Wagner LK (2001) Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 1, characteristics of radiation injury. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177(1):3–11
Miller DL, Balter S, Cole PE, Lu HT, Schueler BA, Geisinger M et al (2003) Radiation doses in interventional radiology procedures: the RAD-IR study: part I: overall measures of dose. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(6):711–727
Miller DL, Kwon D, Bonavia GH (2009) Reference levels for patient radiation doses in interventional radiology: proposed initial values for U.S. practice. Radiology 253:753–764
Miller TR, Zhuo J, Jindal G, Shivashankar R, Beaty N, Gandhi D (2017) The efficacy of shielding Systems for Reducing Operator Exposure during Neurointerventional procedures: a real-world prospective study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38(3):450–454
NCRP Report 168 | NCRP | Bethesda, MD. n.d. Available from: https://ncrponline.org/publications/reports/ncrp-report-168/
Perry BC, Ingraham CR, Stewart BK, Valji K, Kanal KM (2019) Monitoring and follow-up of high radiation dose cases in interventional radiology. Acad Radiol 26(2):163–169
Riabroi K, Khanungwanitkul K, Wattanapongpitak P, Krisanachinda A, Hongsakul K (2018) Patient radiation dose in Neurointerventional radiologic procedure: a tertiary care experience. Neurointervention. 13(2):110–116
Roguin A, Goldstein J, Bar O, Goldstein JA (2013) Brain and neck tumors among physicians performing interventional procedures. Am J Cardiol 111(9):1368–1372
Söderman M, Mauti M, Boon S, Omar A, Marteinsdóttir M, Andersson T et al (2013) Radiation dose in neuroangiography using image noise reduction technology: a population study based on 614 patients. Neuroradiology. 55(11):1365–1372
Srinivasan D, Than KD, Wang AC, La Marca F, Wang PI, Schermerhorn TC et al (2014) Radiation safety and spine surgery: systematic review of exposure limits and methods to minimize radiation exposure. World Neurosurg 82(6):1337–1343
Stecker MS, Balter S, Towbin RB, Miller DL, Vañó E, Bartal G et al (2009) Guidelines for patient radiation dose management. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(7 Suppl):S263–S273
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jacob J. Bundy, MD, MPH: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Ian W. McCracken, BS: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. David S. Shin, MD: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Eric J. Monroe, MD: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Guy E. Johnson, MD, PharmD: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Christopher R. Ingraham, MD: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Kalpana M. Kanal, PhD, FACR, FAAPM, FSCBTMR: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Richa. A. Bundy, MPH: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, statistical analyusis, final approval. Sean T. Jones, MD: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Karim Valji, MD, FSIR: Data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. Jeffrey Forris Beecham Chick, MD, MPH, FCIRSE, FSVM: Concept and design, data analysis, drafting manuscript, critical revision, final approval. All authors have read and contributed to this manuscript. Authors have no relevant disclosures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted with Institutional Review Board approval and complied with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent was waived from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bundy, J.J., McCracken, I.W., Shin, D.S. et al. Fluoroscopically-guided interventions with radiation doses exceeding 5000 mGy reference point air kerma: a dosimetric analysis of 89,549 interventional radiology, neurointerventional radiology, vascular surgery, and neurosurgery encounters. CVIR Endovasc 3, 69 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42155-020-00159-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42155-020-00159-6