Abstract
Background
The effectiveness of laparoscopic total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy (LTGD2) remains controversial. This meta-analysis compares surgical and survival outcomes of LTGD2 and open total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy (OTGD2) for gastric cancer.
Methods
Controlled studies comparing LTGD2 and OTGD2 published before November 2021 were retrieved via database searches. We compared intraoperative outcomes, pathological data, postoperative outcomes, 5-year disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results
17 studies were included, containing 4742 patients. Compared with OTGD2, the LTGD2 group had less blood loss (mean difference [MD] = − 122.48; 95% CI: − 187.60, − 57.37; P = 0.0002), fewer analgesic medication (MD = -2.48; 95% CI: − 2.69, − 2.27; P < 0.00001), earlier first flatus (MD = − 1.03; 95% CI: − 1.80, − 0.26; P = 0.009), earlier initial food intake (MD = − 0.89; 95% CI: − 1.09, − 0.68; P < 0.00001) and shorter hospital stay (MD = − 3.24; 95% CI: − 3.75, − 2.73; P < 0.00001). The LTGD2 group had lower postoperative total complication ratio (OR = 0.76; 95% CI: 0.62, 0.92; P = 0.006), incision (OR = 0.50; 95% CI:0.31, 0.79; P = 0.003) and pulmonary (OR = 0.57; 95% CI: 0.34, 0.96; P = 0.03) complication rates, but similar rates of other complications and mortality. Total number of dissected lymph nodes were similar, but the number of No. 10 dissected nodes was less with LTGD2 (MD = − 0.31; 95% CI: − 0.46, − 0.16; P < 0.0001). There was no difference in 5-year OS (P = 0.19) and DFS (P = 0.34) between LTGD2 and OTGD2 groups.
Conclusions
LTGD2 produces small trauma, fast postoperative recovery and small length of hospital stays than OTGD2, and had similar long-term clinical efficacy as OTGD2. However, these results still need further high-quality prospective randomized controlled trials confirmation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common gastrointestinal tumors, and it is especially frequent in East Asia. New cases of GC in China account for 2/5 of all new cases across the world annually [1]. Radical surgery remains an important method of treatment for GC, but overall prognosis is relatively poor. In recent years, morbidity due to GC has been increasing. According to Japanese treatment guidelines for gastric cancer established by the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association, patients with upper- and middle-third GC, as well as large gastric tumors, should be treated with total gastrectomy (TG), accompanied by an appropriate extent of lymphadenectomy. Traditional open total gastrectomy (OTG) is the most popular and extensively used form of TG. However, OTG cannot meet patients’ increasing requests for painless, non-invasive surgery because it involves a long surgical incision, extensive surgical trauma due to strong intraoperative traction, substantial postoperative pain, and slow postoperative recovery [2].
In 1994, Kitano et al. initially reported the use of laparoscopic gastrectomy in the treatment of early GC in Japan [3]. With the increasing publication of high-quality evidence, laparoscopy has been used more extensively in the treatment of early GC and has demonstrated favorable short- and long-term clinical efficacy, similar to that achieved with open gastrectomy. In the 4th edition of Japanese Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines, laparoscopic distal gastrectomy (LDG) has been considered as one of accepted treatments for patients with Stage I GC. In 1999, Azagra et al. reported the surgical safety and feasibility of laparoscopic total gastrectomy (LTG), accompanied by differing extents of lymphadenectomy [4], in 13 patients with GC.
Although laparoscopic radical surgery is an accepted treatment for early GC, it still remains controversial in treating advanced GC, especially LTG combined with D2 lymphadenectomy (LTGD2) [5, 6]. Multiple single-center retrospective studies have demonstrated that LDG combined with D2 lymphadenectomy (LDGD2) is a feasible and safe non-invasive technique. Compared with OTGD2, LTGD2 has higher operative requirements and involves a larger extent of surgery, more complex gastrointestinal reconstruction, and higher risk of seeding and metastasis of detached cancerous cells [7]. However, few reports have been published regarding long-term survival outcomes of LTGD2.
This study aims to compare surgical and survival outcomes of LTGD2 versus OTGD2 for the treatment of GC through meta-analysis of the available literature to provide objective and reliable evidence-based rationale for the use of LTGD2 in GC.
Material and methods
Ethics statement
This study was deemed exempt from institutional review board approval by Nantong University Affiliated Hospital, and informed consent was waived. We conducted this study in accordance with the ethical standards of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki.
Literature retrieval
Studies published in English before November 2021 were retrieved from electronic searches of PubMed, Elsevier, Cochrane Library, and OVID databases. We used these key words: GC, stomach neoplasms, gastric tumor, laparoscopic, laparoscopy, TG, total gastric resection, D2 dissection, and D2 lymphadenectomy.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The study inclusion criteria were as follows: any type of controlled study; LTGD2 was compared to OTGD2 for the treatment of GC; LTGD2 included hand-assisted, laparoscope-assisted, or total laparoscopic surgery methods; data were presented for surgical safety and efficacy, as well as means and standard deviations of the constant variables; and the study had a quality score of > 5 points according to the Newcastle–Ottawa scoring system (NOS) [8].
The study exclusion criteria were as follows: enrollment of patients without GC; non-D2 lymphadenectomy or partial gastrectomy were included in the study, unless the data were presented separately for TG with D2; no data directly compared LTGD2 and OTGD2; received neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and adjuvant chemotherapy; conversion to laparotomy; robot-assisted surgery; and reviews or meta-analyses.
Data collection
Risk of bias of the included studies was assessed using the risk of bias algorithm outlined by the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook, and data were collected by two authors independently [9]. A third author was invited to resolve disputes, when necessary. The collected clinical data included surgical duration, intraoperative blood loss, analgesic use, time of first flatus, time of initial food intake, length of hospital stay, proximal resection margin, distal resection margin, total number of dissected lymph nodes, number of No. 10 dissected lymph nodes, mortality within 30 days postoperatively, occurrence of postoperative complications (including stomal leak, anastomotic stenosis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, abdominal hemorrhage, pulmonary complications, incision complications, abdominal infection, intestinal obstruction, duodenal stump fistula, and pancreatic fistula), and long-term clinical efficacy (5-year disease-free survival [DFS] and overall survival [OS]).
Statistical data analysis
RevMan 5.4 software was used for the meta-analyses. The summary statistic used for second-classification data was the odds ratio (OR), and the summary statistic used for constant variable data was the weighted mean difference (MD). The results are expressed by 95% confidence interval (CI), and a forest plot was used to evaluate statistical significance. Heterogeneity of the included studies was assessed using the I2 test. Heterogeneity was considered significant if I2 was 50% or greater. Random effect models were used when heterogeneity was significant; otherwise, fixed effect models were used. Funnel plots were used to evaluate possible publication bias.
Results
Number and quality of included studies and publication bias
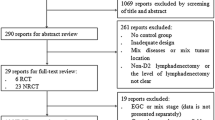
A total of 1,109 studies comparing LTGD2 and OTGD2 were initially retrieved; 546 remained after excluding duplicate studies. After screening the abstracts of these 546 articles, the full texts of 116 potentially relevant studies were reviewed. Of these, 17 studies were included in the current study based on inclusion and exclusion criteria (Fig. 1) [6, 10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
The quality assessment results (NOS score) for each study are summarized in Additional file 1: Table S1. According to the funnel plots, there was no evidence of significant publication bias in this meta-analysis (Fig. 2). When significant heterogeneity was found, we eliminated the articles responsible for the heterogeneity and re-performed the meta-analysis.
Characteristics of included studies
From the 17 included studies, which were published from 2008 to 2021 (Additional file 1: Table S1), a total of 4742 patients were enrolled in this meta-analysis: 1993 underwent LTGD2 and 2749 underwent OTGD2 (Additional file 1: Table S1). Most studies included both early and advanced GC. When considering all studies, there were no significant differences in patient age, body mass index (BMI), size and site of tumor, American Society of Anesthesiologists’ class, or distribution of tumor node metastasis (TNM) stages between the LTGD2 and OTGD2 groups (P > 0.05; Additional file 1: Table S1).
Intraoperative and postoperative recovery
Compared with the OTGD2 group, the LTGD2 group had less blood loss (MD = − 122.48; 95% CI: − 187.60, − 57.37; P = 0.0002), fewer days of analgesic medication (MD = − 2.48; 95% CI: -2.69, − 2.27; P < 0.00001), earlier time of first postoperative flatus per rectum (MD = − 1.03; 95% CI: − 1.80, − 0.26; P = 0.009), earlier time of initial food intake (MD = − 0.89; 95% CI: − 1.09, -0.68; P < 0.00001) and shorter length of postoperative hospital stay (MD = − 3.24; 95% CI: − 3.75, − 2.73; P < 0.00001; Additional file 2: Figure S1). However, the LTGD2 group had a longer operation time (MD = 40.44; 95% CI: 27.41, 53.47; P < 0.00001). Subgroup analysis was performed for operation time based on the year of study publication. These results showed that the LTGD2 group had a longer operation time than the OTGD2 group for the 5 studies published before 2013 (MD = 42.53; 95% CI: 16.23, 68.82; P = 0.002), as well as the 6 studies published after 2013 (MD = 39.29; 95% CI: 25.05, 53.49; P < 0.00001; Additional file 2: Figure S1F).
Pathological data
There were no significant differences between LTGD2 and OTGD2 groups with regard to the total number of dissected lymph nodes (MD = − 1.00; 95% CI: − 2.16, -0.16; P = 0.09; Fig. 3A), proximal resection margin (MD = − 0.06; 95% CI: − 0.28, 0.17; P = 0.63; Fig. 3B), and distal resection margin (MD = 0.18; 95% CI: − 0.00, 0.36; P = 0.06; Fig. 3C). However, the number of No. 10 dissected lymph nodes was significantly less in the LTGD2 group than in the OTGD2 group (MD = − 0.31; 95% CI: − 0.46, − 0.16; P < 0.0001; Fig. 3D).
Analysis comparing (A) total number of harvested lymph nodes during D2 dissection, (B) proximal resection margin, (C) distal resection margin, and (D) number of No. 10 harvested lymph nodes. LTGD2, laparoscopic total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy; OTGD2, open total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy
Postoperative mortality and complications
The postoperative mortality rate was similar in the LTGD2 and OTGD2 groups (OR = 0.70; 95% CI: 0.29, 1.73; P = 0.44; Additional file 2: Figure S2A). The rate of total postoperative complications was less in the LTGD2 group than in the OTGD2 group (OR = 0.76; 95% CI: 0.62, 0.92; P = 0.006; Additional file 2: Figure S2B). Subgroup analysis of specific types of postoperative complications found no significant differences between groups for anastomotic leakage (OR = 0.94; 95% CI: 0.61, 1.47; P = 0.80), anastomotic stenosis (OR = 2.01; 95% CI: 0.81, 4.99; P = 0.13), anastomotic bleeding (OR = 0.52; 95% CI: 0.20, 1.36, P = 0.18), abdominal hemorrhage (OR = 0.87; 95% CI: 0.33, 2.27; P = 0.29), abdominal infection (OR = 0.59; 95% CI: 0.28, 1.23; P = 1.41), intestinal obstruction (OR = 1.54; 95% CI: 0.81, 2.92; P = 0.19), internal hernia (OR = 1.53; 95% CI: 0.21, 11.08; P = 0.68), lymph leakage (OR = 0.46; 95% CI: 0.10, 2.13; P = 0.32), and pancreatic fistula (OR = 0.74; 95% CI: 0.22, 2.56; P = 0.64; Table 1). However, LTGD2 group had notably lower rates of postoperative complications related to the incision (OR = 0.50; 95% CI: 0.31, 0.79; P = 0.003; Additional file 2: Figure S2C) and pulmonary complications (OR = 0.57; 95% CI: 0.34, 0.96; P = 0.03; Additional file 2: Figure S2D) than the OTGD2 group.
Long-term clinical efficacy
Survival data were available for seven included studies. The pooled analysis showed there is no significant difference in 5-year OS (OR = 1.15; 95% CI: 0.94, 1.40; P = 0.19; Fig. 4A) and DFS (OR = 1.14; 95% CI: 0.87, 1.48; P = 0.34; Fig. 4B) between the LTGD2 and OTGD2 groups.
Discussion
This meta-analysis found that LTGD2 was associated with a markedly longer surgical duration than OTGD2, but there were no significant differences between groups in the rates of total postoperative complications and postoperative mortality. Furthermore, the LTGD2 group had less intraoperative blood loss and fewer postoperative analgesic injections, time of initial postoperative flatus per rectum, time of initial food intake, and shorter length of postoperative hospital stay, when compared with the OTGD2 group. These results indicate that LTGD2 has substantial advantages over OTGD2 with regard to postoperative recovery of patients with GC. In addition, we found that there were no significant differences between two LTGD2 and OTGD2 in the total number of dissected lymph nodes, proximal resection margin, and distal resection margin. Although the number of dissected No. 10 lymph nodes was fewer in the LTGD2 group, there were no significant differences between groups for 5-year OS and DFS, indicating that LTGD2 and OTGD2 had similar long-term clinical efficacy.
Of the 16 enrolled studies, 14 were from East Asia (1 from Japan, 6 from South Korean, and 7 from China), 1 was from Brazil in South America, 1 was from Europe, and none were from North America. This is consistent with the distribution of GC. D2 lymphadenectomy has been established as the current standard for treating patients with advanced GC in a number of countries, including China, Japan, and South Korea [18, 19], but no published prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated better survival with D2 lymphadenectomy than D1 lymphadenectomy in Western countries [20, 21]. Furthermore, some western study results suggest that survival is similar with D1+ and D2 lymphadenectomy, whereas surgical risks and difficulty are much less with D1 + lymphadenectomy [22, 23]. In addition, experts generally agree that an increased BMI increases the risks of laparoscopic GC surgery with D2 lymphadenectomy [24, 25]. D1+ lymphadenectomy is generally preferred in Europe and America for treating patients with advanced GC, and D2 lymphadenectomy is performed infrequently in these countries. In addition, studies have shown that compared with OTGD2, minimally invasive surgery for locally advanced gastric cancer will not harm the overall short-term mortality and morbidity. Moreover, studies have further shown that laparoscopic gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer is better in terms of short-term and long-term outcomes [26,27,28,29,30].
Although LTGD2 has the advantages over OTGD2 of less surgical trauma and faster recovery, our results indicated that the LTGD2 group had a notably longer surgical duration. The degree of familiarity of surgeons with laparoscopic instruments and the degree of coordination with their assistants are two important factors influencing LTGD2 surgical duration [31]. A study involving experienced surgeons reported no significant differences in duration between LDGD2 and ODGD2 [25, 32]. The technical difficulty of mini-incision or total laparoscopic esophagojejunostomy is also an important cause of the long surgical duration of LTGD2. In mini-incision surgery, it is difficult to create the purse-string suture and imbed the anastomosis through the small incision, and it is difficult to complete the esophagojejunostomy because of the small incision and limited operative field. With total laparoscopy, it is also difficult to create the purse-string suture at the esophageal stump, and improper anastomosis may lead to severe or even fatal complications [33]. To overcome these problems, numerous new techniques are emerging, including use of a transorally inserted anvil device (OrVil™ system) to perform end-to-side esophagojejunostomy or an endoscopic linear stapler to conduct side-to-side esophagojejunostomy [34]. These two methods not only eliminate the need for a small upper abdominal incision, but also avoid the laparoscopic purse-string suture, which greatly shortens the surgical duration. With the accumulation of surgical experience and development of new instruments and techniques, differences in surgical duration between LTGD2 and OTGD2 will likely decrease. Despite the longer duration of LTGD2 at present, our results indicate that this was of little clinical importance, as it did not negatively influence postoperative recovery.
Postoperative mortality and complications are important indices for assessing surgical feasibility and postoperative short-term clinical efficacy. The current meta-analysis found that postoperative mortality was low and similar in both groups. TGD2-related complications mainly included stomal leak, anastomotic stenosis, anastomotic bleeding, duodenum stump fistula, and abdominal hemorrhage. TGD2-related complications have differed among studies because of different surgeons’ experiences and varied definitions and classification of complications [5, 16, 17, 24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32, 34,35,36,37,38,39]. In the current meta-analysis, the rate of total postoperative complications was less in the LDGD2 group than in the ODGD2 group. The rates were similar between groups for most complications, but the LTGD2 group had markedly lower rates of incision-related and pulmonary postoperative complications. The lower rates may be attributed to the shorter abdominal incision with LTGD2, which facilitates postoperative coughing and mobility, accelerates recovery, and shortens the hospital length of stay. Several previous meta-analyses have also shown that LTGD2 has improved short-term results, especially in terms of length of stay in laparoscopic surgery, which is balanced with the time-consuming and technical challenges of laparoscopic surgery [40, 41].
Long-term survival rates are another index of surgical advantages and disadvantages. LTGD2 can only replace OTGD2 if it achieves long-term survival rates that are similar to those of OTGD2. Some studies have shown that LTGD2 exhibits not only radical efficacy similar to that observed with ODGD2, but also similar 5-year survival rates [5, 6, 11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Lin et al. found no significant differences between LTGD2 and OTGD2 during median follow-up of 24.0 months [42]. Our current results also demonstrated that LTGD2 could provide comparable 5-year OS and DFS as OTGD2, further indicating that LTGD2 is safe and feasible for GC.
This meta-analysis was limited by the retrospective nature, small sample size, and short follow-up of most of the included studies. There was also heterogeneity of results between studies. This heterogeneity may be due to several factors, including differences in expertise of the surgeons, pathological stages of the tumors, clinical pathways, methods of measuring outcomes, and patient populations. With respect to the surgeons’ expertise, LTGD2 lacks a mature quality control system, which contributes to interregional gaps in the development of technical skills for this surgery. Furthermore, the learning curve varies for surgeons with different levels of experience [31, 37], and surgeons participating in the studies may be in different stages of the learning curve; thus, the skills of surgeons even in the same region may vary considerably [38]. Regarding pathological stages, enrolled patients may have a different TNM stage, and the ratio of patients with various TNM stages may vary between studies; advanced GC is more difficult to treat surgically than early GC. Perioperative management varies between hospitals, as there are no uniform clinical pathways for these operations. Methods of outcome measurement often vary because of lack of uniform standards for quantitative analysis of such outcomes as intraoperative blood loss or patient condition at hospital discharge. Likewise, the number of dissected lymph nodes is closely associated with the sampling experience of the pathologist. Regional variations in populations due to differences in living and diet habits, as well as body types, may also contribute to heterogeneous study results. Therefore, further prospective randomized studies from Western countries are necessary.
Conclusion
The result of our meta-analysis demonstrates that LTGD2 is safe and feasible, with advantages of limited trauma, fast recovery, mild pain, and short length of hospital stay. However, it should be used with caution in patients with GC who have a high-risk of hilus lienis lymph node metastasis. Certainly, the results of this study require further verification by large, multi-center RCTs. Both LTGD2 and OTGD2 are reasonable surgical methods; prognosis depends mainly on the surgeon operating with a high degree of skill and safety, not on whether laparoscopic or open surgery is chosen. No matter which surgical approach is used, the most important issue is understanding the appropriate indications for TG.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- TG:
-
Total gastrectomy
- OTG:
-
Open total gastrectomy
- LDG:
-
Laparoscopic distal gastrectomy
- LTG:
-
Laparoscopic total gastrectomy;
- LTGD2:
-
LTG combined with D2 lymphadenectomy
- LDGD2:
-
LDG combined with D2 lymphadenectomy
- NOS:
-
Newcastle–Ottawa scoring system
- DFS:
-
Disease-free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- MD:
-
Mean difference
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- TNM:
-
Tumor node metastasis
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Sakamoto T, Fujiogi M, Matsui H, Fushimi K, Yasunaga H. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopic and open total gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a nationwide retrospective cohort analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;27:1534–4681.
Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, Sugimachi K. Laparoscopy-assisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1994;4:146–8.
Azagra JS, Goergen M, De Simone P, Ibanez-Aguirre J. Minimally invasive surgery for gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 1999;13:351–7.
Zhang GT, Zhang XD, Xue HZ. Open versus hand-assisted laparoscopic total gastric resection with D2 lymph node dissection for adenocarcinoma: a case-control study. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017;27:42–50.
Topal B, Leys E, Ectors N, Aerts R, Penninckx F. Determinants of complications and adequacy of surgical resection in laparoscopic versus open total gastrectomy for adenocarcinoma. Surg Endosc. 2008;22:980–4.
Fang C, Hua J, Li J, et al. Comparison of long-term results between laparoscopy-assisted gastrectomy and open gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for advanced gastric cancer. Am J Surg. 2014;208:391–6.
Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, et al. Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies. Health Technol Assess. 2003;7:1–173.
Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 5.1.0. 2011. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/archive/v5.1/.
Kawamura H, Yokota R, Homma S, Kondo Y. Comparison of invasiveness between laparoscopy-assisted total gastrectomy and open total gastrectomy. World J Surg. 2009;33:2389–95.
Ramagem CA, Linhares M, Lacerda CF, Bertulucci PA, Wonrath D, de Oliveira AT. Comparison of laparoscopic total gastrectomy and laparotomic total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2015;28:65–9.
Kim HS, Kim BS, Lee IS, Lee S, Yook JH, Kim BS. Comparison of totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy and open total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013;23:323–31.
Kim MG, Kim BS, Kim TH, Kim KC, Yook JH, Kim BS. The effects of laparoscopic assisted total gastrectomy on surgical outcomes in the treatment of gastric cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 2011;80:245–50.
Guan G, Jiang W, Chen Z, Liu X, Lu H, Zhang X. Early results of a modified splenic hilar lymphadenectomy in laparoscopy-assisted total gastrectomy for gastric cancer with stage cT1-2: a case-control study. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:1923–31.
Du J, Zheng J, Li Y, et al. Laparoscopy-assisted total gastrectomy with extended lymph node resection for advanced gastric cancer–reports of 82 cases. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:1589–94.
Lee SR, Kim HO, Son BH, Shin JH, Yoo CH. Laparoscopic-assisted total gastrectomy versus open total gastrectomy for upper and middle gastric cancer in short-term and long-term outcomes. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2014;24:277–82.
Lee MS, Lee JH, Park DJ, Lee HJ, Kim HH, Yang HK. Comparison of short- and long-term outcomes of laparoscopic-assisted total gastrectomy and open total gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2598–605.
Sasako M, Saka M, Fukagawa T, Katai H, Sano T. Modern surgery for gastric cancer–Japanese perspective. Scand J Surg. 2006;95:232–5.
Sano T. Tailoring treatments for curable gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2007;94:263–4.
Bonenkamp JJ, Songun I, Hermans J, et al. Randomised comparison of morbidity after D1 and D2 dissection for gastric cancer in 996 dutch patients. Lancet. 1995;345:745–8.
Cuschieri A, Fayers P, Fielding J, et al. Postoperative morbidity and mortality after D1 and D2 resections for gastric cancer: preliminary results of the MRC randomised controlled surgical trial. Surg Cooperative Group Lancet. 1996;347:995–9.
Galizia G, Lieto E, De Vita F, et al. Modified versus standard D2 lymphadenectomy in total gastrectomy for nonjunctional gastric carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. Surgery. 2015;157:285–96.
Degiuli M, Sasako M, Ponti A, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing survival after D1 or D2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2014;101:23–31.
Chen H, Sui W. Influence of obesity on short- and long-term outcomes after laparoscopic distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J BUON. 2017;22:417–23.
Son SY, Jung DH, Lee CM, et al. Laparoscopic gastrectomy versus open gastrectomy for gastric cancer in patients with body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or more. Surg Endosc. 2015;29:2126–32.
Beyer K, Baukloh AK, Kamphues C, Seeliger H, Heidecke CD, Kreis ME, Patrzyk M. Laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. World J Surg Oncol. 2019;17(1):68.
Shibuya K, Kawamura H, Takahashi S, Ohno Y, Ichikawa N, Yoshida T, Homma S, Ishizu H, Takahashi M, Taketomi A. Short-term and long-term outcomes following laparoscopic gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer compared with open gastrectomy[J]. Surg Laparosc EWndosc Percutaneous Tech. 2019;29(4):297.
Shi Y, Xianhui Xu, Zhao Y, Qian F, Tang Bo, Hao Y, Luo H, Chen J, Peiwu Yu. Long-term oncologic outcomes of a randomized controlled trial comparing laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy with D2 lymph node dissection for advanced gastric cancer[J]. Surgery. 2019;165(6):1211–6.
Chen X, Feng X, Wang M, Yao X. Laparoscopic versus open distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and high-quality nonrandomized comparative studies. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020;46(11):1998–2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2020.06.046.
Lee HJ, Hyung WJ, Yang HK, et al. Short-term outcomes of a multicenter randomized controlled trial comparing laparoscopic distal gastrectomy with d2 lymphadenectomy to open distal gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer (KLASS-02-RCT). Ann Surg. 2019;270(6):983–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000003217.
Yoshikawa T, Cho H, Rino Y, et al. A prospective feasibility and safety study of laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy for clinical stage I gastric cancer initiated by surgeons with much experience of open gastrectomy and laparoscopic surgery. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16:126–32.
Zhou D, Quan Z, Wang J, Zhao M, Yang Y. Laparoscopic-assisted versus open distal gastrectomy with D2 lymph node resection for advanced gastric cancer: effect of learning curve on short-term outcomes. a meta-analysis. J Laparoendosc Adv SurgTech A. 2014;24:139–50.
Kinoshita T, Oshiro T, Ito K, Shibasaki H, Okazumi S, Katoh R. Intracorporeal circular-stapled esophagojejunostomy using hand-sewn purse-string suture after laparoscopic total gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:2908–12.
Jung YJ, Kim DJ, Lee JH, Kim W. Safety of intracorporeal circular stapling esophagojejunostomy using trans-orally inserted anvil (OrVil) following laparoscopic total or proximal gastrectomy—comparison with extracorporeal anastomosis. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:209.
Shin SH, Jung H, Choi SH, et al. Clinical significance of splenic hilar lymph node metastasis in proximal gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:1304–9.
Zhu GL, Sun Z, Wang ZN, et al. Splenic hilar lymph node metastasis independently predicts poor survival for patients with gastric cancers in the upper and/or the middle third of the stomach. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105:786–92.
Sano T, Yamamoto S, Sasako M, Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study LM . Randomized controlled trial to evaluate splenectomy in total gastrectomy for proximal gastric carcinoma: Japan clinical oncology group study JCOG 0110-MF.JPn. J Clin Oncol. 2002;32:363–4.
Hu WG, Ma JJ, Zang L, et al. Learning curve and long-term outcomes of laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2014;24:487–92.
Chen XZ, Li YY, Hu JK, et al. Spread and development of laparoscopic surgery for gastric tumors in mainland China: initial experiences. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59:654–8.
Jiang L, Yang KH, Guan QL, Cao N, Chen Y, Zhao P, Chen YL, Yao L. Laparoscopy-assisted gastrectomy versus open gastrectomy for resectable gastric cancer: an update meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2466–80.
Cheng QY, Pang TCY, Hollands MJ, Richardson AJ, Pleass H, Johnston ES, Lam VWT. Systematic review and meta-analysis of laparoscopic versus open distal gastrectomy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18:1087–99.
Lin J, Huang C, Zheng C, et al. A matched cohort study of laparoscopy-assisted and open total gastrectomy for advanced proximal gastric cancer without serosa invasion. Chin Med J. 2014;127:403–7.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank BioScience Writers (http://www.biosciencewriters.com) in the literature content proofreading and editing work.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81672409).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QM and WX completed the research concept and design and approved the final draft. YF completed the data analysis. YH completed the collected data (laboratory or clinical).YY and YC completed the drafting and revision of the original manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No ethical approval or patient consent was required because all the analyses were based on previously published studies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Details and characteristics of the studies included in this meta-analysis.
Additional file 2
: Figure S1. Analysis comparing (A) blood loss, (B) times of analgesic medication injections, (C) time of first flatus per rectum, (D) time of initial diet, (E) postoperative hospital length of stay, and (F) subgroup analysis of operation time according to year of surgery. LTGD2, laparoscopic total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy; OTGD2, open total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy. Figure S2. Analysis comparing (A) postoperative mortality, (B) postoperative total complications, (C) postoperative incision-related complications, and (D) postoperative pulmonary complications. LTGD2, laparoscopic total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy; OTGD2, open total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Chen, Y., Hu, Y. et al. Outcomes of laparoscopic versus open total gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Med Res 27, 124 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-022-00748-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-022-00748-2